FAQ
Performance
Cloud function calls take a long time
You can check the cloud function logs to analyze the time-consuming parts. If the logs contain entries like Coldstart: xxxms, it indicates cloud function cold start latency. To resolve this issue, refer to Provisioned Concurrency.
How to handle cloud function execution timeout?
When a timeout occurs, the client will disconnect and report an error. It's recommended to control function execution time and avoid placing time-consuming operations in cloud functions that are directly called by the client.
What if I need to perform long-running processing in cloud functions?
To ensure a good client experience, direct calls to long-running cloud functions are not allowed.
- It's recommended to adjust the timeout setting in the cloud console to the required value (maximum 60s), and use callback() to return success within the cloud function, so the client doesn't wait for the execution result.
- The cloud function will continue to execute until completion or timeout within the timeout period, write the execution result to a database or other storage service, and then retrieve the result on the client side.
Configuration
Adjusting cloud function memory configuration doesn't take effect
Cloud function configuration takes effect on the $LATEST version. If the request is not for the $LATEST version, configuration changes will not take effect.
Solution:
- Ensure you're requesting the
$LATESTversion - Or publish a new version based on
$LATEST, which will use the current snapshot, including code and configuration (timeout, environment variables, memory configuration, etc.)
How to use built-in modules in cloud functions?
- Built-in modules in cloud functions are already integrated into the runtime environment and can be used directly.
- If the version of a built-in module doesn't meet your requirements, you can install the module in your cloud function, and it will be used by default with priority.
Currently supported built-in modules include request 2.87.1.
How to save secrets and other configuration information in cloud functions
Cloud functions are stateless. Configuration information should be stored in CloudBase database services.
Deployment
Why does cloud function update return exit status 11?
Please check the function packaging method and entry method.
- When creating a cloud function, the default execution method is index.main, with the entry file being index.js, and index.js must export the main method using export.
- When updating a cloud function, if you choose to upload a zip package, pay attention to the packaging method. The first level of content after unzipping the zip package must include the entry file (a common incorrect packaging method is to place the cloud function code in a folder and compress the folder, so that the unzipped file is a folder that doesn't include the entry file index.js).
Windows environment cloud function layer deployment failure
When packaging a cloud function layer zip file in a Windows environment, you may encounter an An internal error has occurred error when deploying to cloud functions.
Problem Description
When using the Windows built-in compression tool or PowerShell's Compress-Archive command to package a cloud function layer, an error occurs during upload and deployment:
Function update failed
An internal error has occurred. Retry your request, but if the problem persists, contact us with details
Root Cause
Zip files packaged on Windows systems use backslash \ as the path separator internally, while cloud function build environments are Linux systems that require forward slash / as the path separator.
This causes the Linux environment to be unable to correctly parse file paths in the zip package, resulting in deployment failure.
Solutions
Solution 1: Use 7-Zip for packaging (Recommended)
7-Zip is an open-source compression tool that uses Unix-style path separators when packaging.
- Download and install 7-Zip
- Right-click the folder to package
- Select "7-Zip" -> "Add to archive"
- Select "zip" as the compression format
Solution 2: Use WSL for packaging
If you have WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) installed, you can use the zip command in the WSL environment to package:
# Enter WSL environment
wsl
# Navigate to the layer file directory
cd /mnt/c/your/layer/path
# Use zip command to package
zip -r layer.zip ./*
Solution 3: Use Git Bash for packaging
Git Bash, which comes with Git for Windows, can also use Unix-style zip commands:
# Open Git Bash and navigate to the layer file directory
cd /c/your/layer/path
# Package
zip -r layer.zip ./*
Debugging
Some logs are missing when testing cloud functions?
- When testing cloud functions with synchronous invocation (timeout less than 20 seconds), the returned logs are limited to 4k maximum, and logs exceeding 4k won't be displayed.
- With asynchronous invocation (timeout greater than or equal to 20 seconds), the returned logs are limited to 6M maximum, and logs exceeding 6M won't be displayed.
Why do cloud function calls to other cloud functions report socket timeout, but the called cloud function actually executes successfully and returns data?
You can set the timeout duration for cloud functions in the function configuration - basic information section on the page. At the same time, if using the SDK, the SDK's default timeout is 15 seconds, and the shorter of the two will take effect.
Usage
How to call cloud functions from cloud functions
Currently, you can only call through the SDK provided by CloudBase, there is no other method.
Can different cloud functions share code files (directories)?
Not yet available.
Do Node.js cloud functions support both asynchronous and synchronous syntax?
Yes, the synchronous (async/await) syntax is recommended.
Cloud function HTTP access reports MISSING_CREDENTIALS error after configuring authentication
When a cloud function is configured with HTTP access service, enabling identity authentication for the cloud function in environment configuration will cause the previously accessible URL to report a MISSING_CREDENTIALS error.
Problem Description
- Cloud function has HTTP access service path configured and can be accessed directly via URL
- After enabling identity authentication for the cloud function in environment configuration
- Accessing the URL returns a
MISSING_CREDENTIALSerror
Root Cause
After enabling identity authentication, all requests need to carry valid identity credentials (such as Access Token or API Key) to access the cloud function. This is CloudBase's security mechanism to protect cloud functions from unauthorized access.
Solutions
Solution 1: Use Access Token authentication
Carry Access Token in the request header:
// First obtain Access Token through login
const response = await fetch('https://your-env-id.api.tcloudbasegateway.com/v1/functions/your-function-name', {
headers: {
'Authorization': 'Bearer your-access-token'
}
});
For Access Token acquisition methods, please refer to AccessToken Usage Guide
Solution 2: Use API Key authentication
For server-side calls, you can use API Key:
const response = await fetch('https://your-env-id.api.tcloudbasegateway.com/v1/functions/your-function-name', {
headers: {
'Authorization': 'Bearer your-api-key'
}
});
Solution 3: Use Publishable Key authentication
For client-side public access scenarios, you can use Publishable Key:
const response = await fetch('https://your-env-id.api.tcloudbasegateway.com/v1/functions/your-function-name', {
headers: {
'Authorization': 'Bearer your-publishable-key'
}
});
Solution 4: Disable authentication
If the cloud function needs public access, you can disable identity authentication:
- Log in to CloudBase Console
- Go to [Environment] - [HTTP Access Service]
- Find the corresponding cloud function path and disable identity authentication
Disabling identity authentication means anyone can access the cloud function. Please ensure the cloud function has appropriate security validation logic internally.
Online Development
Online editor Python runtime environment differs from cloud function actual runtime environment
Root Cause
The online editor's development environment is a separate environment, independent from the cloud function's actual runtime environment. The online editor environment is primarily used for code writing and simple development, and does not automatically synchronize runtime versions when cloud functions are deleted or recreated.
Additionally, the online editor needs to download code from the runtime environment before online development can begin, which may result in multiple cloud function code bases being simultaneously downloaded to the online editor.
Solutions
Work in the current function directory during online development - The online editor may contain code from multiple cloud functions. Simply ensure you are operating in the code directory of your current cloud function, which will not affect the cloud function's actual execution.
Local development and deployment (Recommended) - If you have strict dependencies on Python minor versions, it's recommended to develop in your local development environment using the corresponding Python version, then deploy to the cloud function via the console or command-line tools.
The cloud function's actual runtime environment is independent from the online editor's development environment. After creating a Python 3.10 cloud function, the function's actual runtime environment in the cloud is Python 3.10, unaffected by the online editor environment version.
Cloud function and other online development features cannot be used properly
Root Cause
The online development feature in the CloudBase platform uses CloudStudio as the editor and relies on the "Tencent CloudBase Toolkit V2" extension to implement CloudBase online development capabilities. Therefore, you need to ensure that the "Tencent CloudBase Toolkit V2" extension is always up to date.
Solutions
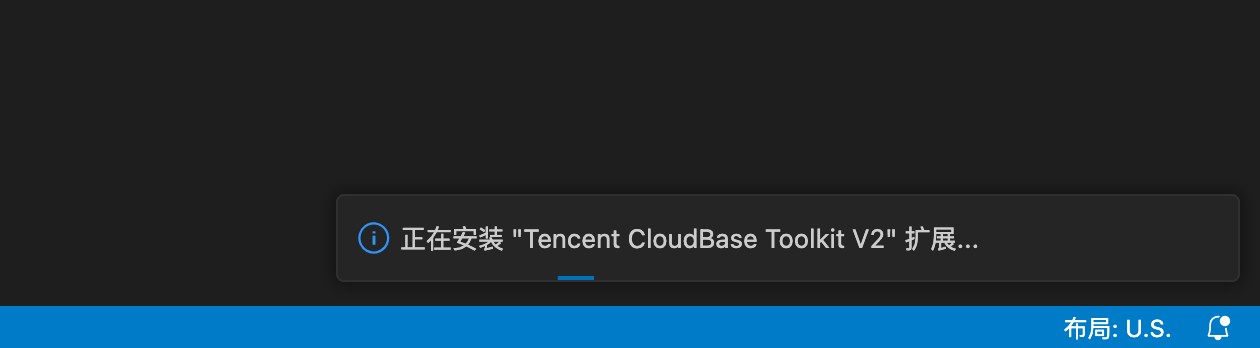
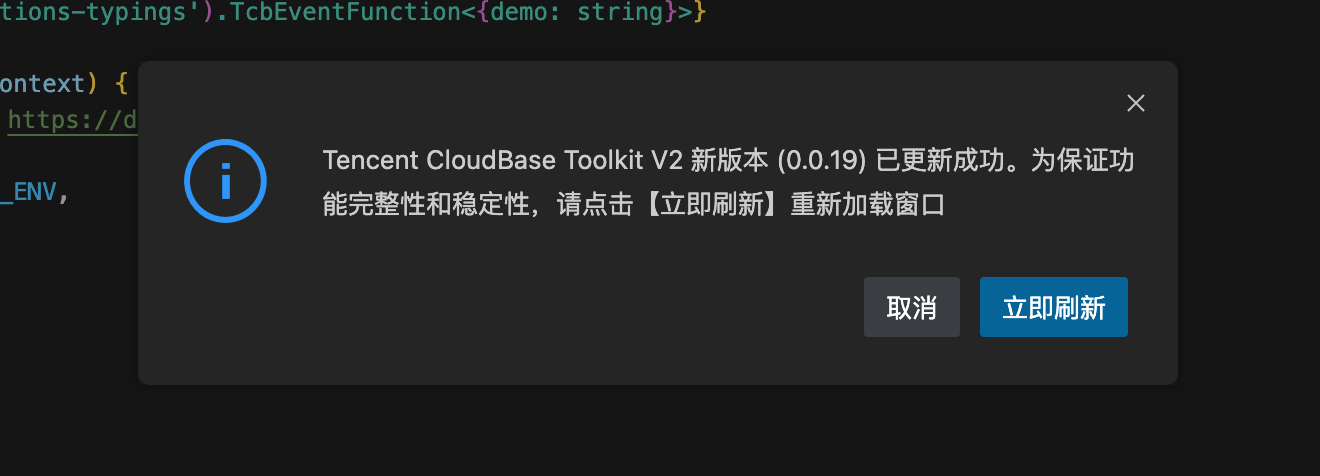
- Try reopening the online editor
When you reopen the online editor, the system will automatically detect and update the extension. After a successful update, you will be prompted to refresh, as shown below:
- Manually update the extension
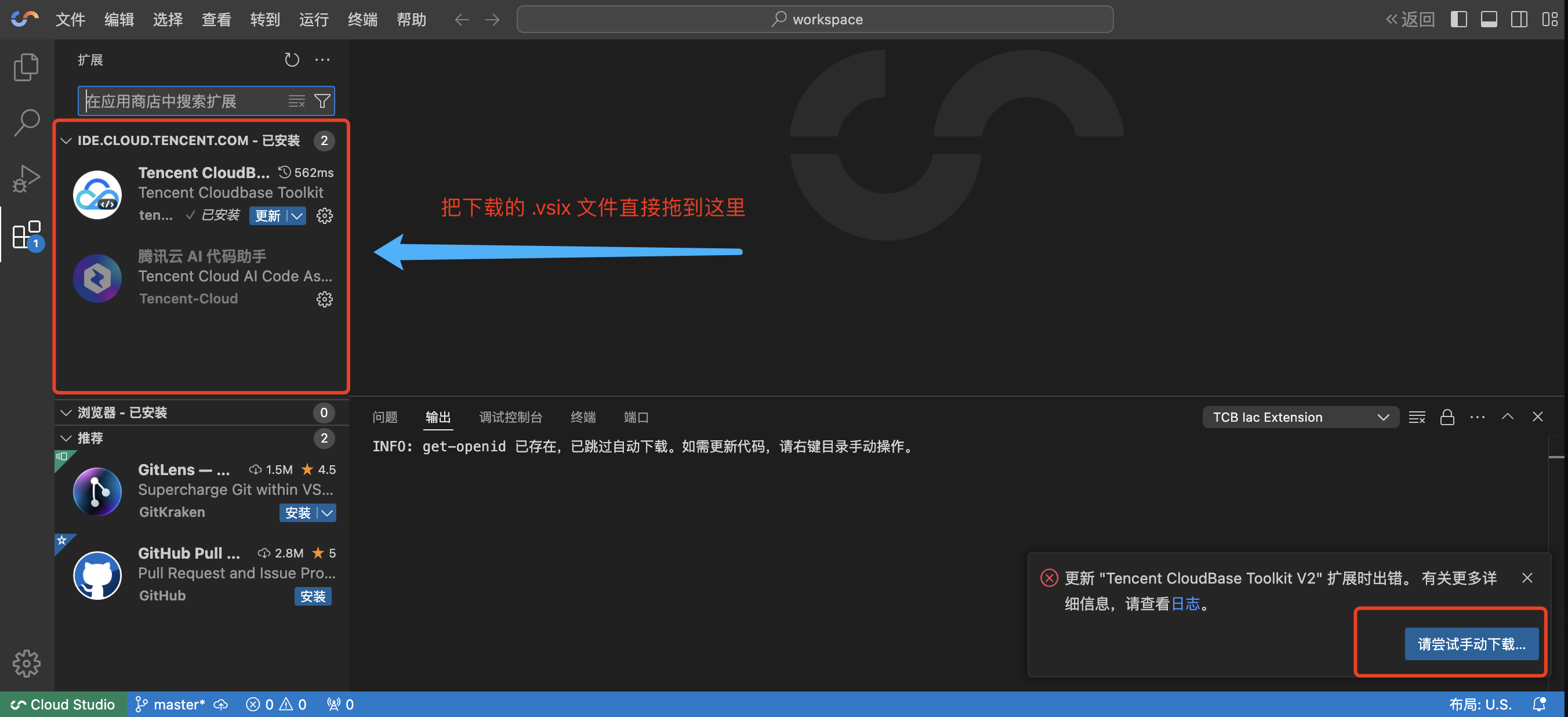
Sometimes, automatic updates may fail due to extension marketplace network issues. In this case, you can try manually updating the extension, as shown below:
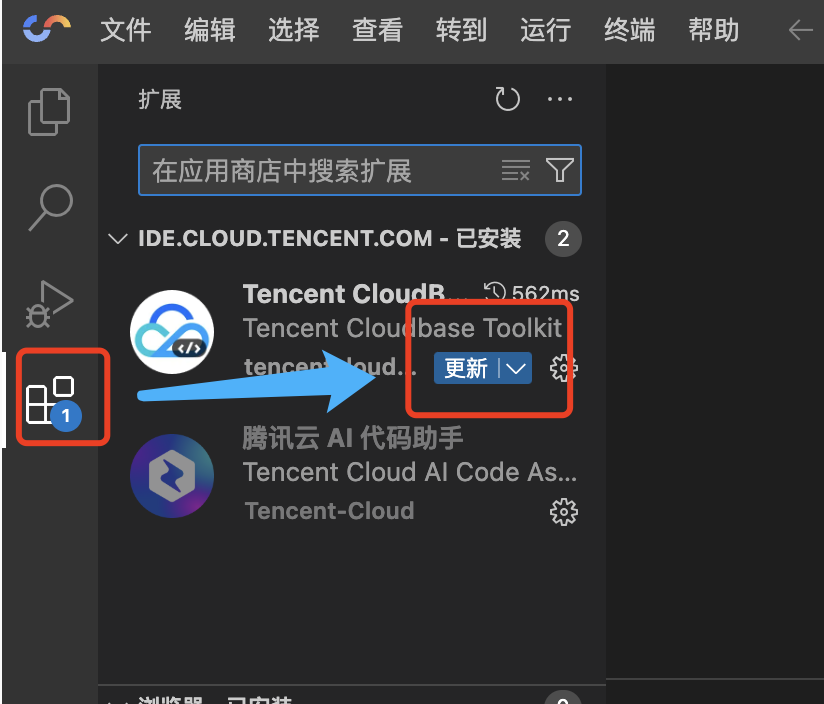
If the update still fails, you can download the extension locally according to the prompts, and then drag it into the editor to install, as shown below:
After deleting a cloud function on the CloudBase platform, it still exists in the online editor
Root Cause
On the CloudBase platform, cloud functions are deployed services, while the online editor is used to store cloud function code. These two are independent of each other, and deleting a cloud function deployment does not automatically delete the corresponding code.
For example, we write code for a service locally and then deploy it to the online environment. When the service is no longer needed, we can take it offline by deleting the deployment. However, at this point, the local service code will still be retained and will not automatically disappear due to the deletion of the online service.
The online editor on the CloudBase platform is essentially a remote version of the local editor. It's essentially just changing the place where you write code. Its code storage mechanism is consistent with the principle of local writing and deployment.
Solution
If you have confirmed that you no longer need a cloud function's code, you can directly delete the cloud function code in the online editor.
After deleting and recreating a cloud function with the same name on the CloudBase platform, the online editor still shows the previous version
Root Cause
This is related to the online editor's automatic download strategy. When a cloud function with the same name already exists in the workspace, the online editor will automatically skip the download process to avoid overwriting code, and prompt the user to manually download updates.
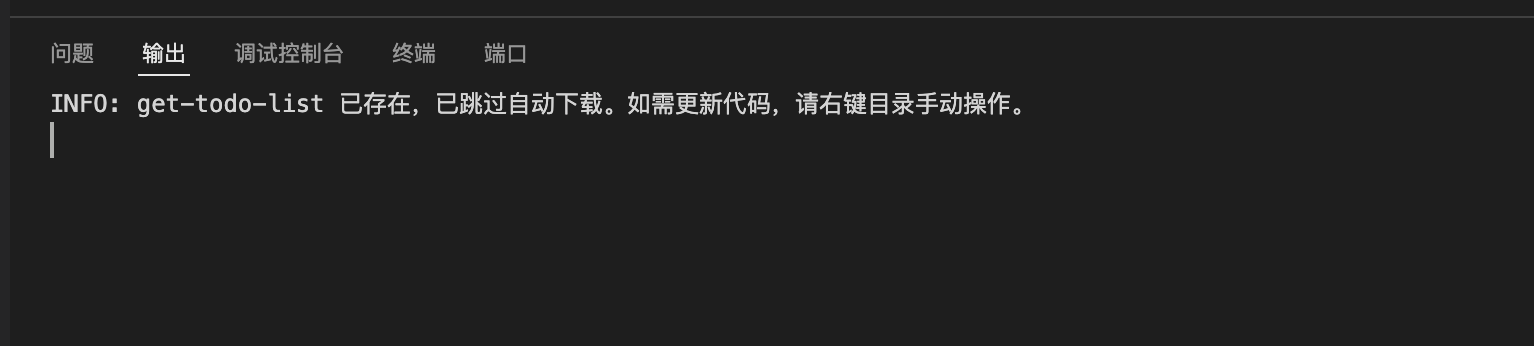
Solution
Synchronize cloud function code through manual download.
For specific steps, refer to the download section in the Cloud Function Online Development manual.
Download fails when entering online development after creating a function-based CloudRun
Root Cause
Function-based CloudRun is based on CloudRun. Without deployment history, online development cannot download the corresponding code package, resulting in the following prompt:
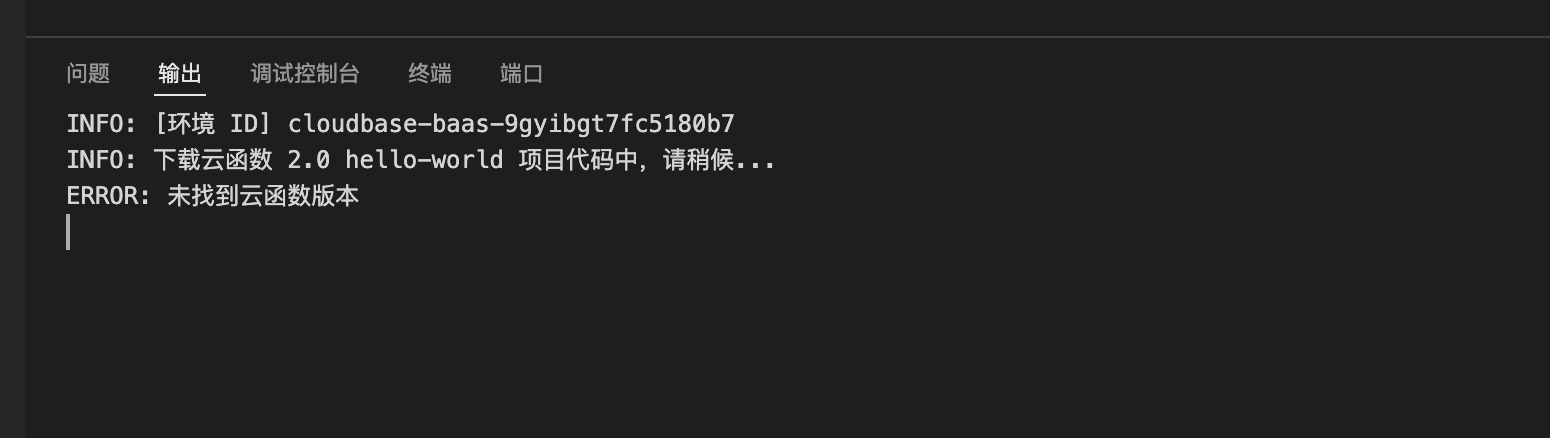
Solution
Please wait patiently for the cloud function deployment to complete, then enter online development for operations.
Where is the function operation menu for online development?
Please refer to Cloud Function Online Development
pnpm install dependencies error

Root Cause
The pnpm version declared in the project's package.json is inconsistent with the pnpm version installed in the current environment.
Solution
Open the terminal and execute the command corepack enable.
Online editor prompts high disk usage
When the online editor's disk space usage exceeds 85%, you will see the following prompt:
You can click the [Auto Clean Cache] button to clean npm / yarn / pnpm / pip and other dependency caches. At the same time, please check if there are large files in the workspace (such as compressed packages, binary installation files, etc.), and it's recommended to keep only necessary code files.
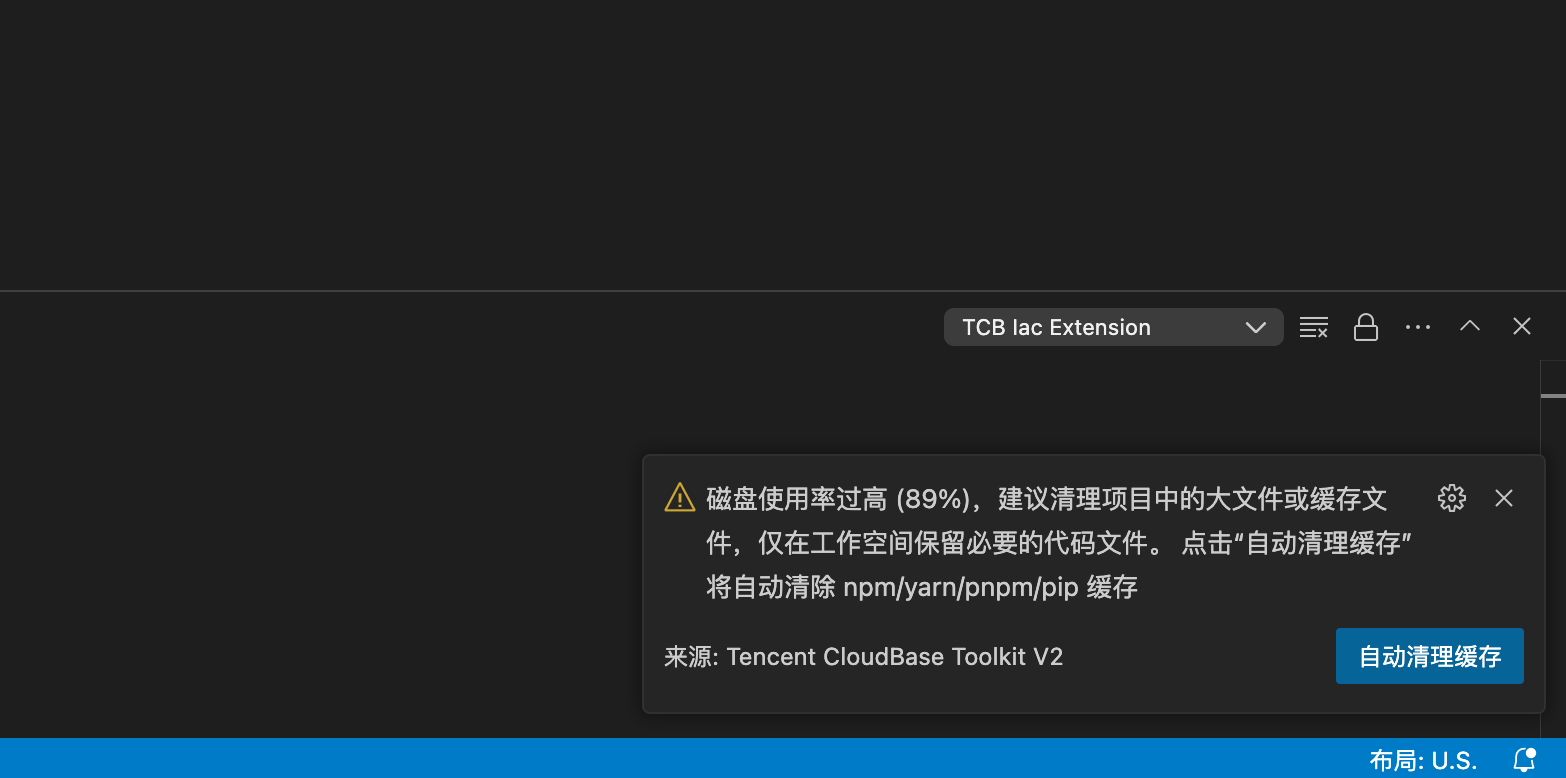
If the disk space usage exceeds 90%, to ensure the normal operation of the online editor, the system will automatically perform cache cleaning.
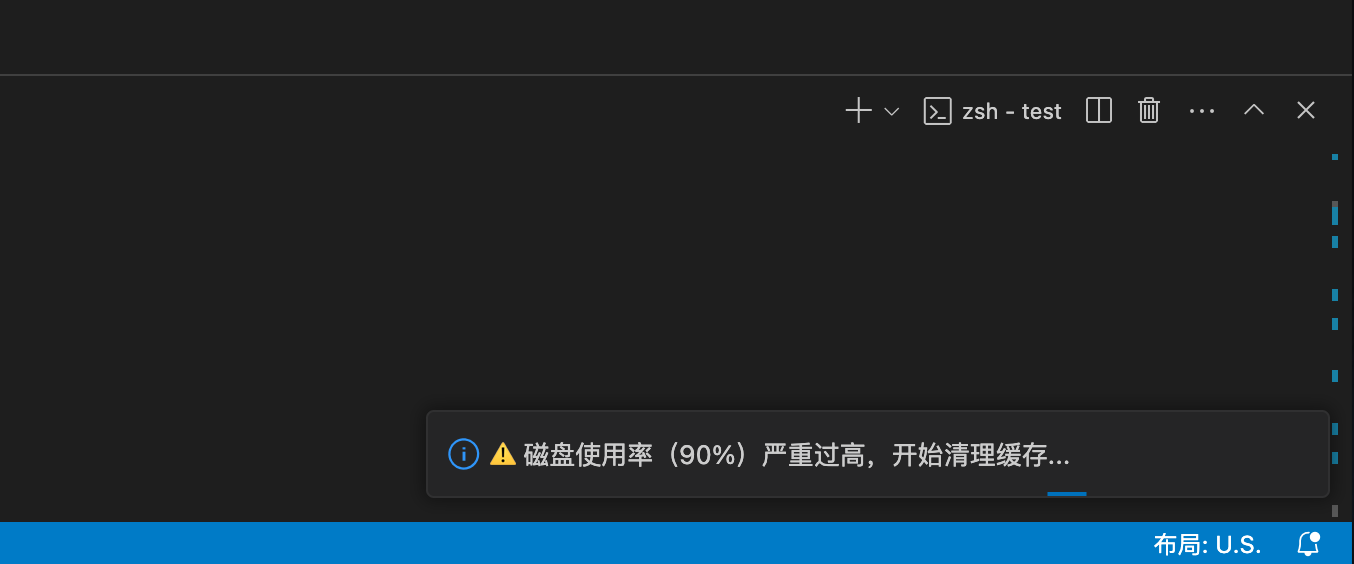
You can execute the command "df -h" to view the disk usage of the workspace.
Timeout getting temporary credentials, some features of the online editor will not work properly

Root Cause
When you encounter the above prompt, first check if the "Tencent CloudBase Toolkit V2" extension is installed in the online editor. If not installed, please search for the keyword "Tencent CloudBase Toolkit V2" in the extension marketplace to find and install the extension, then refresh the page and retry.
If it's not the above issue, it's likely that the online editor's disk space is insufficient, causing the extension to execute abnormally. Please follow the solution below.
Solution
Usually, there will be relevant prompts when entering the online editor. Refer to Online editor prompts high disk usage
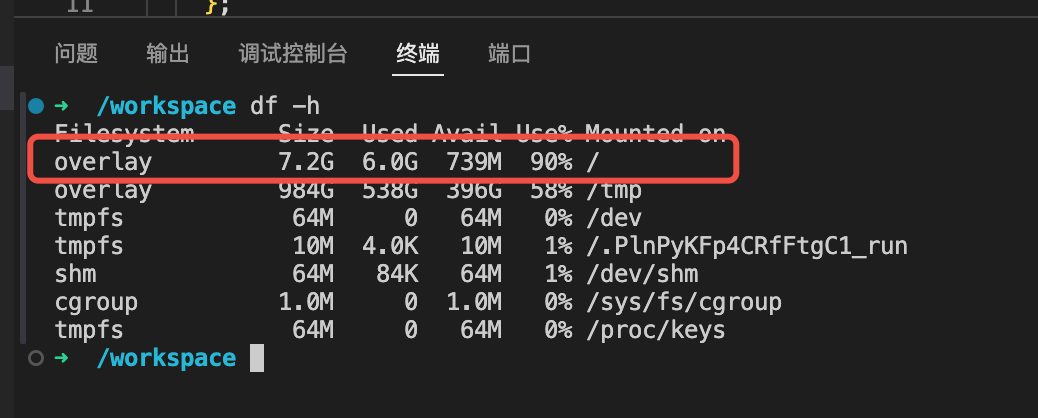
If there is no prompt, you can first open the terminal and execute the command df -h to view the remaining disk space.
If you find that disk space is running out, you can first try running the following commands to clear the cache, while cleaning up unnecessary large files in the workspace:
npm cache clean --force
pnpm store prune
yarn cache clean
pip cache purge
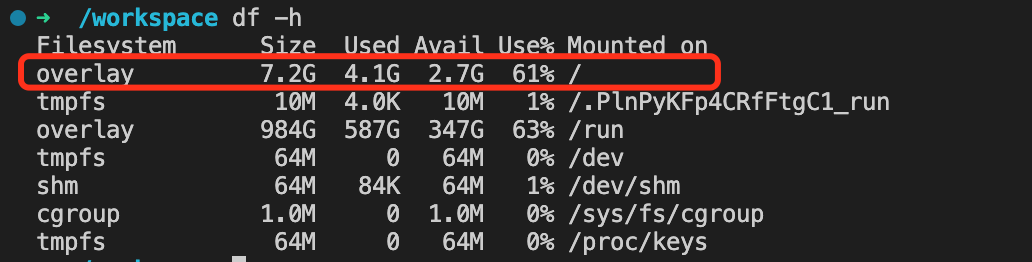
Finally, check the disk space usage again with the df -h command to see if it has decreased. If the space usage has decreased, you can re-enter the online editor for operations.
Prompted to log in when opening the cloud function debugging service link
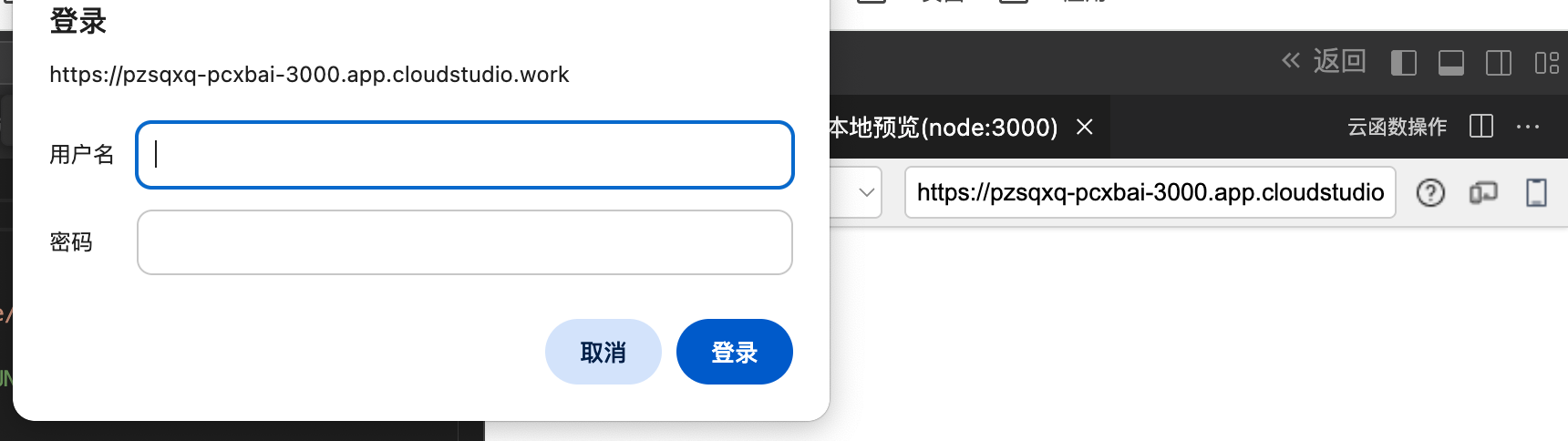
Root Cause
The debugging link is only valid within the online editor. To prevent external access, the debugging link can only be accessed within the [Test Panel], and cannot be accessed from other locations.
Solution
Please use the [Test Panel] that automatically opens when debugging in the online editor for debugging operations, as shown below: