CI/CD Integration with Git Platform
As frontend projects grow increasingly complex, automated deployment has become a critical component for enhancing development efficiency and ensuring code quality. Tencent CloudBase (CloudBase) provides a static hosting service that, combined with its powerful CLI tool, enables rapid deployment of frontend projects.
This article details how to leverage CloudBase CLI in conjunction with pipeline capabilities of mainstream Git platforms such as GitHub Actions, GitLab CI/CD, and Gitee Go to achieve automated deployment of frontend projects from Git repositories to CloudBase Static Hosting services.
Prerequisites
Install CLI Tool
# Global Installation (Recommended)
npm install -g @cloudbase/cli
# Verify the installation
tcb --version
💡 Tip: If not installed yet, please refer to the CLI Installation Guide
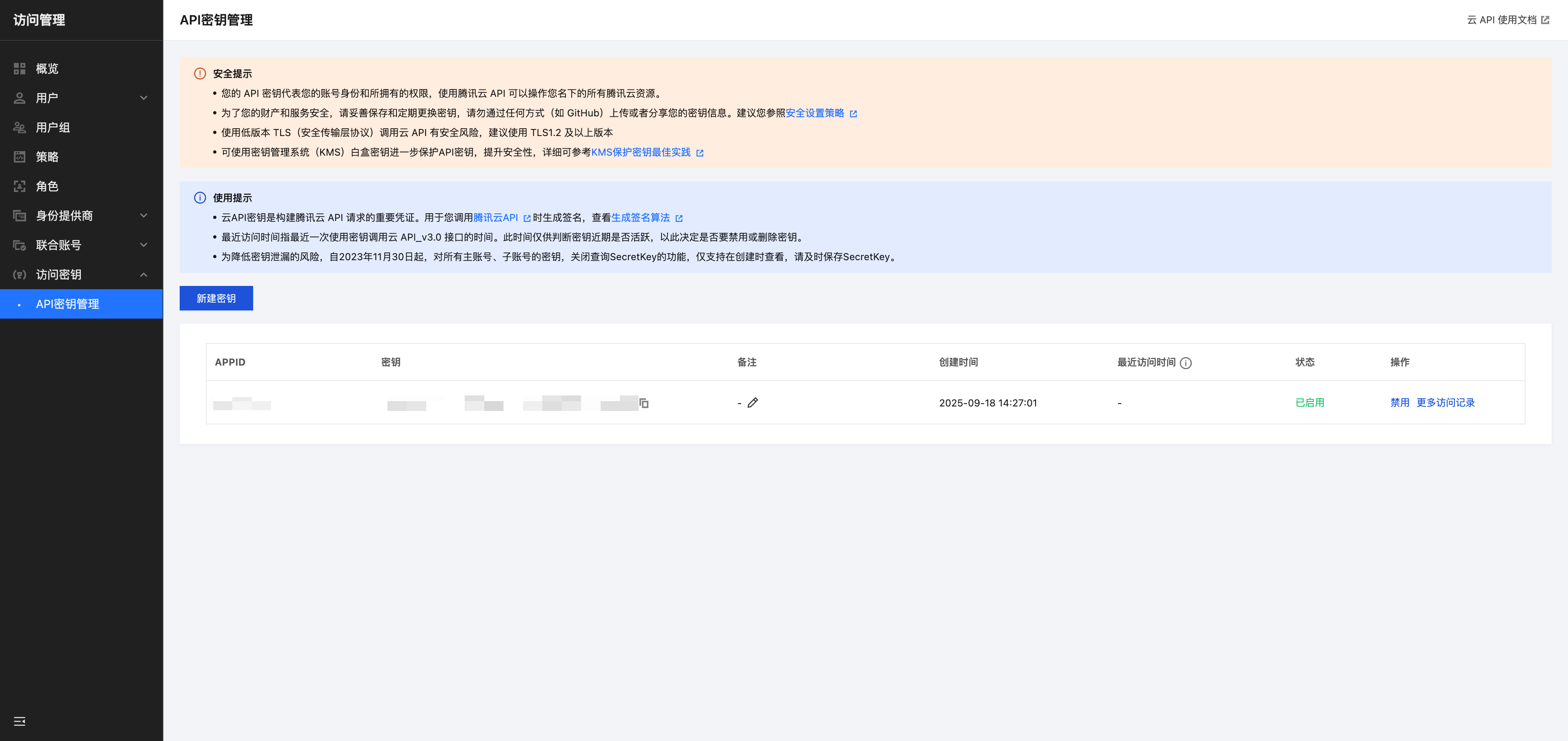
Obtain API Key
- Log in to Tencent Cloud Console/Access Management/API Key Management
- Create or obtain the existing
SecretIdandSecretKey - Record your CloudBase Environment ID (can be viewed in the CloudBase console)
⚠️ Security Reminder: Keep your API keys secure. Avoid hardcoding them in your code and be sure to use the secret management feature of your CI/CD platform
Prepare project configuration
Ensure your project meets the following conditions:
- ✅ The project root directory contains a build script (e.g.,
npm run build) - ✅ Static files directory generated after build (e.g.,
dist/,build/, etc.) - ✅ The project can be built successfully in a CI/CD environment
- ✅ The correct Node.js version is configured
Platform Integration Guide
GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions is a CI/CD service provided by GitHub, allowing you to configure workflows directly in your GitHub repositories.
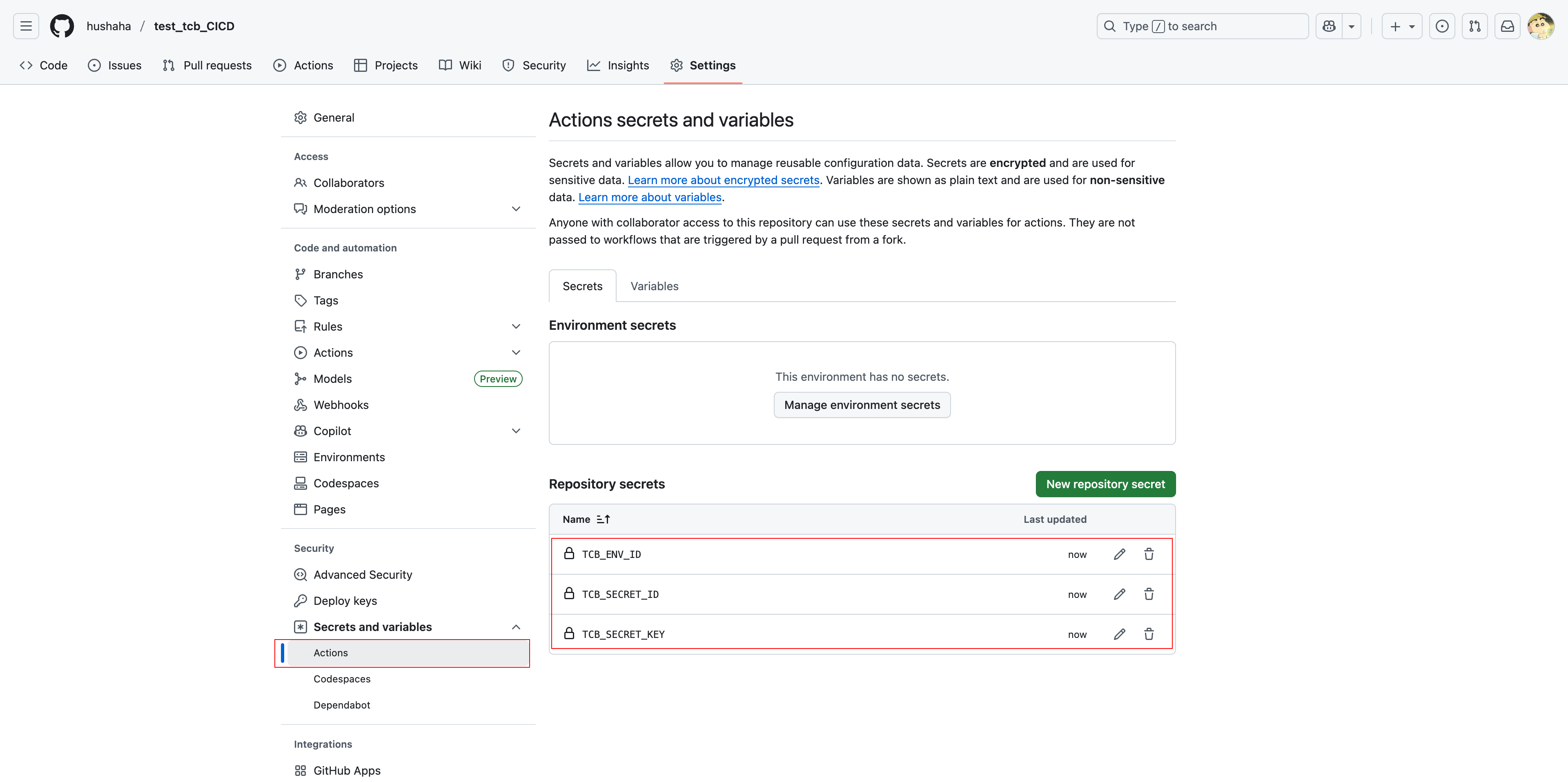
Step 1: Configure GitHub Secrets
In your GitHub repository, go to Settings → Secrets and variables → Actions → New repository secret.
Add the following Secrets:
TCB_SECRET_ID: Your Tencent Cloud SecretIdTCB_SECRET_KEY: Your Tencent Cloud SecretKeyTCB_ENV_ID: Your CloudBase environment ID
💡 Multi-environment tip: It is recommended to create separate Secrets for different environments, such as
TCB_ENV_ID_DEVandTCB_ENV_ID_PROD
Step 2: Create a workflow file
Create .github/workflows/deploy.yml in the project root directory:
Example reference:
name: Deploy to CloudBase Static Hosting
on:
push:
branches:
- main # Trigger on push to the main branch
pull_request:
branches:
- main # Trigger on PR (optional)
jobs:
build-and-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: '18'
cache: 'npm' # Enable npm cache to speed up the build
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci # Use npm ci instead of npm install, which is more suitable for CI environments
- name: Build project
run: npm run build
- name: Install CloudBase CLI
run: npm install -g @cloudbase/cli
- name: Login CloudBase CLI
run: tcb login --apiKeyId ${{ secrets.TCB_SECRET_ID }} --apiKey ${{ secrets.TCB_SECRET_KEY }}
- name: Deploy to CloudBase Static Hosting
run: tcb hosting deploy ./dist /home -e ${{ secrets.TCB_ENV_ID }}
Configuration Parameters Instructions
For details on Static Hosting commands, see: CLI Management
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
./dist | Build artifact directory | ./build, ./public |
/home | Cloud target path | /, /static |
GitLab CI/CD
GitLab CI/CD is a built-in CI/CD service provided by GitLab, configured via the .gitlab-ci.yml file.
Step 1: Configure CI/CD Variables
In your GitLab project, go to Settings → CI/CD → Variables → Add variable.
Add the following variables:
TCB_SECRET_ID: Your Tencent Cloud SecretIdTCB_SECRET_KEY: Your Tencent Cloud SecretKeyTCB_ENV_ID: Your CloudBase environment ID
🔒 Security Recommendation: Mark variables as "Protected" and "Masked" to enhance security
Step 2: Create the .gitlab-ci.yml file
Create .gitlab-ci.yml in the project root directory:
Example reference:
stages:
- build
- deploy
variables:
NODE_VERSION: "18"
CACHE_KEY: "$CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG-$CI_PROJECT_DIR"
# Cache Configuration
cache:
key: ${CACHE_KEY}
paths:
- node_modules/
- .npm/
build:
stage: build
image: node:18-alpine
before_script:
- npm config set cache .npm
- npm ci
script:
- npm run build
artifacts:
paths:
- dist/
expire_in: 1 hour
only:
- main
- merge_requests
deploy:
stage: deploy
image: node:18-alpine
dependencies:
- build
before_script:
- npm install -g @cloudbase/cli
script:
- tcb login --apiKeyId $TCB_SECRET_ID --apiKey $TCB_SECRET_KEY
- tcb hosting deploy ./dist /home -e $TCB_ENV_ID
only:
- main
when: on_success
GitLab CI/CD Features
- Pipeline cache: Automatically cache the
node_modulesand.npmdirectories - Artifacts management: Build artifacts are passed between stages
- Environment Management: Supports multi-environment deployment and environment variables
- Conditional Deployment: Branch-based conditional deployment
Gitee Go
Gitee Go is a CI/CD service provided by Gitee (code cloud), with syntax similar to GitHub Actions.
Step 1: Configure environment variables
In your Gitee repository, go to Management → WebHooks → Gitee Go → Environment Variables.
Add the following environment variables:
TCB_SECRET_ID: Your Tencent Cloud SecretIdTCB_SECRET_KEY: Your Tencent Cloud SecretKeyTCB_ENV_ID: Your CloudBase environment ID
🔐 Security Tip: Check "Sensitive Information" to protect your keys
Step 2: Create a workflow file
Create .gitee/workflows/deploy.yml in the project root directory:
Example reference:
name: Deploy to CloudBase Static Hosting
on:
push:
branches:
- main # Trigger on push to the main branch
pull_request:
branches:
- main # Trigger on PR (optional)
jobs:
build-and-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Node.js environment
uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: '18'
cache: 'npm' # Enable npm cache to speed up the build
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci # Use npm ci instead of npm install, which is more suitable for CI environments
- name: Build project
run: npm run build
- name: Install CloudBase CLI
run: npm install -g @cloudbase/cli
- name: Login to CloudBase CLI
run: tcb login --apiKeyId ${{ secrets.TCB_SECRET_ID }} --apiKey ${{ secrets.TCB_SECRET_KEY }}
- name: Deploy to CloudBase Static Hosting
run: tcb hosting deploy ./dist /home -e ${{ secrets.TCB_ENV_ID }}
- name: Deployment success notification
if: success()
run: echo "🎉 Deployment successful! The project has been published to CloudBase Static Hosting"
- name: Deployment failure notification
if: failure()
run: echo "❌ Deployment failed. Please check the configuration and logs"