Overview
CloudRun (Tencent CloudBase Run) is a new-generation cloud-native application engine that supports hosting containerized applications written in any language and framework. It provides developers with highly available, automatically elastic scaling cloud services, avoiding the tedious server setup and operations during application development, enabling developers to focus on implementing business logic, thereby lowering the development threshold and improving efficiency.
CloudRun supports two modes:
- Container Mode: Suitable for deploying containerized applications in any language and framework.
- Function Mode: Suitable for hosting cloud function code, enabling simpler and more efficient development. 👉 For details, see: Function CloudRun
If you are using CloudRun for the first time, it is recommended to read the Quick Start document to quickly experience the basic features of CloudRun.
Use AI to develop, integrate and manage CloudRun services
Features
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| 🚀 Serverless Operations | No need to purchase, manage, or maintain servers, reducing operational costs |
| 📈 Automatic Elastic Scaling | The number of instances automatically adjusts with traffic, supporting scaling down to 0 and scaling out on demand |
| 💰 Pay-as-you-go | Pay only for the resources you actually use, with a minimum granularity of 0.25 cores, avoiding resource waste |
| 🏁 Low Entry Barrier | No need for cluster operations or writing YAML configurations, focus on business development |
| 🛠️ Supports Multiple Language Frameworks | Supports mainstream languages and frameworks such as Java, PHP, Go |
| 🔄 Low Migration Cost | Existing applications can be migrated to CloudRun without refactoring |
| 🖼️ Flexible Image/Code Deployment | Supports uploading images or directly uploading/pulling code for automatic building |
Resource Model
The resource model of CloudRun is divided into three layers: Service → Version → Instance.
- Service: Your business unit, each service has an independent access domain.
- Version: Different deployment versions of a service, which can be used for canary release, A/B testing, etc.
- Instance: An actual running container whose quantity automatically scales with traffic.
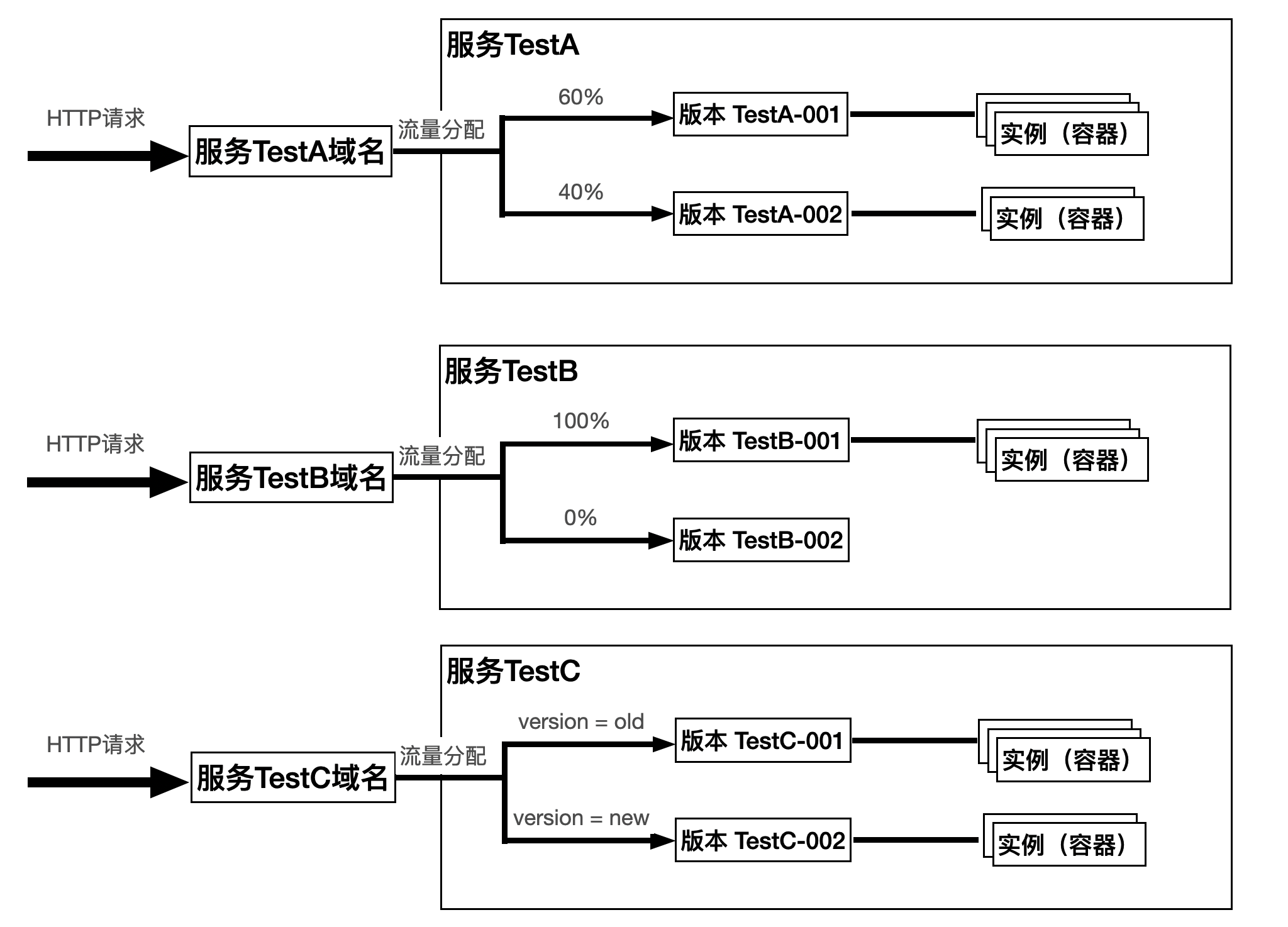
The diagram above shows three example services TestA, TestB, and TestC. Each service contains two versions, and each version corresponds to a group of 0 to N instance (container) resources.
Access and Traffic Allocation
- Each service has a system-assigned default domain (customizable).
- When a user accesses a service, the system routes the request to the corresponding version based on traffic allocation rules.
- The number of instances automatically adjusts based on request volume. It can scale down to zero when there are no requests, incurring no costs.