SQL Template
The SQL template provides a way to execute SQL commands on the MySQL data model, supporting parameterized queries and access control, and can be securely invoked on mini-program and Web clients.
Basic Usage
Creating a Template
Go to TCB platform/MySQL database/data model, select the corresponding data model, and click the 'SQL Template Management' tab.
Click the 'New' button, fill in the template name and SQL statement, then save.
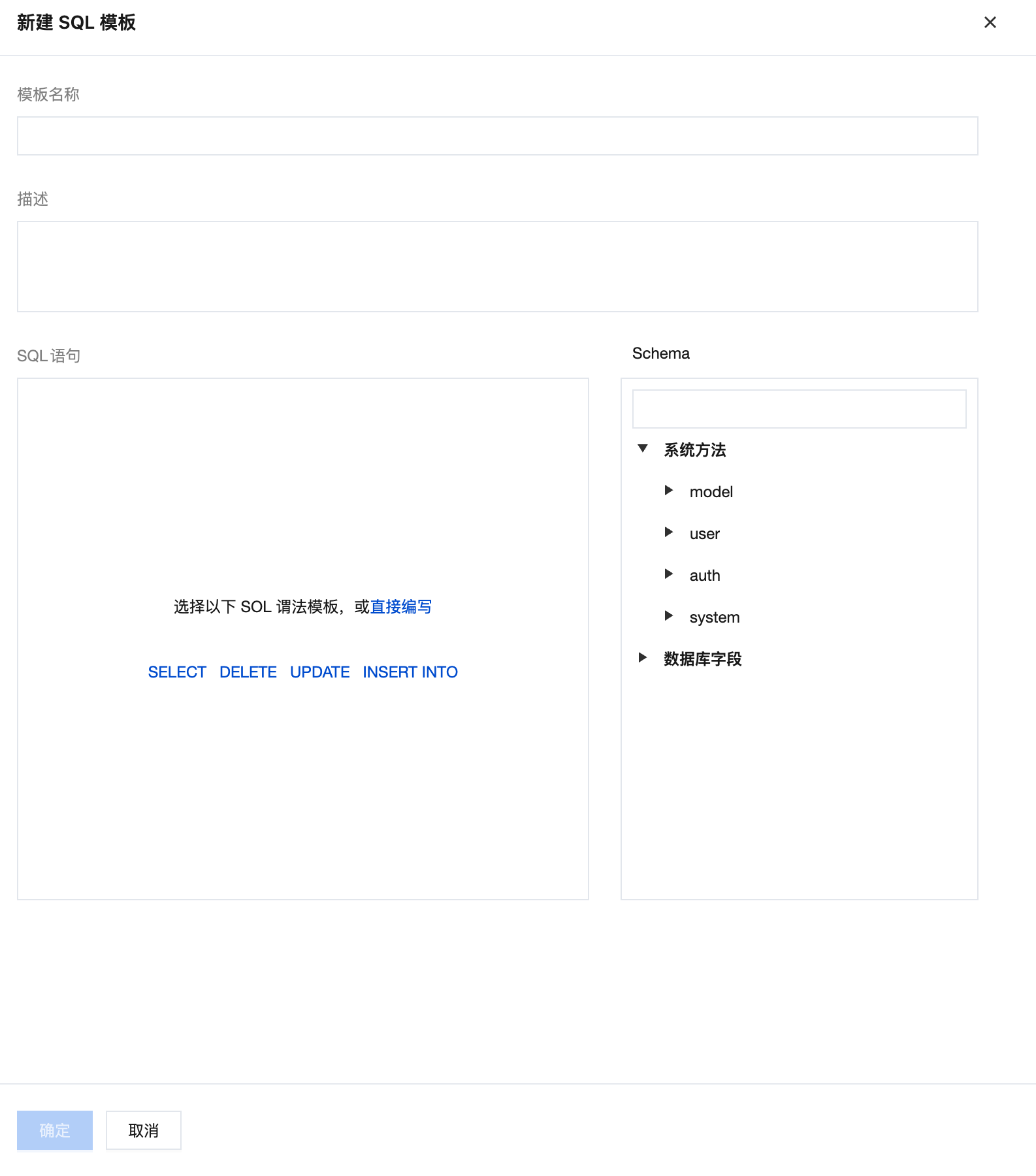
Calling an SQL Template
Select the corresponding SDK to call:
| SDK Type | Applicable Platform |
|---|---|
| JS SDK | Web browser |
| Node SDK | Node.js environment |
Calling Example
Using the Node SDK as an example, the sample calling code is as follows:
import cloudbase from "@cloudbase/node-sdk";
// Initialize the application
const app = cloudbase.init({
env: "your-env-id", // Replace with your environment ID
});
// Call the SQL template for the user table
const res = await app.models.user.runSQLTemplate({
templateName: "template_name",
params: {
key: "value",
},
});
SQL Statement Specification
Supported Commands
SELECTINSERT INTOREPLACE INTOUPDATEDELETE
Basic Rules
- Each template supports only one SQL command.
- The primary table must be the table of the current model.
- In join queries, the sub-table can be any table within the same database.
INSERT/REPLACEoperations must include theownerand_openidsystem fields.
Parameter Syntax
Using the {{ param }} syntax to introduce variable parameters.
SELECT * FROM {{ model.tableName() }}
WHERE status = {{ status }}
Built-in Functions
SQL templates support the following built-in functions, which can be used directly in the templates:
| Category | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Model | model.tableName() | Obtain the current model's table name |
| Model | model.tableName('model_name') | Obtain the specified model table name |
| Model | model.dataId() | Generate data ID |
| User | user.userId() | Obtain the user ID |
| User | user.openId() | Obtain the user openId |
| Permission | auth.rowPermission() | Obtain the current model's row permission |
| Permission | auth.rowPermission('model_name') | Obtain the specified model's row permission |
| System | system.currentEpoch() | Obtain the second-level timestamp |
| System | system.currentEpochMillis() | Obtain the millisecond-level timestamp |
Usage Example
Referencing Table Names
-- Use the current model table.
SELECT * FROM {{ model.tableName() }}
-- Join tables
SELECT a.*, b.*
FROM {{ model.tableName() }} a
JOIN {{ model.tableName('other_model') }} b
ON a.id = b.ref_id
Data Operations
-- Insert data.
INSERT INTO {{ model.tableName() }}
(_id, name, owner, _openid, createBy, updatedAt)
VALUES (
{{ model.dataId() }},
{{ name }},
{{ user.userId() }},
{{ user.openId() }},
{{ user.userId() }},
{{ system.currentEpochMillis() }}
)
-- Update data.
UPDATE {{ model.tableName() }}
SET name = {{ name }},
updatedAt = {{ system.currentEpochMillis() }}
WHERE _id = {{ id }}
AND {{ auth.rowPermission() }}
-- Query data.
SELECT * FROM {{ model.tableName() }}
WHERE status = {{ status }}
AND {{ auth.rowPermission() }}
NULL Value Handling
Since IS NULL and IS NOT NULL are not supported, use the following alternative syntax:
-- Query null values.
WHERE column <=> NULL
-- Query non-null values.
WHERE !(column <=> NULL)