Security Source
Security Source configuration is the core security mechanism of cloud development services, ensuring only authorized sources can access your cloud development resources through strict access control. This article details how to configure and manage Web security domains and mobile application security sources.
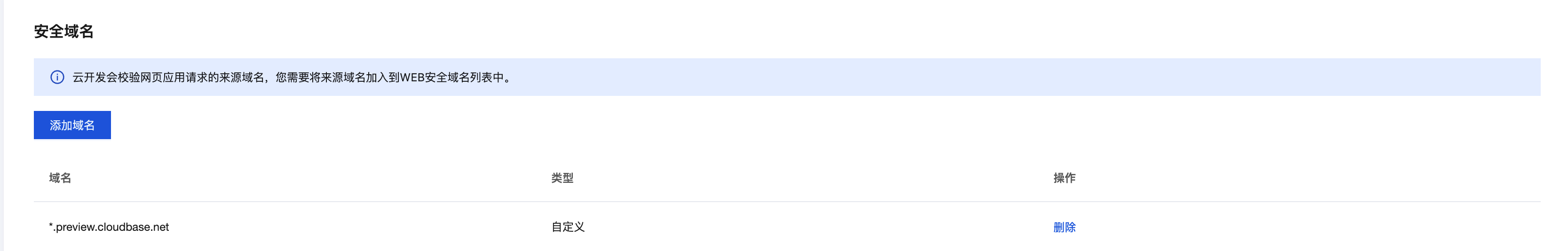
Security Domain Configuration
What Is a Security Domain?
Security Domain is an access control mechanism that ensures only domains on the allowlist can access cloud development resources, effectively preventing unauthorized access.
Configuration Method
Console Operation Steps
- Log in to Cloud Development Console / Environment Configuration / Security Source
- In the "Security Domain" section, click the [Add Domain] button.
- In the pop-up dialog box, fill in the domain name to be authorized:
- Supports full domain names (e.g.,
www.example.com) - Supports wildcards (e.g.,
*.example.com) - Supports port numbers (e.g.,
example.com:8080)
- Supports full domain names (e.g.,
- Click [OK] to complete the addition
Configuration Example
# Allow All Subdomains
*.example.com
# Allow Specific Domain Names
www.example.com
# Allow Domain Names with Ports
localhost:3000
Notes
- Quota Limit: Each environment can configure up to 50 secure domains.
- Effective Time: Takes effect approximately 1-2 minutes after configuration
- Format Requirement: Do not include the protocol prefix (e.g.,
https://) - Default Secure Domains: The system automatically configures the following domains:
localhost- Local development and debuggingenv-id.<your-env-region>.app.tcloudbase.com- HTTP access serviceenv-id.tcb.qcloud.la- File Storage Serviceenv-id.tcloudbaseapp.com- Static Website Hosting Service (requires activation)
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Why is the domain name still inaccessible after configuration?
Please check the following points:
- Whether the domain name is spelled correctly (including case sensitivity)
- Whether the protocol prefix (e.g.,
https://) has been incorrectly included - Whether it is accessed within an iframe (requires adding a special tag after the secure domain)
- Whether sufficient effective time has been waited (1-2 minutes)
- Whether there are any relevant error messages in the browser console
Mobile App Security Source
Why Mobile Application Security Sources Need to Be Configured
Mobile application security sources prevent your cloud resources from being accessed by unauthorized applications, effectively protecting your data security and business logic.
Configuration Process
Console Operation Steps
On the [Security Sources] configuration page, click [Add Application]
Fill in the application information
Application Name: A name for easy identification (e.g., "MyApp-iOS-Production")
Application Identifier:
- iOS applications: Use Bundle ID (e.g.,
com.example.myapp) - Android applications: use the application package name (e.g.,
com.example.myapp) - Mini Program: use AppID (e.g.,
wx1234567890)
- iOS applications: Use Bundle ID (e.g.,
Click [Save] to complete the configuration
Obtaining and Using Application Credentials
- In the actions column of the added application, click [Obtain Credentials]
- The system generates and displays environment information
- Click [Copy] to save private key information
Security Notice:
- Private key information is highly sensitive and should not be hardcoded or stored in plain text
- It is recommended to use secure storage mechanisms or remote configuration to obtain credentials
- Regularly rotate application credentials
- Different credentials should be used for different environments (development, testing, production)
Best Practices
Security Policy
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant permissions only to necessary domains and applications
- Environment Isolation: Testing environment and production environment use different configurations
- Platform Differentiation: Create independent configurations for iOS, Android, and Mini Programs
- Version Control: Rotate application credentials during major version updates
Credential Management
- Use Key Management System (KMS) to store sensitive credentials
- Credentials used by departing employees should be revoked immediately
- Use CI/CD pipelines to automatically inject credentials and avoid manual operations
Monitoring and Auditing
- Configure abnormal access alarm rules (e.g., abnormal geolocation, sudden surge in access volume)
- Monitor API call source distribution and frequency
- Regularly audit security source configuration
- Enable access logs and regularly analyze them
Configuration Checklist
- Is access to unnecessary domains and applications restricted
- Are development, testing, and production environments separated
- Are credentials rotated regularly (3-6 months)
- Have obsolete configurations and unused credentials been removed
- Has a monitoring and alarm mechanism been configured
- Is there an emergency response process for credential leakage established
Frequently Asked Questions
What to do in case of credential leakage?
If credential leakage is discovered, please immediately follow the procedure below:
- Immediately generate new credentials in the console
- Update the application code and release a new version
- Revoke the old credentials in the console
- Check the Cloud Development logs to investigate abnormal access