MySQL Many-to-Many Relationships
A many-to-many relationship refers to scenarios where two data models have a "bidirectional multiple association", for example:
- Students and Courses: A student can enroll in multiple courses, and a course can be taken by multiple students
- Users and Roles: A user can have multiple roles, and a role can be assigned to multiple users
- Products and Orders: An order can contain multiple products, and a product can appear in multiple orders
In relational databases, many-to-many relationships cannot be implemented through a single foreign key and require a "junction table" to store the association between two entities.
Many-to-Many Junction Table Mechanism
CloudBase data models automatically create "junction tables" for many-to-many relationships, eliminating the need for manual creation and maintenance. Junction tables are specifically designed to store associations between two models, ensuring data integrity and query efficiency.
Purpose of Junction Tables
- Store Associations: Record which primary table record is associated with which secondary table record
- Support Bidirectional Queries: Allow querying associated data from either end
- Ensure Data Consistency: Guarantee validity of associated data through foreign key constraints
- Improve Query Performance: Optimize many-to-many association queries through indexing
Finding Junction Tables
When you need to directly manipulate or view junction table data, follow these steps to locate the junction table:
Step 1: Get Junction Model Identifier
Go to CloudBase Platform / MySQL Database / Data Models, and find the "Junction Model Identifier" in the model field configuration:
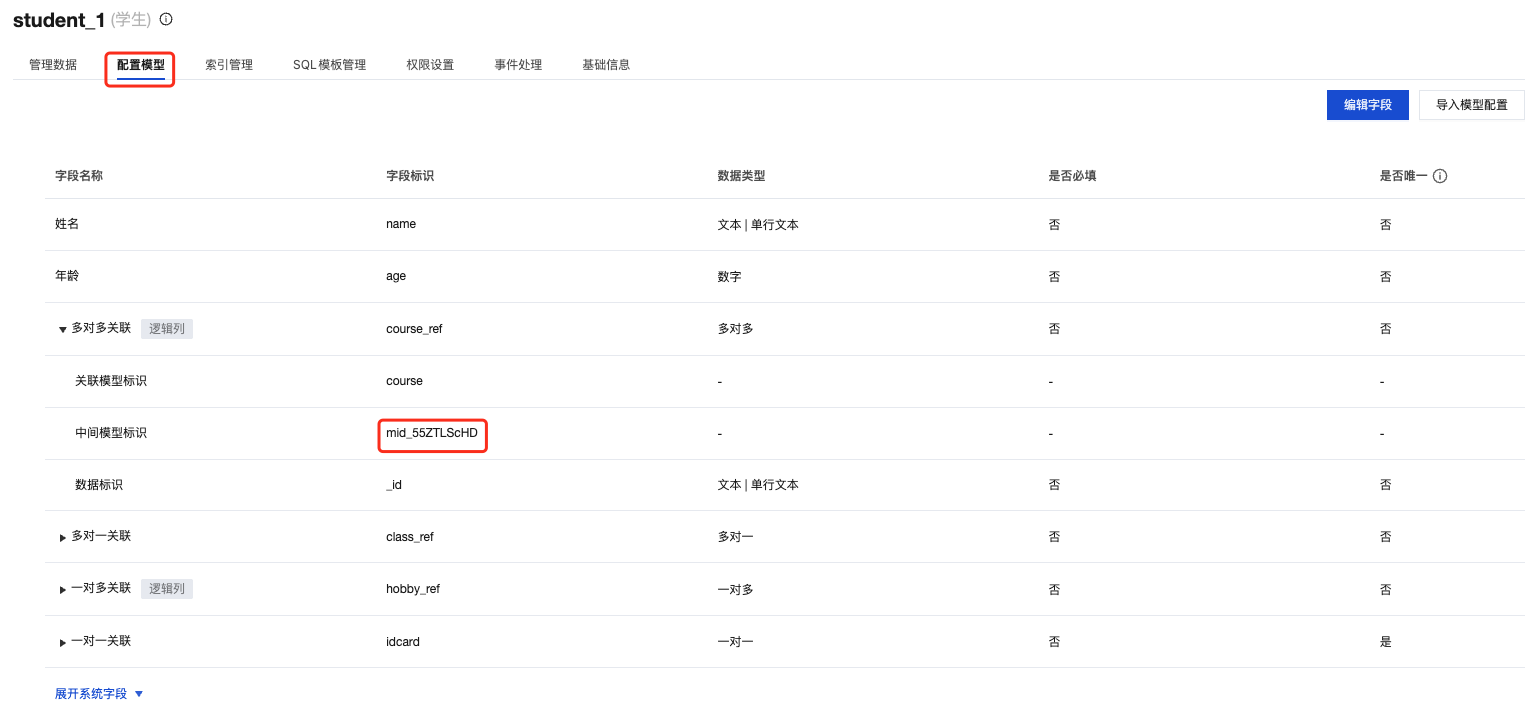
💡 Tip: The "Junction Model Identifier" is a system-generated unique identifier used to locate the corresponding junction table in the database.
Step 2: Search for Junction Table in Database
Search for the junction table in the database table list using the "Junction Model Identifier":
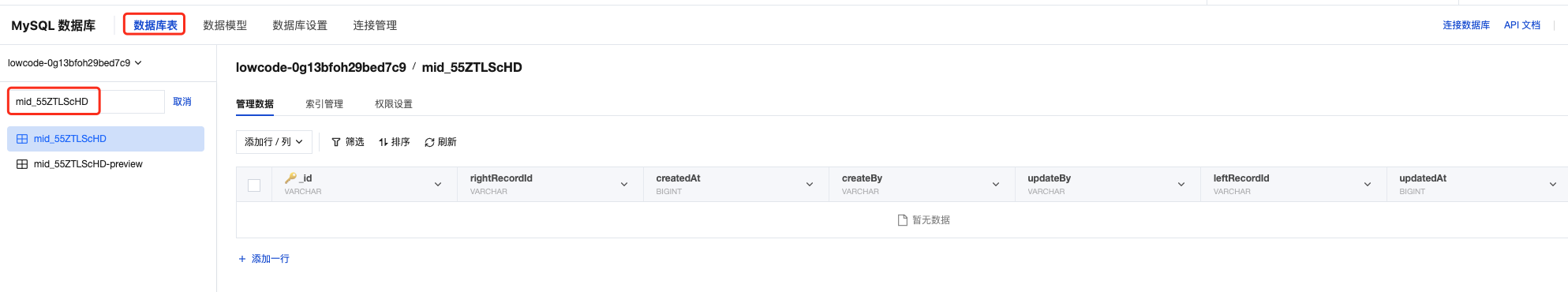
⚠️ Environment Distinction:
- Table name ends with
-preview: Junction table in preview environment- Table name does not end with
-preview: Junction table in production environment
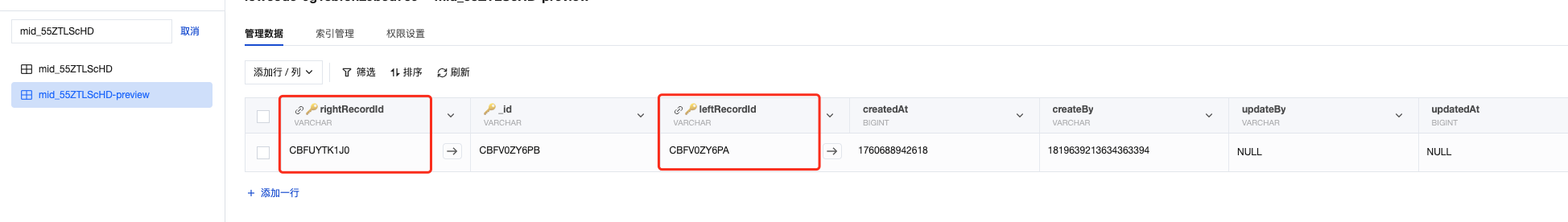
Junction Table Field Description
Junction tables typically contain the following core fields:
| Field Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
leftRecordId | Primary key ID of the primary (left) table record | Student table's _id, such as STUDENT_001 |
rightRecordId | Primary key ID of the secondary (right) table record | Course table's _id, such as COURSE_101 |
Field Description Diagram
Practical Example
Taking the "student course selection" scenario as an example, the junction table data structure is as follows:
| leftRecordId | rightRecordId | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
STUDENT_001 | COURSE_101 | Student 001 enrolled in Course 101 |
STUDENT_001 | COURSE_102 | Student 001 enrolled in Course 102 |
STUDENT_002 | COURSE_101 | Student 002 enrolled in Course 101 |
This design enables:
- Query all courses enrolled by a student through
STUDENT_001(COURSE_101,COURSE_102) - Query all students enrolled in a course through
COURSE_101(STUDENT_001,STUDENT_002)