WeDa Private Deployment Cloud Function Operation Guide
This document will guide you through the development, deployment, and invocation of cloud functions in the WeDa private deployment environment.
Currently, WeDa private deployment version only supports HTTP API for cloud function invocation.
Step 1: Writing Cloud Functions
1.1 Development Reference Documentation
Before starting cloud function development, it is recommended to read the following official documentation:
1.2 Development Recommendations
- It is recommended to complete development and testing locally first, ensuring the function runs properly before uploading and deploying
- Ensure all dependency packages are correctly installed
- Pay attention to the function's entry file and handler method configuration
Step 2: Deploying Cloud Functions
2.1 Download Deployment Tool
First, you need to download the cloud function publishing and uploading tool private-cloud-function (abbreviated as pcf).
Linux System
# Download tool
wget https://software-1302110647.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/rc/lastest/tools/amd64/linux/pcf
# Add execution permission
chmod +x pcf
Windows System
# Download URL
https://software-1302110647.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/rc/lastest/tools/amd64/windows/pcf.exe
macOS System
# Download tool
wget https://software-1302110647.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/rc/lastest/tools/amd64/macOS/pcf
# Add execution permission
chmod +x pcf
For Windows system users, you can press Win + R to open the Run dialog, type cmd to open Command Prompt. After downloading pcf.exe, use .\pcf.exe instead of ./pcf to execute commands in the command line.
2.2 Configure Login Information
Use the following command to add login information for the WeDa environment:
./pcf add-host <aliasname> --host=<login_address> --username=<username> --password=<password>
Parameter Description:
aliasname: Host alias, used to identify different WeDa environments (optional, defaults todefault)host: WeDa private deployment access addressusername: Administrator usernamepassword: Administrator password
Example:
./pcf add-host --host=http://192.168.1.100 --username=admin --password="Weda@123456"
2.3 Upload Cloud Function Code
Upload the locally developed cloud function code to the WeDa environment:
./pcf func push <funcname> --alias=<aliasname> --path=<code_path>
Parameter Description:
funcname: Unique identifier name for the functionalias: Previously configured host aliaspath: Local cloud function code path
Example:
# Using official template example
# 1. First download template: https://github.com/TencentCloudBase/func-v2-template
# 2. After local testing passes, execute upload
./pcf func push myfunction --path="/data/code/func-v2-template"
- Ensure the code path is correct and contains complete function code and dependencies
- It is recommended to test locally first before uploading
- Check if dependencies in the code are complete before uploading
2.4 Publish Cloud Function
After uploading is complete, you need to publish the cloud function to make it effective:
./pcf func deploy <funcname> --alias=<aliasname>
Example:
./pcf func deploy myfunction
After successful publication, the system will return deployment result information.
Step 3: Calling Cloud Functions in APIs Connector
After the cloud function is successfully published, it can be called through WeDa's APIs connector.
3.1 Select APIs Type
In the WeDa low-code platform:
- Go to Extended Capabilities → Resource Links → APIs Connector
- Select Custom APIs → HTTP Request
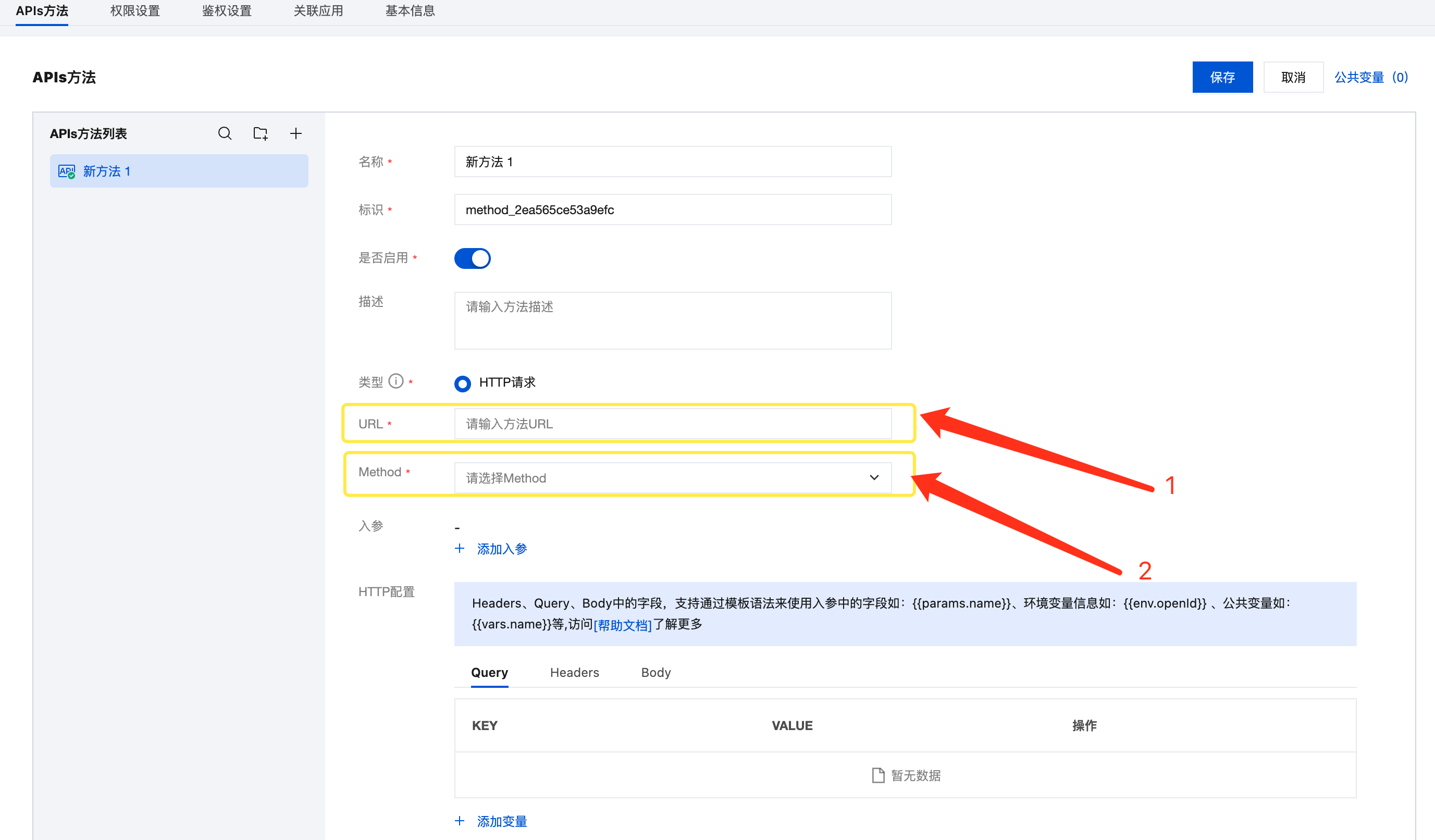
3.2 Configure APIs Method
In the APIs connector configuration interface, fill in the following information:
Basic Configuration:
- URL:
http://func-server:3000 - Request Method: Select according to the method defined in the cloud function code (such as POST, GET, etc.)
- Request Headers: Add as needed (such as
Content-Type: application/json)
3.3 Test APIs Method
After configuration is complete, you can test directly in the APIs connector:
- Click the Test button
- Input test parameters (if needed)
- View the returned results
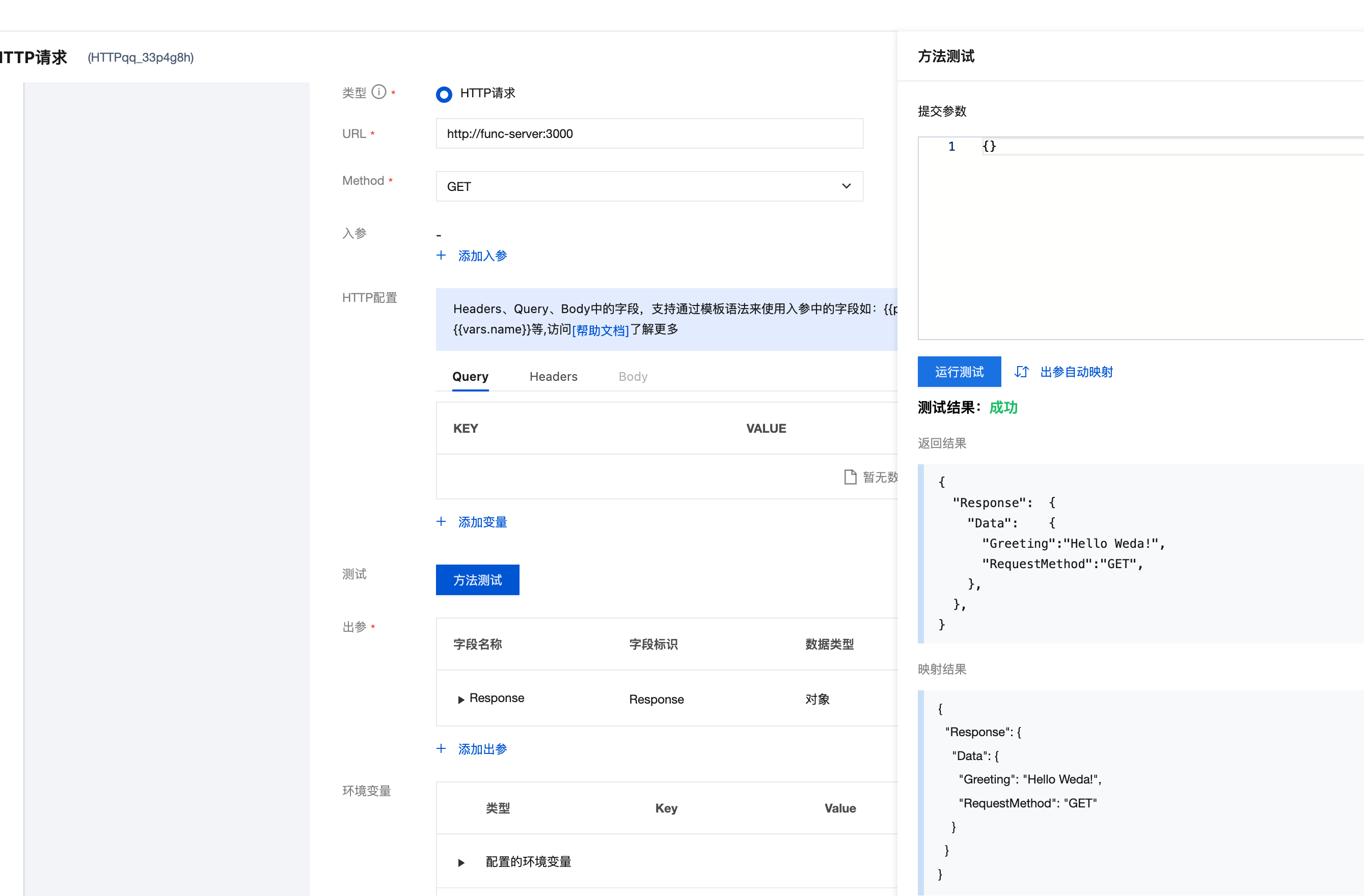
- The cloud function access address is fixed as
http://func-server:3000 - The request method needs to be consistent with the method defined in the cloud function code
- After testing passes, you can bind the APIs to specific page components for use
Step 4: Other Management Commands
4.1 Delete Login Information
To delete configured host login information:
./pcf del-host <aliasname>
4.2 Query Cloud Function List
View all cloud functions in the current environment:
./pcf func list --alias=<aliasname>
The system will return a function list showing the status of each function. Note: Only one function can be in published status at the same time, all other functions are in unpublished status.
4.3 Delete Cloud Function
Delete unwanted cloud functions:
./pcf func del <funcname> --alias=<aliasname>
Step 5: Troubleshooting
When cloud function deployment or runtime issues occur, you can troubleshoot through the following methods.
5.1 View Service-Level Logs
If the cloud function has syntax errors or deployment failures, you need to check the func-server container logs.
Standalone Deployment
# View the latest 100 log entries
docker logs -f -n 100 func-server
Cluster Deployment
# 1. View func-server Pod name
kubectl -n software get pods | grep func-server
# 2. View specified Pod logs
kubectl -n software logs -f --tail=100 <func-server-pod-name>
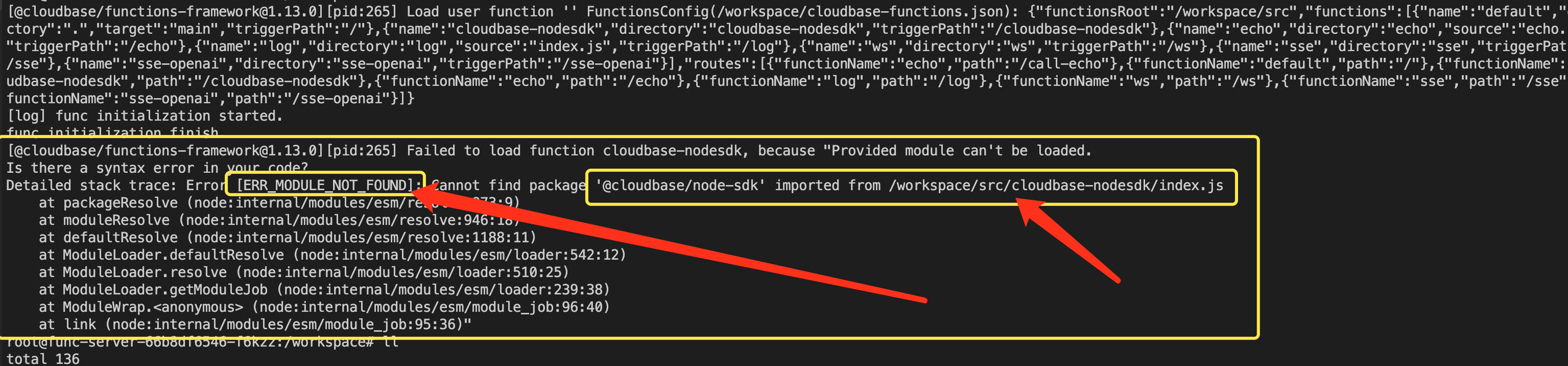
Common Error Examples:
When dependency missing or syntax errors occur, corresponding error information will be displayed in the logs. It is recommended to complete testing locally and install all dependencies before uploading and deploying.
5.2 View User-Level Logs
Enter Container to View Detailed Logs
User-level logs are stored in the following directories:
/workspace/logs/accesslog*.log # Access logs
/workspace/logs/usercodelog*.log # User code logs
Methods to Enter Container
Standalone Deployment:
docker exec -it func-server bash
Cluster Deployment:
# 1. View func-server Pod name
kubectl -n software get pods | grep func-server
# 2. Enter specified Pod
kubectl -n software exec -it <func-server-pod-name> -c func-server bash
After entering the container, you can use tail, grep and other commands to view and analyze log files.
Summary
Through the above steps, you have completed:
- ✅ Local development and testing of cloud functions
- ✅ Download and configuration of deployment tools
- ✅ Upload and publication of cloud functions
- ✅ Calling cloud functions through APIs connector in WeDa platform
- ✅ Mastered basic management and troubleshooting methods
Now you can fully utilize cloud function capabilities in the WeDa private deployment environment to provide powerful backend service support for your low-code applications.
- It is recommended to thoroughly test cloud functions locally before uploading and deploying
- Regularly check logs to discover and resolve issues promptly
- Plan function naming reasonably for easy management and maintenance
- Pay attention to function resource usage to avoid affecting system performance