Quick Start
This guide will walk you through invoking cloud functions via HTTP access services, enabling your cloud functions to be accessed through HTTP requests.
Step 1: Create cloud function
First, we need to create a simple cloud function as an example:
- Go to the Cloud Development Console and select your environment.
- In the left menu bar, choose "Cloud Functions" and click "New Cloud Function".
- Create a cloud function named
helloWorld - Write the following code:
exports.main = async function() {
return "Hello World!";
};
- Click "Save and Install Dependencies" to complete the cloud function deployment
💡 Tip: You can also refer to the Cloud Function Quick Start to get a more detailed Cloud Function creation guide.
Step 2: Configure HTTP Access Route
Next, configure the HTTP access route for the cloud function:
- Go to the CloudBase HTTP Access Service page
- Click the "New" button to create a "Domain-Associated Resource"
- Fill in the configuration according to the following information:
- Associated Resource: Select "Cloud Function", then choose the newly created
helloWorldfunction - Domain Name: Select the default domain name (or choose your configured custom domain name)
- Trigger Path: Fill in
/hello(this will become the access path)
- Associated Resource: Select "Cloud Function", then choose the newly created
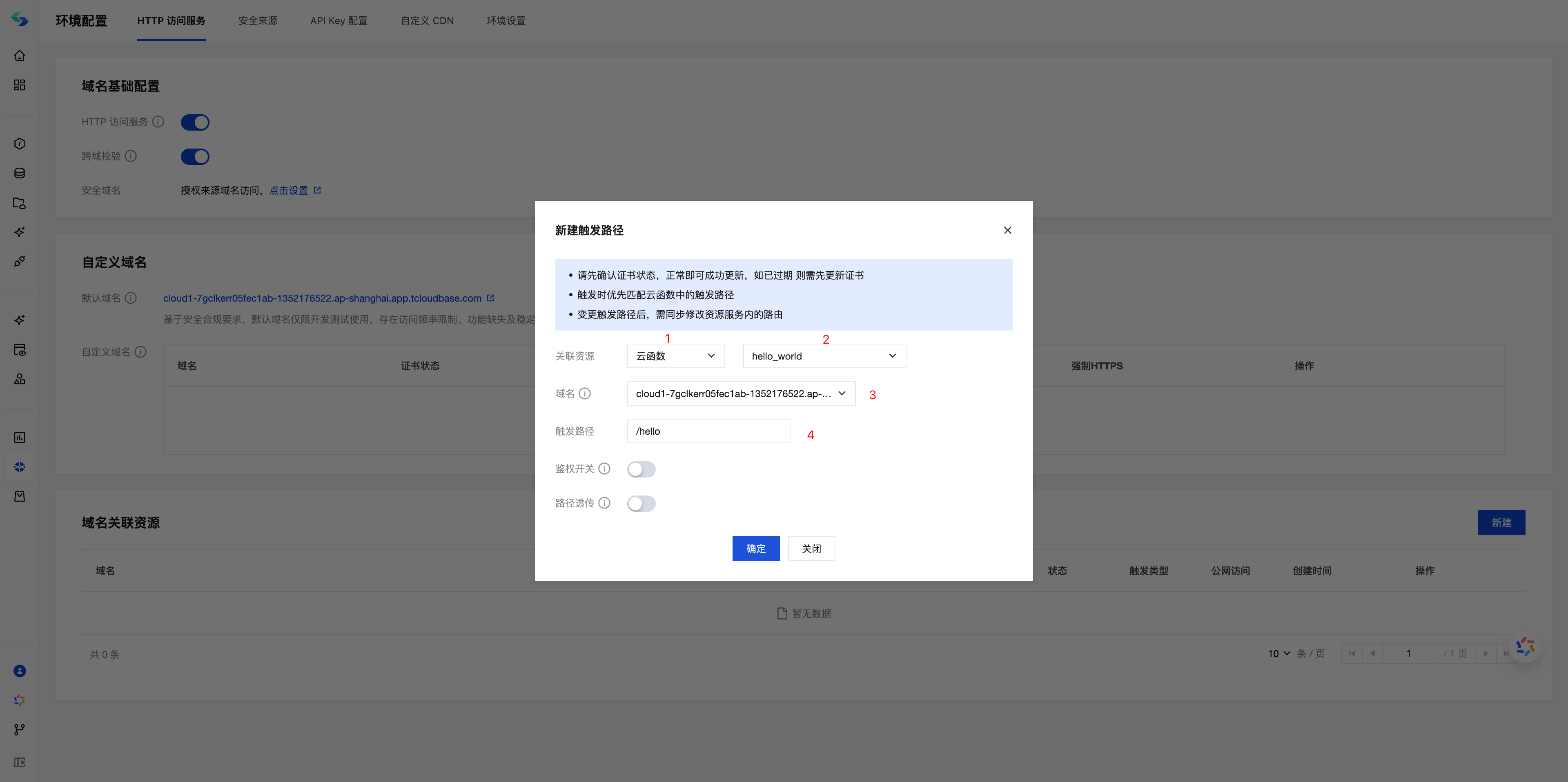
- Click "OK", and the system will begin creating the HTTP service
- Wait for 3-5 minutes, and the HTTP service will be configured and take effect
Step 3: Access Your HTTP Service
After the HTTP service is created, you can access it via the following methods:
- Access via command line:
curl https://{your-domain}/hello
# Result: Hello World!
- Access via browser:
Simply enter
https://{your-domain}/helloin your browser's address bar

📝 Note: The complete address of the HTTP service consists of "domain name" + "trigger path". If you use a custom domain name, please ensure that domain name ICP filing and HTTPS certificate configuration are completed.
For more details on accessing cloud functions, please refer to: Accessing Cloud Functions via HTTP.