Access Cloud Functions via HTTP
Through the HTTP access service, you can configure cloud functions as standard HTTP interfaces and call them via HTTP requests without an SDK. This document explains how to configure HTTP access for cloud functions and how to handle requests and responses.
Prerequisites
- CloudBase environment created
- At least one cloud function deployed
Configure HTTP Access
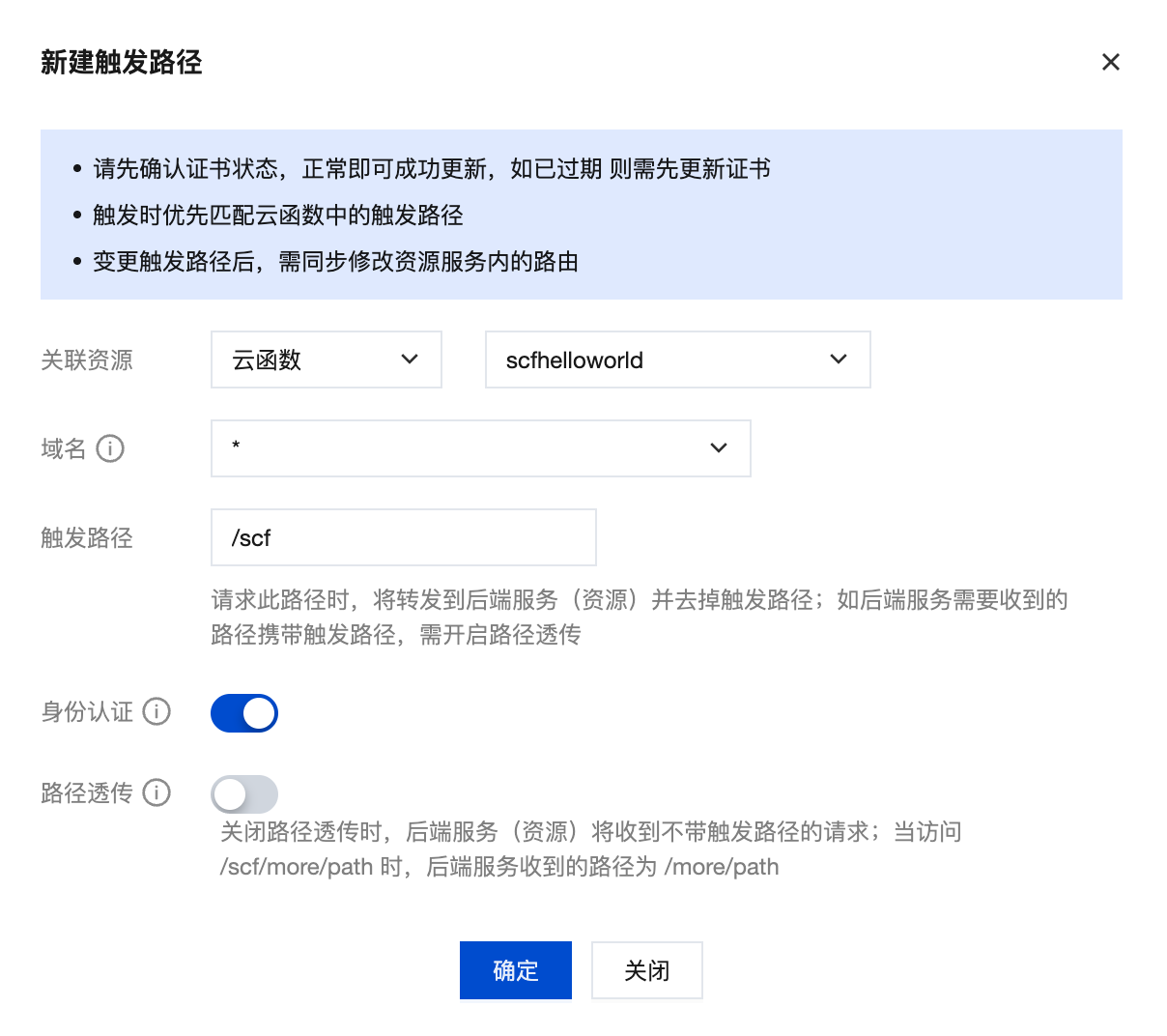
Step 1: Create Domain Association
- Go to CloudBase Console - HTTP Access Service
- Click the "New" button in the "Domain Associated Resources" section
- Configure the following information:
| Configuration Item | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Associated Resource Type | Select "Cloud Function", then choose target cloud function | hello-world |
| Domain | Select default domain, custom domain, or * (matches all domains) | Default domain |
| Trigger Path | Set HTTP access path, supports / or custom path | /api/hello |
💡 Tip: For production environments, it's recommended to bind a filed custom domain to get full service capabilities. Please refer to Custom Domain Configuration for configuration methods.
Step 2: Test Access
After configuration, access domain + trigger path to invoke the cloud function:
# Example: Access cloud function via default domain
curl https://your-env-id.<your-env-region>.app.tcloudbase.com/api/hello
Make HTTP Requests
After configuration, you can use any HTTP client to access cloud functions.
- curl
- JavaScript
- Python
# GET request
curl https://your-domain/your-function-path
# POST request
curl -X POST https://your-domain/your-function-path \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"name": "CloudBase", "version": "1.0"}'
// Using fetch API
const response = await fetch('https://your-domain/your-function-path', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ name: 'CloudBase', version: '1.0' })
});
const data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
import requests
# POST request
response = requests.post(
'https://your-domain/your-function-path',
json={'name': 'CloudBase', 'version': '1.0'}
)
data = response.json()
print(data)
Handle HTTP Requests in Cloud Functions
Receive Request Information
When accessing a cloud function via HTTP, the function's event parameter will contain complete HTTP request information:
exports.main = async (event, context) => {
// event object structure
const {
path, // HTTP request path, e.g. /api/hello
httpMethod, // HTTP request method, e.g. GET, POST, PUT, DELETE
headers, // HTTP request headers object
queryStringParameters, // URL query parameters object, e.g. ?name=value
body, // HTTP request body content (string format)
isBase64Encoded, // Whether body is Base64 encoded
requestContext // CloudBase environment related information
} = event;
// Return response
return { message: 'success' };
};
Example: Handle Different Types of Requests
- GET Request
- POST Request
- RESTful API
exports.main = async (event) => {
const { queryStringParameters } = event;
// Get query parameters
const name = queryStringParameters?.name || 'Guest';
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify({
message: `Hello, ${name}!`,
timestamp: Date.now()
})
};
};
Access Example:
curl "https://your-domain/greet?name=CloudBase"
# Response: {"message":"Hello, CloudBase!","timestamp":1699999999999}
exports.main = async (event) => {
const { body } = event;
// Parse JSON request body
const data = JSON.parse(body);
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify({
received: data,
processed: true
})
};
};
Access Example:
curl -X POST https://your-domain/process \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"userId": 123, "action": "update"}'
exports.main = async (event) => {
const { httpMethod, path, queryStringParameters, body } = event;
// Route handling
if (path === '/users' && httpMethod === 'GET') {
// Get user list
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify([{ id: 1, name: 'User1' }])
};
}
if (path.startsWith('/users/') && httpMethod === 'GET') {
// Get single user
const userId = path.split('/')[2];
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify({ id: userId, name: 'User' })
};
}
// 404
return {
statusCode: 404,
body: JSON.stringify({ error: 'Not Found' })
};
};
Related Documentation
- HTTP Access Service Overview - Understand the core features and advantages of HTTP access service
- Quick Start - Quick start guide
- Route Configuration - Configure flexible routing rules
- Custom Domain Configuration - Bind custom domains
- Cloud Function Development Guide - Cloud function development tutorial