Relation Details
A relation is a connection between data models, linking data from different models through relation fields to achieve logical connections between data.
When creating a relation, the system will establish relation fields in both data models to store the _id of the related data.
⚠️ Note: Relation fields in MySQL data models are associated through intermediate tables, so direct SQL JOIN queries are not supported. You must use the relation query methods provided by the data model to retrieve related data.
Common relation scenarios:
Student belongs to a class (Student → Class)
- Student model relation field: Belongs to class
- Class model relation field: Student list
Article has multiple comments (Article → Comment)
- Article model relation field: Comment list
- Comment model relation field: Belongs to article
User has a profile (User → Profile)
- User model relation field: Profile
- Profile model relation field: Belongs to user
Supported Database Types
| Database Type | Supported Relations |
|---|---|
| Database (Document) | One-to-One, One-to-Many, Many-to-One |
| Database (MySQL) | One-to-One, One-to-Many, Many-to-One, Many-to-Many |
| Custom MySQL Database | One-to-One, One-to-Many, Many-to-One, Many-to-Many |
Relation Types
One-to-One (1:1)
One record can only be related to one record from another model, both sides have a unique correspondence.
Example: User ↔ Profile
// User model
{
name: "Zhang San",
profile: {
_id: "profile_123"
}
}
// Profile model
{
_id: "profile_123",
avatar: "avatar.jpg",
bio: "Personal bio"
}
One-to-Many (1:N)
One record can be related to multiple records from another model.
Example: Class ↔ Student
// Class model
{
name: "Grade 1 Class 1",
students: [
{ _id: "student_1" },
{ _id: "student_2" }
]
}
Many-to-One (N:1)
Multiple records are related to one record from another model.
Example: Student ↔ Class
// Student model
{
name: "Xiao Ming",
class: {
_id: "class_123"
}
}
Many-to-Many (M:N)
Multiple records can be related to multiple records from another model.
Example: Student ↔ Course
// Student model
{
name: "Xiao Ming",
courses: [
{ _id: "course_1" }, // Chinese
{ _id: "course_2" } // Math
]
}
Relation Operations
When using relations, pay attention to data format and error handling. Operations are consistent in both client and server (cloud function) environments.
💡 Note: All relation field operations must use the
{_id: "xxx"}format, wherexxxis the_idof the related data. No need to pass other fields.
Query Operations
💡 Note: For MySQL databases, relation queries must use the query methods provided by the data model. Direct SQL JOIN statements are not supported.
⚠️ Important Limitation: Relation queries currently only support one level of relation, nested relation queries are not supported.
Relation Query Level Limitation
Supported queries (one-level relation):
// ✅ Correct: Query article with related author information (one-level relation)
const { data } = await models.post.get({
filter: {
where: { _id: { $eq: "post_123" } }
},
select: {
_id: true,
title: true,
author: { // Relation field: one level
_id: true,
name: true,
email: true,
profile: true // Non-relation field, can be queried
}
}
});
Unsupported queries (multi-level relation):
// ❌ Wrong: Multi-level nested relation query does not work
const { data } = await models.post.get({
filter: {
where: { _id: { $eq: "post_123" } }
},
select: {
title: true,
author: { // First level relation
name: true,
profile: { // ❌ Second level relation: not supported
address: { // ❌ Third level relation: not supported
city: true
}
}
}
}
});
// Query result will not return profile.address data
Distinguish relation fields from regular fields:
// ✅ Correct: Query regular fields (non-relation fields) within relation fields
const { data } = await models.post.get({
filter: {
where: { _id: { $eq: "post_123" } }
},
select: {
title: true,
author: { // Relation field (one level)
name: true,
email: true,
avatar: true, // Regular field
bio: true // Regular field
// All above are regular fields of author model, not relation fields
}
}
});
Alternatives for multi-level relations:
If you need to query multi-level relation data, use step-by-step queries:
// Solution 1: Step-by-step query
// Step 1: Query article and author
const post = await models.post.get({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "post_123" } } },
select: {
title: true,
author: {
_id: true,
name: true,
profileId: true // Get profile ID
}
}
});
// Step 2: Query profile details by profileId
if (post.data.author.profileId) {
const profile = await models.profile.get({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: post.data.author.profileId } } },
select: {
address: {
city: true,
street: true
}
}
});
// Manually combine data
post.data.author.profile = profile.data;
}
// Solution 2: Data redundancy
// Redundant common profile information in author model
{
_id: "author_123",
name: "Zhang San",
email: "zhang@example.com",
profileId: "profile_456", // Relation field
city: "Beijing", // Redundant field: from profile.address.city
bio: "Personal bio" // Redundant field: from profile.bio
}
// This allows retrieving required information in one-level query
const { data } = await models.post.get({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "post_123" } } },
select: {
title: true,
author: {
name: true,
city: true, // Redundant city field
bio: true // Redundant bio field
}
}
});
Query Results Including Related Data
// Query article with its comments (one-level relation)
const { data } = await models.post.get({
filter: {
where: {
_id: { $eq: "post_123" }
}
},
select: {
_id: true,
title: true,
content: true,
// Include related comment data (one-level relation)
comments: {
_id: true,
content: true,
createdAt: true
}
}
});
Filter by Relation Conditions
// Query articles with comments
const { data } = await models.post.list({
filter: {
relateWhere: {
comments: {
where: {
content: { $nempty: true }
}
}
}
},
select: {
_id: true,
title: true,
comments: {
content: true
}
}
});
Create Operations
You can establish relations when creating records:
// Create student and relate to class and courses
const { data } = await models.student.create({
data: {
name: "Xiao Ming",
age: 8,
// Relate to class (many-to-one)
class: {
_id: "class_123"
},
// Relate to multiple courses (many-to-many)
courses: [
{ _id: "course_1" },
{ _id: "course_2" }
]
}
});
Update Operations
Update One-to-One Relation
// Client/Cloud Function: Update user's profile relation
const { data } = await models.user.update({
filter: {
where: {
_id: { $eq: "user_123" }
}
},
data: {
profile: {
_id: "profile_456"
}
}
});
// Using doc() method in cloud function
exports.main = async (event) => {
const { userId, profileId } = event;
try {
const result = await cloudbase.model('user').doc(userId).update({
profile: {
_id: profileId
}
});
return { success: true, result };
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'INVALID_RELATION_FORMAT') {
return {
success: false,
message: 'Invalid relation field format, please use {_id: "xxx"} format'
};
}
throw error;
}
};
Update One-to-Many Relation
// Client/Cloud Function: Update class's student list
const { data } = await models.class.update({
filter: {
where: {
_id: { $eq: "class_123" }
}
},
data: {
students: [
{ _id: "student_1" },
{ _id: "student_2" },
{ _id: "student_3" }
]
}
});
// Cloud function example: Batch processing from parameters
exports.main = async (event) => {
const { classId, studentIds } = event;
try {
const result = await cloudbase.model('class').doc(classId).update({
students: studentIds.map(id => ({ _id: id }))
});
return { success: true, result };
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'INVALID_RELATION_FORMAT') {
return {
success: false,
message: 'Invalid relation field format, each item in array must use {_id: "xxx"} format'
};
}
throw error;
}
};
Update Many-to-Many Relation
// Client/Cloud Function: Update student course selection
const { data } = await models.student.update({
filter: {
where: {
_id: { $eq: "student_123" }
}
},
data: {
courses: [
{ _id: "course_1" },
{ _id: "course_2" }
]
}
});
// Cloud function example: Update student course selection
exports.main = async (event) => {
const { studentId, courseIds } = event;
try {
const result = await cloudbase.model('student').doc(studentId).update({
courses: courseIds.map(id => ({ _id: id }))
});
return { success: true, result };
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'INVALID_RELATION_FORMAT') {
return {
success: false,
message: 'Invalid relation field format, please use array of {_id: "xxx"} format'
};
}
throw error;
}
};
Add Related Data
Add new related records to existing relation list:
// Add new course to existing student
// Step 1: Query current course list
const student = await models.student.get({
filter: {
where: { _id: { $eq: "student_123" } }
},
select: {
courses: true
}
});
const currentCourses = student.data.courses || [];
// Step 2: Check if already exists to avoid duplication
const courseExists = currentCourses.some(c => c._id === "course_3");
if (!courseExists) {
// Step 3: Update course list
await models.student.update({
filter: {
where: { _id: { $eq: "student_123" } }
},
data: {
courses: [
...currentCourses,
{ _id: "course_3" }
]
}
});
}
// Cloud function wrapper example
exports.main = async (event) => {
const { studentId, newCourseId } = event;
try {
// First query current course list
const student = await cloudbase.model('student').doc(studentId).get();
const currentCourses = student.data.courses || [];
// Add new course (avoid duplication)
const courseExists = currentCourses.some(c => c._id === newCourseId);
if (courseExists) {
return { success: false, message: 'Course already exists' };
}
// Update course list
const result = await cloudbase.model('student').doc(studentId).update({
courses: [
...currentCourses,
{ _id: newCourseId }
]
});
return { success: true, result };
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to add course', error);
throw error;
}
};
Remove Related Data
Remove specified related records from relation list:
// Remove a course from student
// Step 1: Query current course list
const student = await models.student.get({
filter: {
where: { _id: { $eq: "student_123" } }
},
select: {
courses: true
}
});
const currentCourses = student.data.courses || [];
// Step 2: Filter out the course to be removed
const updatedCourses = currentCourses.filter(c => c._id !== "course_2");
// Step 3: Update course list
await models.student.update({
filter: {
where: { _id: { $eq: "student_123" } }
},
data: {
courses: updatedCourses
}
});
// Cloud function wrapper example
exports.main = async (event) => {
const { studentId, courseId } = event;
try {
// First query current course list
const student = await cloudbase.model('student').doc(studentId).get();
const currentCourses = student.data.courses || [];
// Filter out the course to be removed
const updatedCourses = currentCourses.filter(c => c._id !== courseId);
// Update course list
const result = await cloudbase.model('student').doc(studentId).update({
courses: updatedCourses
});
return { success: true, result };
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to remove course', error);
throw error;
}
};
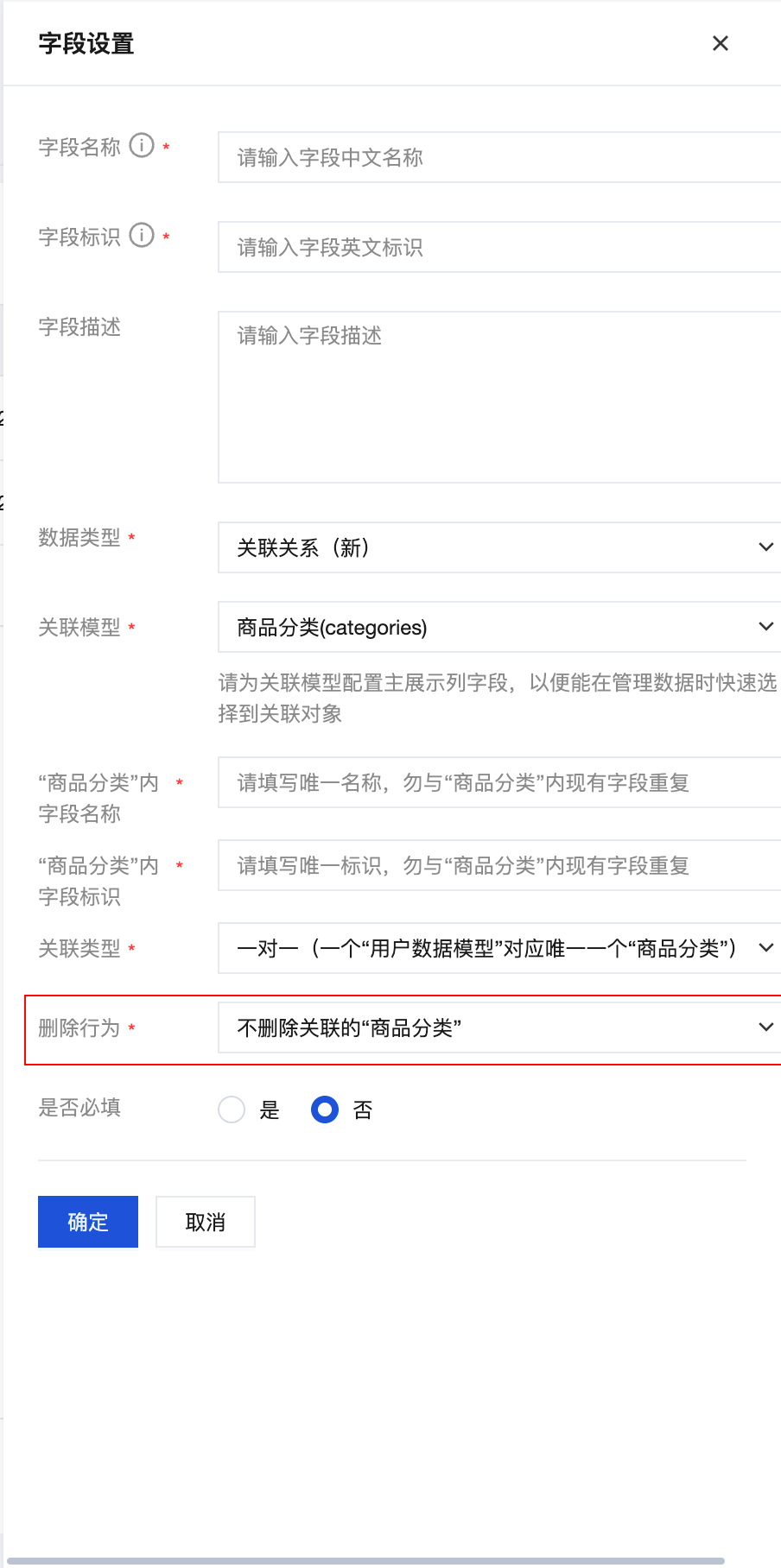
Delete Operations
When configuring relations, you can set different deletion behaviors:
- Delete related model data: Delete related records when deleting the main record
- Do not delete related model data: Only delete the main record, keep related records
- Prohibit deletion of data with relations: Prohibit deletion of the main record if related records exist
Relation Field Limitations
Field Length Limits
⚠️ Note: Relation fields store
_idvalues with the following length limits:
| Limit Item | Maximum Length | Description |
|---|---|---|
Single _id | 256 bytes | ID length limit for a single related record |
| One-to-Many/Many-to-Many Array | 1024 bytes | Total length limit for array storing multiple _ids |
| Image CloudID | 100-200+ bytes | Cloud storage image IDs may be long, need special attention |
Many-to-Many Relation Count Limits
For many-to-many relations, due to the total length limit of 1024 bytes, the number of related records is limited:
Single _id Length | Maximum Relation Count | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 20 bytes | ~50 records | MongoDB ObjectId standard length |
| 36 bytes | ~28 records | UUID format |
| 10 bytes | ~100 records | Custom short ID |
Recommendations:
- For scenarios requiring many relations (e.g., user favorites may exceed 100 items), consider using a separate relation table
- Using custom short IDs can increase relation count
- Evaluate actual business needs and choose appropriate solution
Many-to-Many Intermediate Table Operations
For many-to-many relations in MySQL data models, the system automatically creates intermediate tables. Although direct SQL JOIN is not supported, you can work with intermediate tables through the following methods.
Finding Intermediate Table Name
Example: Many-to-many relation between student and course
- Intermediate table structure:
course_student
├── course_id (foreign key)
├── student_id (foreign key)
└── created_at (creation time)
Query Intermediate Table Data
Although direct JOIN is not supported, you can retrieve related data through the data model's relation query:
// Query student and all their enrolled courses
const { data } = await models.student.get({
filter: {
where: {
_id: { $eq: "student_123" }
}
},
select: {
_id: true,
name: true,
courses: {
_id: true,
courseName: true,
credits: true
}
}
});
// Result contains complete related data
console.log(data.courses);
// [
// { _id: "course_1", courseName: "Mathematics", credits: 4 },
// { _id: "course_2", courseName: "English", credits: 3 }
// ]
Reverse Query
// Query course and all students enrolled in it
const { data } = await models.course.get({
filter: {
where: {
_id: { $eq: "course_1" }
}
},
select: {
_id: true,
courseName: true,
students: {
_id: true,
name: true,
age: true
}
}
});
console.log(data.students);
// [
// { _id: "student_1", name: "Zhang San", age: 20 },
// { _id: "student_2", name: "Li Si", age: 21 }
// ]
Query with Relation Conditions
// Query all students enrolled in "Mathematics" course
const { data } = await models.student.list({
filter: {
relateWhere: {
courses: {
where: {
courseName: { $eq: "Mathematics" }
}
}
}
},
select: {
_id: true,
name: true,
courses: {
courseName: true
}
}
});
Troubleshooting
Relation Field Update Failed
Error 1: Format Error
Error Message: Invalid relation field format or 关联字段格式不正确
Cause: Not using {_id: "xxx"} format
Wrong Examples:
// ❌ Wrong: Passing string directly
await models.student.update({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "student_123" } } },
data: { class: "class_456" } // Wrong format
});
// ❌ Wrong: Passing complete object
await models.student.update({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "student_123" } } },
data: {
class: {
_id: "class_456",
name: "Grade 1 Class 1" // No need to pass other fields
}
}
});
Correct Example:
// ✅ Correct: Using {_id: "xxx"} format
await models.student.update({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "student_123" } } },
data: {
class: {
_id: "class_456"
}
}
});
Error 2: Array Format Error
Error Message: Expected array of objects with _id field
Cause: Incorrect array format in one-to-many or many-to-many relations
Wrong Example:
// ❌ Wrong: Passing string array directly
await models.student.update({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "student_123" } } },
data: {
courses: ["course_1", "course_2"] // Wrong format
}
});
Correct Example:
// ✅ Correct: Each item in array uses {_id: "xxx"} format
await models.student.update({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "student_123" } } },
data: {
courses: [
{ _id: "course_1" },
{ _id: "course_2" }
]
}
});
Error 3: Related Data Not Found
Error Message: Related record not found or 关联记录不存在
Cause: The related _id does not exist in the target model
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check if the related
_idis correct - Query whether the record exists in the target model
- Confirm the spelling and format of
_idare correct
Solution:
// First verify if related record exists
const classExists = await models.class.get({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "class_456" } } }
});
if (classExists.data) {
// Record exists, safe to relate
await models.student.update({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "student_123" } } },
data: { class: { _id: "class_456" } }
});
} else {
console.error("Related class does not exist");
}
Error 4: Field Length Exceeds Limit
Error Message: Relation field length exceeds limit or 字段长度超出限制
Cause:
- Single
_idexceeds 256 bytes - One-to-many/many-to-many array total length exceeds 1024 bytes
Solution: Refer to the "Relation Field Limitations" section above
Relation Query Returns Empty
Reason 1: Permission Configuration Issue
Relation model permissions are independent from main model, need to be set separately.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check main model's permission configuration
- Check relation model's permission configuration
- Confirm if current user has permission to access related data
Example:
// Query article with comments, but when comment permissions insufficient, comment data is empty
const { data } = await models.post.get({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "post_123" } } },
select: {
title: true,
comments: { // If comment model has insufficient permissions, returns empty array
content: true
}
}
});
Solution:
- Check relation model's permission settings in console
- Ensure current user has read permission for relation model data
- Or use admin permissions in cloud function to query
Reason 2: Related Data Actually Does Not Exist
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Directly view the relation field value of main record in console
- Check if relation field is empty or contains invalid
_id - Query whether corresponding records exist in relation model
Solution:
// First query main record, check relation field
const post = await models.post.get({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "post_123" } } },
select: { comments: true }
});
console.log('Related comment IDs:', post.data.comments);
// Check if empty array or contains invalid IDs
// Verify if related records exist
const commentIds = post.data.comments.map(c => c._id);
const comments = await models.comment.list({
filter: {
where: {
_id: { $in: commentIds }
}
}
});
console.log('Actually existing comments:', comments.data);
Reason 3: Select Field Configuration Error
Wrong Example:
// ❌ Wrong: Not including relation field in select
const { data } = await models.post.get({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "post_123" } } },
select: {
title: true,
content: true
// Missing comments field, will not return related data
}
});
Correct Example:
// ✅ Correct: Explicitly specify relation field in select
const { data } = await models.post.get({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "post_123" } } },
select: {
title: true,
content: true,
comments: { // Must explicitly specify relation field
_id: true,
content: true
}
}
});
Reason 4: Multi-Level Relation Query Not Supported
Relation queries currently only support one level, multi-level nested relations will not return data.
Wrong Example:
// ❌ Wrong: Multi-level relation query returns no data
const { data } = await models.post.get({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "post_123" } } },
select: {
title: true,
author: { // First level relation ✅
name: true,
profile: { // ❌ Second level relation: not supported, will not return data
address: { // ❌ Third level relation: not supported
city: true
}
}
}
}
});
// Query result:
// {
// title: "Article Title",
// author: {
// name: "Zhang San"
// // profile field will not be returned
// }
// }
Correct Example:
// ✅ Correct: Only query one level relation
const { data } = await models.post.get({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "post_123" } } },
select: {
title: true,
author: { // One level relation ✅
_id: true,
name: true,
email: true,
bio: true // Regular fields can be queried normally
}
}
});
Solution: Refer to step-by-step query or data redundancy solutions in "Relation Query Level Limitation" section above
Many-to-Many Relation Operation Issues
Issue: Cannot Find Intermediate Table
Cause: For MySQL data models, intermediate tables are automatically created and managed by the system
Solution:
- No need to manually create intermediate tables
- Use relation query methods provided by data model
- Do not try to query intermediate tables directly through SQL JOIN
Issue: Intermediate Table Data Inconsistency
Cause: Directly modified intermediate table data, causing relation inconsistency
Solution:
- Always modify relations through data model's update methods
- Do not directly operate intermediate table data
- If data is inconsistent, reset relations through data model's update methods
// ✅ Correct: Update relations through data model
await models.student.update({
filter: { where: { _id: { $eq: "student_123" } } },
data: {
courses: [
{ _id: "course_1" },
{ _id: "course_2" }
]
}
});
// ❌ Wrong: Do not directly operate intermediate table
// await db.query("INSERT INTO course_student ..."); // Not recommended