Deployment Guide
This guide explains how to configure and deploy frontend projects to CloudBase Static Hosting service.
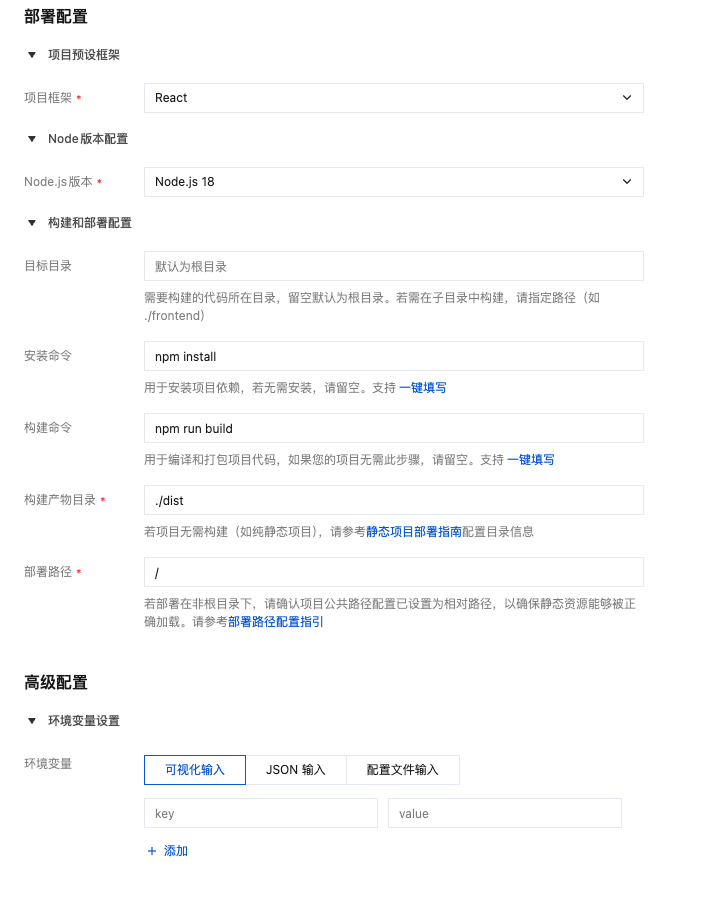
1. Configuration Instructions
1.1 Basic Configuration
| Configuration | Description | Example | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project Name | Custom project identifier | my-project | ✅ |
| Project Framework | Select frontend framework | React, Vue, Angular, Other | ✅ |
| Node.js Version | Build environment version (16/18/20/22/24) | Node.js 18 | ✅ |
1.2 Build Configuration
| Configuration | Description | Example | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target Directory | Code location directory (default root) | /frontend | - |
| Install Command | Install dependencies | npm install | Optional for static projects |
| Build Command | Compile and build | npm run build | Optional for static projects |
| Build Output Directory | Output directory | ./dist, ./build | ✅ |
| Deploy Path | Access path | /, /app | - |
If your project consists of pure HTML/CSS/JS files, no build required:
- Leave Install Command and Build Command empty
- Set Build Output Directory to the static files location (e.g.,
.,./public) - For details, see: Pure Static Project Deployment
1.3 Environment Variables (Optional)
Configure build-time environment variables:
NODE_ENV=production
VITE_API_URL=https://api.example.com
REACT_APP_ENV=production
2. Deployment Log Display
After submitting configuration, the system executes the build and deployment process. You can view real-time logs in the console:
Log Examples
Successful Deployment Log
Deployment complete 👉 https://lowcode-0gwpl9v4xxxxxxx-1258057692.tcloudbaseapp.com
✔ Total files: 4
✔ Successfully uploaded 4 file(s)
┌────────┬─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Status │ File │
├────────┼─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ✔ │ /cosdesign/cosdesign.code-workspace │
├────────┼─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ✔ │ /cosdesign/index.html │
├────────┼─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ✔ │ /cosdesign/script.js │
├────────┼─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ✔ │ /cosdesign/style.css │
└────────┴─────────────────────────────────────┘
✖ Failed to upload 0 file(s)
[2026-01-27 20:03:33] 自定义部署完成
Finished, code: 0, duration: 6.9s
How to Determine if Deployment Succeeded
The following key indicators confirm successful deployment:
✅ ✔ Successfully uploaded X file(s) - Number of successfully uploaded files
✅ Deployment complete 👉 Access URL - Deployment complete with access link displayed
✅ Finished, code: 0 - Process exit code 0 (no errors)
✅ All files in list show ✔ status - All files uploaded successfully
If you see the following, deployment failed or partially failed:
- ❌
✖ Failed to upload X file(s)where X > 0 - Some files failed to upload - ❌
Finished, code: 1or other non-zero value - Build or deployment process error - ❌ Log contains
Error:orFailed:error messages
3. Quick Configuration Examples
Pure Static Project
Project Framework: Other
Install Command: (leave empty)
Build Command: (leave empty)
Build Output Directory: .
Deploy Path: /my-static-site
React (Vite)
Project Framework: React
Install Command: npm install
Build Command: npm run build
Build Output Directory: ./dist
Deploy Path: /my-react-app
Vue (Vue CLI)
Project Framework: Vue
Install Command: npm install
Build Command: npm run build
Build Output Directory: ./dist
Deploy Path: /my-vue-app
Angular
Project Framework: Angular
Install Command: npm install
Build Command: npm run build
Build Output Directory: ./dist/project-name
Deploy Path: /my-angular-app
4. Framework Configuration Reference
React
Create React App
- Build Output Directory:
./build - package.json:
{
"scripts": {
"build": "react-scripts build"
}
}
Vite + React
Build Output Directory:
./distvite.config.js:
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import react from '@vitejs/plugin-react'
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [react()],
base: './', // Use relative path for subdirectory deployment
build: {
outDir: 'dist'
}
})
Vue
Vue CLI
- Build Output Directory:
./dist - vue.config.js:
module.exports = {
publicPath: './', // Use relative path for subdirectory deployment
outputDir: 'dist'
}
Vite + Vue
Build Output Directory:
./distvite.config.js:
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vue()],
base: './', // Use relative path for subdirectory deployment
build: {
outDir: 'dist'
}
})
Angular
- Build Output Directory:
./dist/project-name - angular.json:
{
"projects": {
"your-project": {
"architect": {
"build": {
"options": {
"outputPath": "dist/your-project",
"baseHref": "./" // Use relative path for subdirectory deployment
}
}
}
}
}
}
5. Deploy Path Configuration
Root Path Deployment (/)
Use Cases:
- Single application occupying entire static hosting environment
- Official website, product homepage requiring direct domain access
- Access URL:
https://example.com/
Root path deployment overwrites existing files in static hosting root directory:
- Same-name files will be overwritten and cannot be automatically recovered
- Multiple projects deployed to root path will overwrite each other
- Recommendation: Use subdirectories for multi-project scenarios (e.g.,
/app1,/app2)
Subdirectory Deployment (/app)
Use Cases:
- Deploy multiple projects in the same environment
- Isolate different application files
- Access URL:
https://example.com/app/
Configuration Requirements:
Set the public path to relative path ./ in project configuration to avoid static resource loading failures.
| Framework | Config File | Config Option |
|---|---|---|
| Vite | vite.config.js | base: './' |
| Vue CLI | vue.config.js | publicPath: './' |
| Create React App | package.json | "homepage": "./" |
| Angular | angular.json | "baseHref": "./" |
6. Special Scenario Configuration
Monorepo Projects
Frontend code in subdirectory:
Target Directory: /packages/web
Install Command: npm install
Build Command: npm run build
Build Output Directory: ./dist
Multi-Application Projects
Project contains multiple applications:
Target Directory: /apps/admin
Install Command: npm install
Build Command: npm run build
Build Output Directory: ./dist
Common Questions
Q: Static resources 404 after deployment?
A: Check if correct base/publicPath is configured. Subdirectory deployment requires relative path ./
Q: How to deploy multiple projects?
A: Configure different deploy paths for each project, such as /app1, /app2, to avoid file conflicts
Q: How to choose Node.js version?
A: Recommend using the same version as your local development environment to avoid build differences