Custom MySQL Configuration Guide
WeDa Private Deployment supports connecting to custom MySQL databases to meet enterprise-level data storage and management requirements. This document will guide you through the configuration and integration of MySQL databases.
Prerequisites
Before starting the configuration, please ensure your environment meets the following requirements:
Database Version Requirements
- MySQL Version: 8.0.30 and above (supports both standalone and cluster versions)
- Version Limitations: MySQL 8.4 and later versions may not be compatible (due to the disabled
mysql_native_passwordplugin) - Compatibility Check: It is recommended to use MySQL 8.0.30 - 8.3.x versions to ensure optimal compatibility
Permission Requirements
The MySQL user configured for connection needs to have the following permissions:
- Table Operation Permissions:
CREATE,DROP,ALTER - Data Operation Permissions:
SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE - Index Permissions:
INDEX
Production Environment Recommendations
- High Availability: Production environments should use cloud databases or self-built high-availability MySQL clusters
- Avoid Docker: Not recommended to use Docker-started MySQL as production environment data storage
- External Database: Recommended to connect to enterprise-owned external database services
- Backup Strategy: Ensure the database has comprehensive backup and recovery mechanisms
MySQL Configuration Parameters
Basic Configuration Requirements
To ensure compatibility between WeDa Private Deployment and MySQL database, the following MySQL configurations are required. These configurations apply to MySQL 8.0 version.
Recommended Configuration Specifications
Taking Tencent Cloud CDB MySQL as an example:
| Configuration Item | Recommended Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Version | MySQL 8.0 Cluster Edition | Provides high availability guarantee |
| CPU | 2 cores and above | Adjust according to business volume |
| Memory | 8GB and above | Ensure query performance |
| Storage | 200GB and above | Estimate based on data volume |
| Network | Open specified port access permissions | Ensure WeDa can connect |
Required Configuration Parameters
Modify the MySQL configuration file (my.cnf or my.ini) and add the following configurations:
[client]
# MySQL client program configuration
default-character-set = utf8mb4
[mysql]
# MySQL command line client configuration
default-character-set = utf8mb4
[mysqld]
# MySQL server configuration
character-set-server = utf8mb4
collation-server = utf8mb4_unicode_ci
sql_mode = ALLOW_INVALID_DATES
explicit_defaults_for_timestamp = OFF
default-authentication-plugin = mysql_native_password
- Character Set Settings: Use
utf8mb4to ensure complete Unicode support - Collation Rules:
utf8mb4_unicode_ciprovides better internationalization support - Authentication Plugin:
mysql_native_passwordensures compatibility with WeDa - Timestamp Settings: Disable explicit defaults to be compatible with legacy version behavior
Standalone Version Deployment Configuration
WeDa Private Deployment standalone version provides two MySQL configuration methods: visual configuration and script configuration.
Method 1: Visual Configuration Deployment
The standalone version supports configuring external MySQL databases through a visual interface, which is simple and intuitive.
Operation Steps:
Open the installer page: Access in browser:
http://<Server IP>:38080Configure external MySQL: Find the external middleware configuration option in the installer page and enable MySQL configuration:
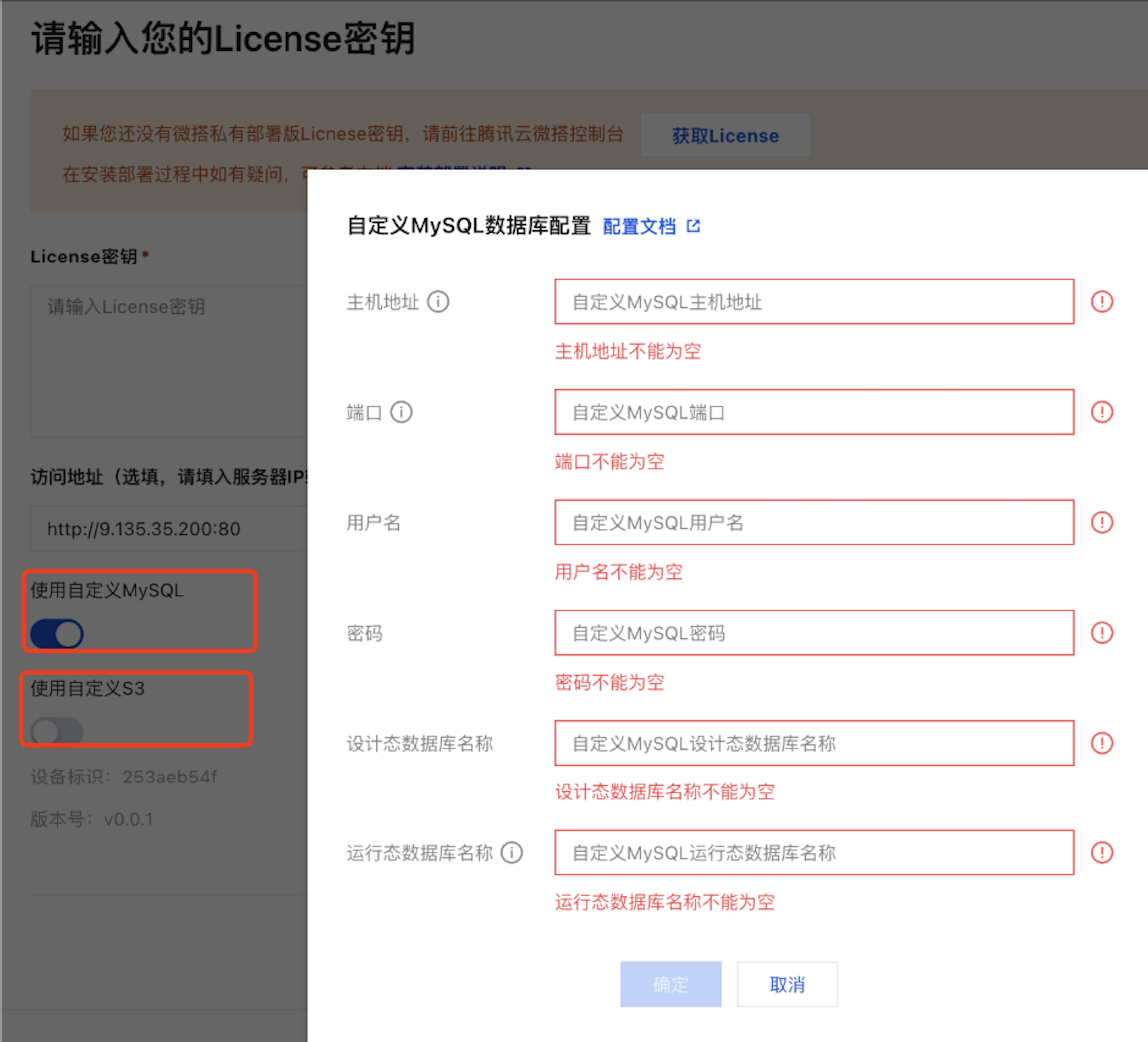
- Fill in database information:
- Database host address
- Port number (default 3306)
- Username and password
- Database name
Method 2: Script Configuration Deployment
Configure MySQL through configuration files, suitable for automated deployment scenarios.
This configuration needs to be performed after running the installation script ./install.sh in the WeDa Deployment Process.
Step 1: Create Configuration File
vim config.yaml
Create a config.yaml file in the current directory and enter the following configuration:
## config.yaml
customMySQL:
enabled: true
host: 192.168.3.14 # MySQL server address
port: 3306 # MySQL port
username: root # Database username
password: your_password # Database password
dbName: lowcode # Main database name
dbRuntimeName: lcruntime # Runtime database name
- Network Connectivity: Ensure the entered MySQL address is accessible from the current server
- Database Pre-creation: Databases specified by
dbNameanddbRuntimeNamemust be created in advance - Database Independence: The two database names cannot be the same, used for different business modules
Step 2: Create Databases
Execute the following SQL statements in MySQL to create the required databases:
-- Create main database
CREATE DATABASE `lowcode` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
-- Create runtime database
CREATE DATABASE `lcruntime` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
Step 3: Verify Configuration
After saving the configuration file, verify that the content is correct:
cat config.yaml
After confirming the configuration information is correct, you can see output similar to the following:

Execute Installation Deployment
Choose the corresponding deployment method based on your usage scenario:
- First Installation
- Upgrade Installation
Applicable Scenario: First time using external MySQL service
Continue with the subsequent installation steps according to the Deployment Process.
Applicable Scenario: Previously installed built-in MySQL, now switching to external MySQL
./upgrade.sh
MySQL upgrade method will not automatically perform data migration. If you need to retain original data, please backup and manually migrate in advance.
Common Problem Troubleshooting
Problem: "Access denied" prompt after executing ./install.sh
Possible Causes:
- Incorrect MySQL connection information configuration
- Network connectivity issues
- Insufficient user permissions
Solutions:
- Check configuration file: Confirm that the MySQL connection information in
config.yamlis correct - Test connectivity: Use MySQL client to test connection on the current server
mysql -h 192.168.3.14 -P 3306 -u root -p - Verify permissions: Confirm that the MySQL user has necessary database operation permissions
- Check firewall: Ensure both server firewall and MySQL server firewall allow connections
Cluster Version Deployment Configuration
WeDa Private Deployment Kubernetes cluster version integrates external MySQL databases by modifying configuration files.
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Edit Configuration File
This configuration needs to be performed after Kubernetes Cluster Version Deployment Guide downloading deployment scripts.
Edit the cluster installation configuration file config.yaml and add MySQL configuration in the middleware section:
middleware:
mysql:
## MySQL database connection information
host: your-mysql-host.com # MySQL server address
port: 3306 # MySQL port number
username: your-username # Database username
password: your-password # Database password
## Database name configuration
dbname: lowcode # Main database name
dbRuntimeName: lcruntime # Runtime database name
- Database Independence:
dbnameanddbRuntimeNamecannot use the same database name - Database Pre-creation: Ensure specified databases are already created in MySQL
- Network Connectivity: Ensure Kubernetes cluster can access MySQL server
- User Permissions: Database user needs to have complete table operation permissions
Step 2: Create Databases
Execute the following SQL statements in the MySQL server:
-- Create main database
CREATE DATABASE `lowcode` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
-- Create runtime database
CREATE DATABASE `lcruntime` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
-- Grant user permissions (adjust according to actual username)
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON lowcode.* TO 'your-username'@'%';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON lcruntime.* TO 'your-username'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Step 3: Execute Deployment
After configuration is complete, run the deployment command:
./wedaCli up