Route Matching Rules
CloudBase HTTP access service provides flexible route configuration capabilities, allowing you to precisely route requests to various backend resources such as cloud run, cloud functions, and static hosting, achieving unified request distribution management.
Route configuration consists of two core elements: domain and path. The system matches based on these two elements according to specific priorities.
Matching Priority
Domain Matching:
- Exact match (e.g.
example.com) has higher priority than wildcard match (e.g.*) - Supports using wildcard
*to match any domain
- Exact match (e.g.
Path Matching:
- Follows longest match principle, the system will prioritize rules with the highest overlap with the request path
- Path matching is prefix matching, e.g.
/barcan match/bar/xxx
Matching Flow Diagram
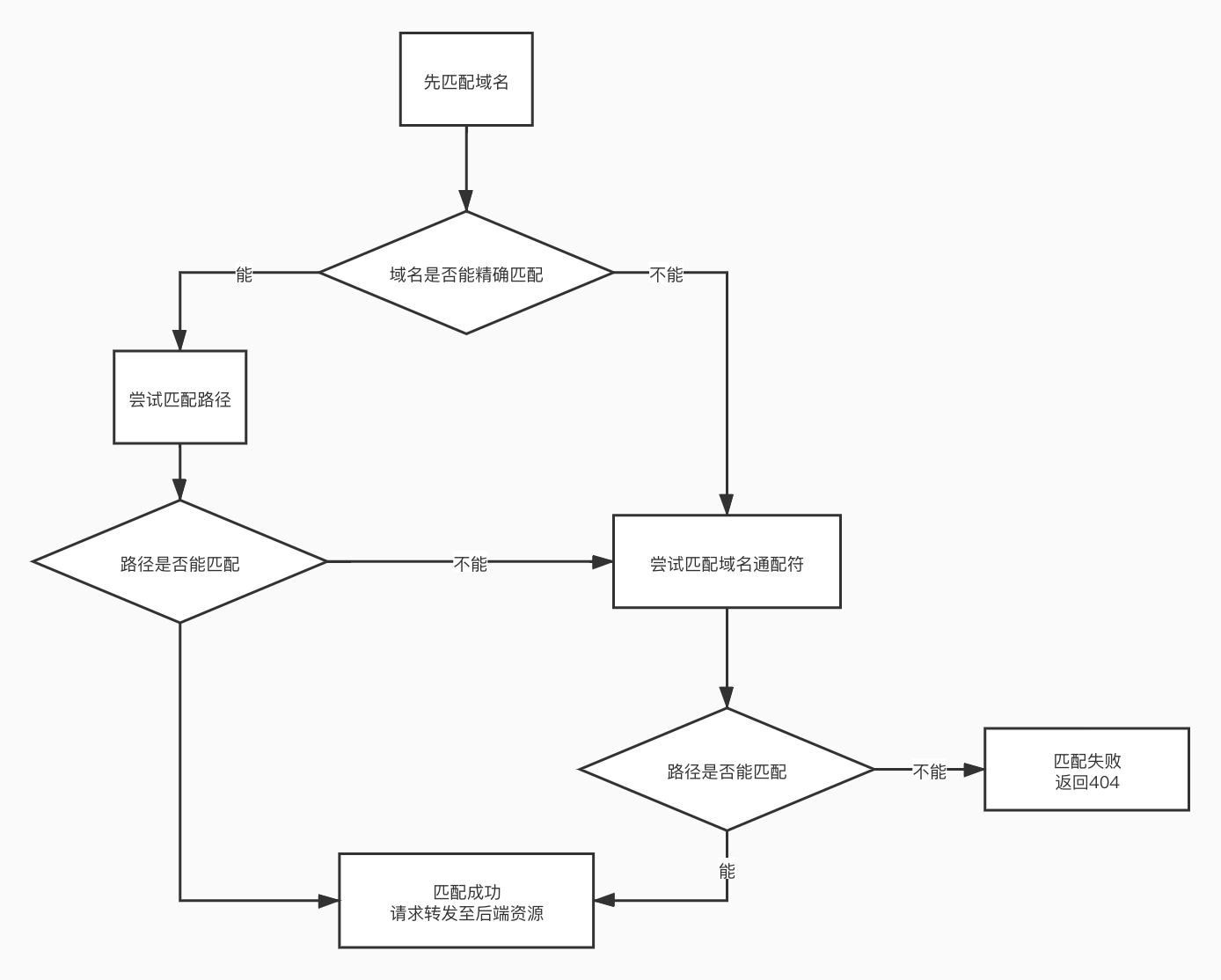
Route Matching Examples
The following table shows a set of route rule configurations:
| Domain | Path | Associated Resource |
|---|---|---|
| * | / | FunctionA |
| * | /bar | FunctionB |
| <Default Domain> | /bar | FunctionC |
| foo.com | / | FunctionD |
| foo.com | /bar | FunctionE |
| foo.com | /bar/baz | FunctionF |
Request Matching Results
Based on the above configuration, different requests will be routed to different resources:
| Access Address | Matched Resource | Matching Reason |
|---|---|---|
| <Default Domain>/xxx | FunctionA | Domain matched via wildcard *, path /xxx matches prefix / |
| <Default Domain>/bar | FunctionC | Exact match default domain, path exact match /bar |
| <Default Domain>/bar/xxx | FunctionC | Exact match default domain, path /bar/xxx matches prefix /bar |
| foo.com/xxx | FunctionD | Exact match domain foo.com, path /xxx matches prefix / |
| foo.com/bar | FunctionE | Exact match domain foo.com, path exact match /bar |
| foo.com/bar/xxx | FunctionE | Exact match domain foo.com, path /bar/xxx matches prefix /bar |
| foo.com/bar/baz | FunctionF | Exact match domain foo.com, path exact match /bar/baz (longest match principle) |