Data Access Control Management
CloudBase provides a multi-level data access control management mechanism, ensuring data security while meeting the access control requirements of different business scenarios.
Model read/write operations use the _openid field to determine data ownership.
Access Control Management System
CloudBase data access control management comprises two levels:
| Permission Type | Granularity | Applicable Scenarios | Configuration Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Access Control | Model Level | Simple Permission Requirements | Low |
| Role-based Permissions | User Level | Organizational Structure Permissions | Medium |
💡 Note: The data model does not support security rule permission configuration.
Permission Priority
Relationships Between Different Permission Types:
- The final permissions are the union of Role-based permissions and Basic permissions.
- It is recommended to select an appropriate access control management approach based on business complexity.
Basic Access Control
Features
Basic Access Control is the simplest permission management approach, suitable for most common business scenarios:
- Model-level Control: Set unified permissions for the entire data model.
- Predefined Permission Templates: Provide commonly used permission configuration templates.
- Simple and Easy to Use: No need to write complex rule expressions.
Configuration Method
On the data model page of the Tencent Cloud Development Platform, set corresponding permissions for each model:
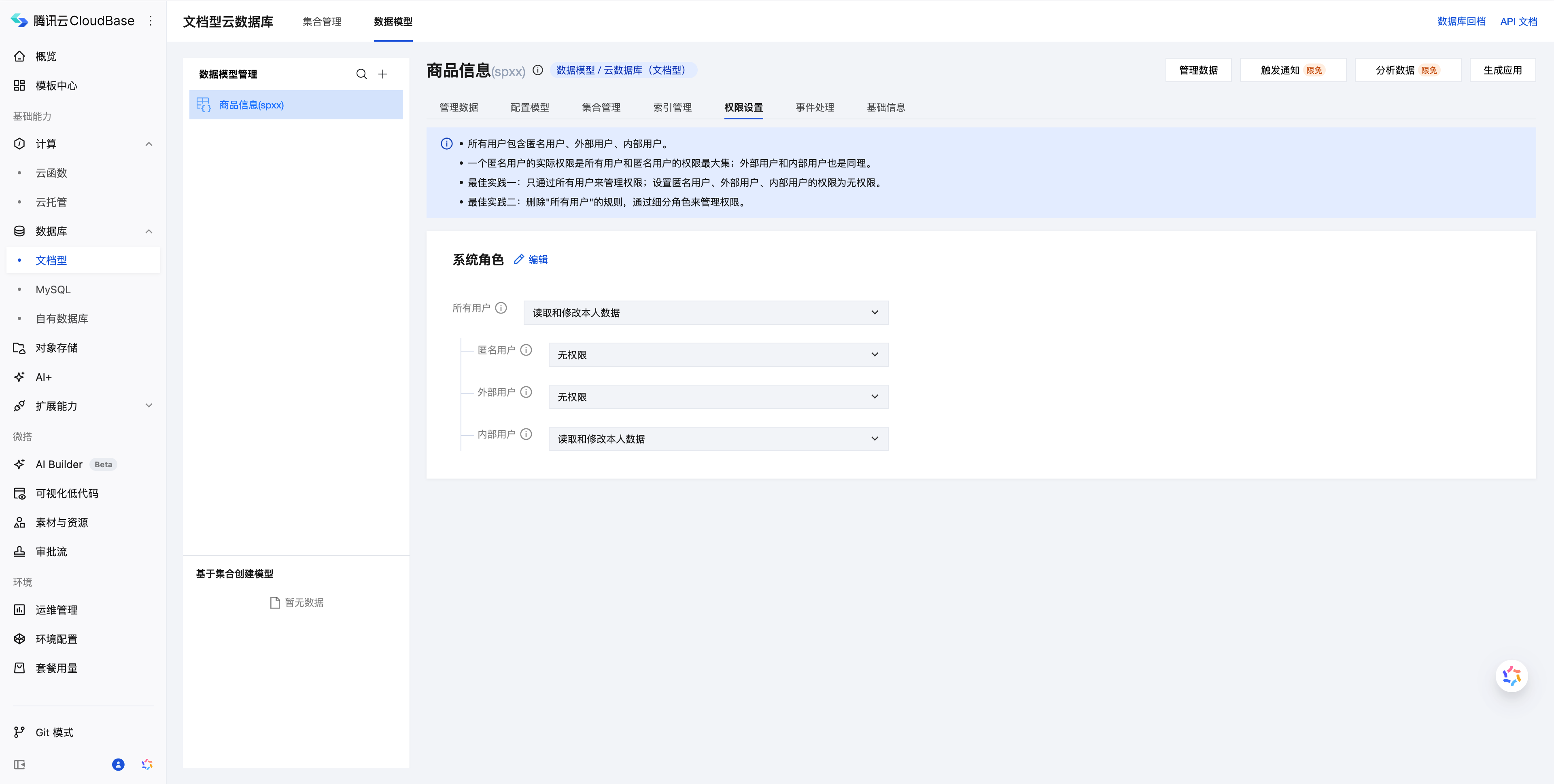
Permission Options
Select corresponding permissions based on user identities.
- All users include anonymous users, external users, and internal users.
- The effective permissions for an anonymous user are the broadest set of permissions granted to both all users and anonymous users; the same principle applies to external users and internal users.
- Best Practice 1: Manage permissions exclusively through the all users group; set permissions for anonymous users, external users, and internal users to no permissions.
- Best Practice 2: Delete the rules for "all users" and manage permissions through granular roles.
| Permission Type | Applicable Scenarios |
|---|---|
| Read all data, modify own data | Public content, such as articles, products |
| Read and modify own data | Private data, such as user profiles |
| Read all data, cannot modify data | Configuration data, such as system settings |
| No access | Sensitive data, such as financial information |
Custom Role Access Control
Feature Overview
Role-based permissions are a permission management approach based on the organizational structure, suitable for hierarchical permission control in enterprise-level applications. It complements basic access control, with the final permissions being the union of both.
Core Features:
- Organizational Structure Support: Permission control based on departments and reporting relationships.
- Role Inheritance: Supports hierarchical inheritance of permissions
- Flexible Combination: Takes the union with basic permissions to provide more flexible permission configuration
Configuration Steps
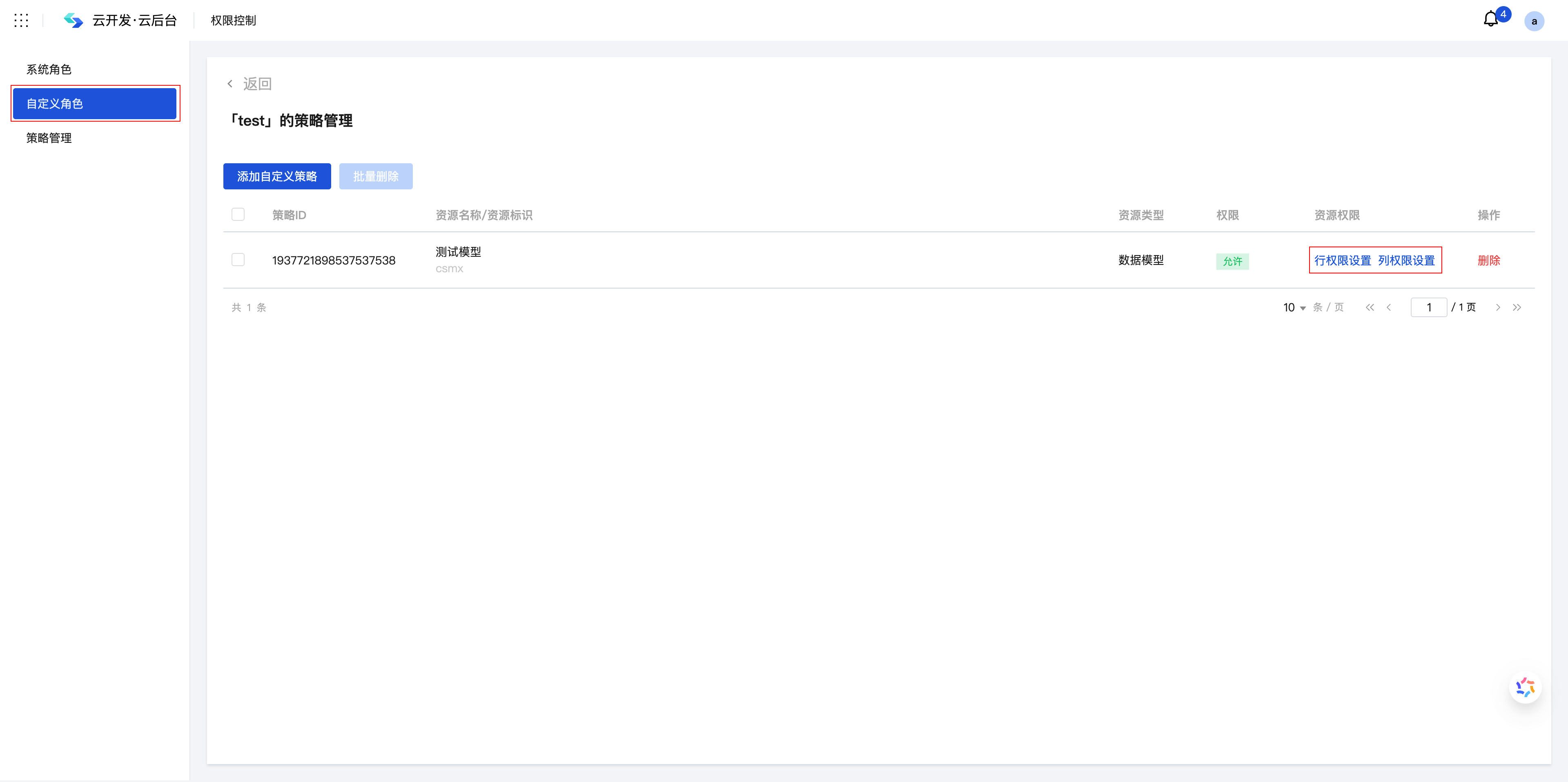
Step 1: Go to Role Management
Access the CloudBase/Custom Roles Page to manage organizational structures and role definitions:
Step 2: Configure Row-level Permissions
Select the target role and click Row Permission Settings to configure details:
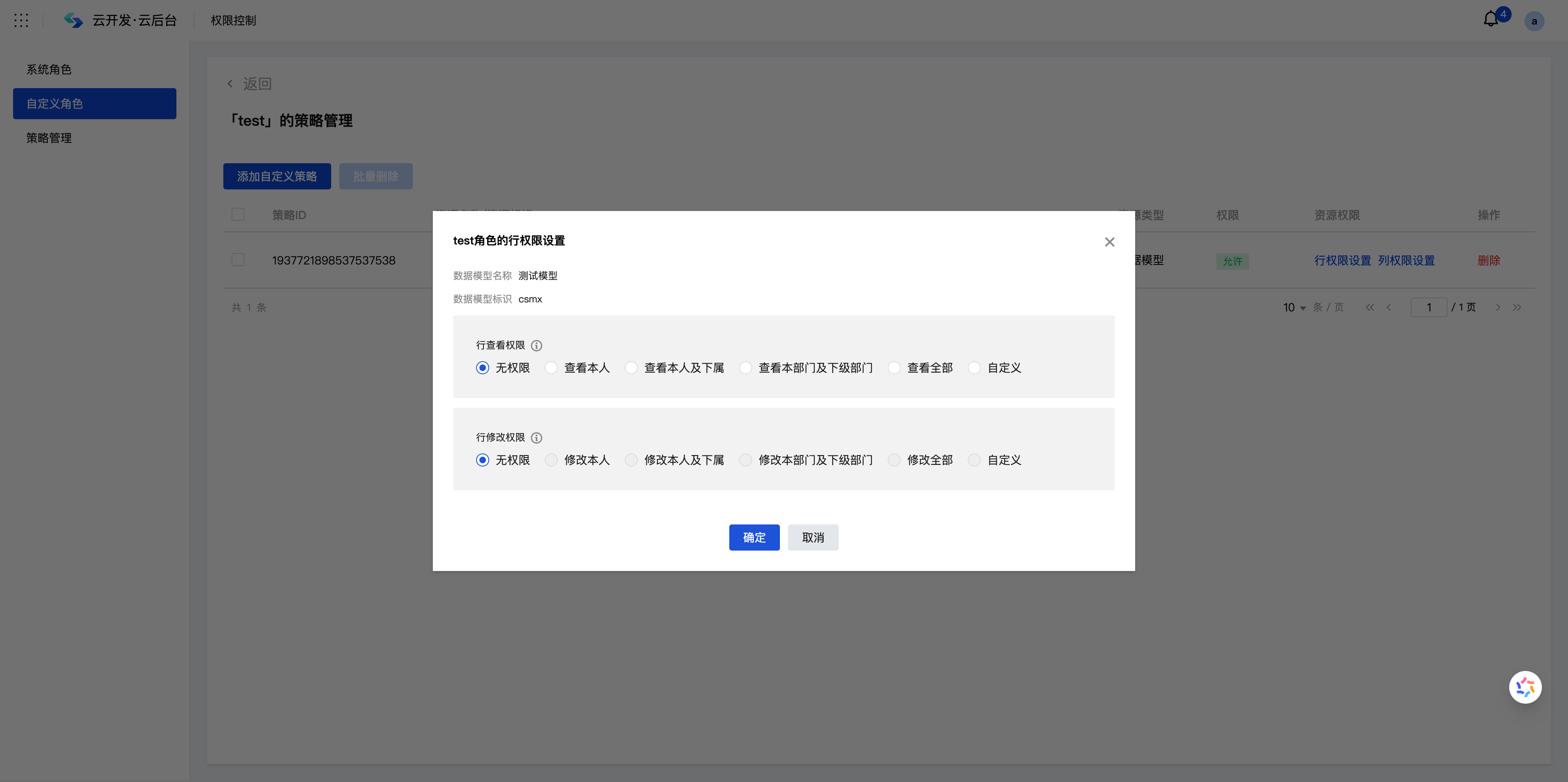
Permission Level Description
| Permission Level | Data Scope | Applicable Scenarios | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| View own | Owner field value is self | Personal data management | Employees can only view their own attendance records |
| View Self and Subordinates | Data of self and subordinates | Team management | Managers can view team members' work reports. |
| View Own Department and Sub-departments | Data of own department and sub-departments | Department management | Department managers can view all projects within the department. |
| View All | All data | System management | Administrators can view company-wide data. |
Permission Combination Rules
Read/Write Permission Relationship
⚠️ Note: Row modification permission automatically includes read permission, meaning that if you have modification permission, you also have read permission.
Permission Union Calculation
Basic permissions + Role-based permissions = Final permissions
Example Scenario:
Basic permissions: Only the creator and administrators have read and write access.
Role-based permissions: View All + No modification permission
─────────────────────────────────
Final permissions: Can view all data, but can only modify data created by oneself.
Practical Application Case
Case 1: Blog Permissions
Business Requirements:
- Can view everyone's blogs
- Update their own blogs
Basic Permissions Configuration
All users/Read all data, modify own data
Case 2: Project Management System
Business Requirements:
- Project members can only view projects they participate in.
- Project managers can manage projects they are responsible for
- Department managers can view all projects in the department.
Basic Permissions Configuration
All users/Read and modify own data
Role-based Permissions Configuration
| Role | Role Data Permissions | Row Modification Permissions | Final Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salesperson | View own | Own | Can only view and modify their own customers |
| Sales Manager | View Self and Subordinates | Self and subordinates | Can manage all customers of the team |
| Sales Director | View all | View all | Can manage all customers |
Permission Design Best Practices
1. Permission Design Principles
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant only the minimum permissions required to complete the work
- Separation of Duties: Different roles assume distinct data responsibilities
- Permission Inheritance: Appropriately leverage the hierarchical relationships of the organizational structure
2. Common Configuration Patterns
Read-Only Scale-Out Mode:
Basic permissions: Only the creator has read and write access.
Role-based permissions: Expanded view scope without modification permissions
Effect: Expanding data visibility while maintaining modification control
Administrator Mode:
Basic permissions: Only the creator has read and write access.
Role-based permissions: View All + Edit All
Effect: Administrators can manage all data
Department Isolation Mode:
Basic permissions: Only the creator has read and write access.
Role-based permissions: View Own Department + Edit Own Department
Effect: Data isolation between departments and sharing within departments
3. Notes
- Permission Testing: Thoroughly test permissions for various roles before production deployment
- Permission Auditing: Regularly review and adjust permission configurations
- Documentation: Record the business logic of permission design in detail
- Change Management: Permission changes must go through an approval process