manage
Managing Static Resources in the Console
This document describes how to manage CloudBase Static Website Hosting, including core features such as resource management, domain configuration, and security settings.
Overview
CloudBase Static Website Hosting provides comprehensive static website management capabilities, supporting features such as file upload, domain binding, cache configuration, and security protection. You can conveniently manage your static websites through CloudBase/Static Website Hosting.
Resource Management
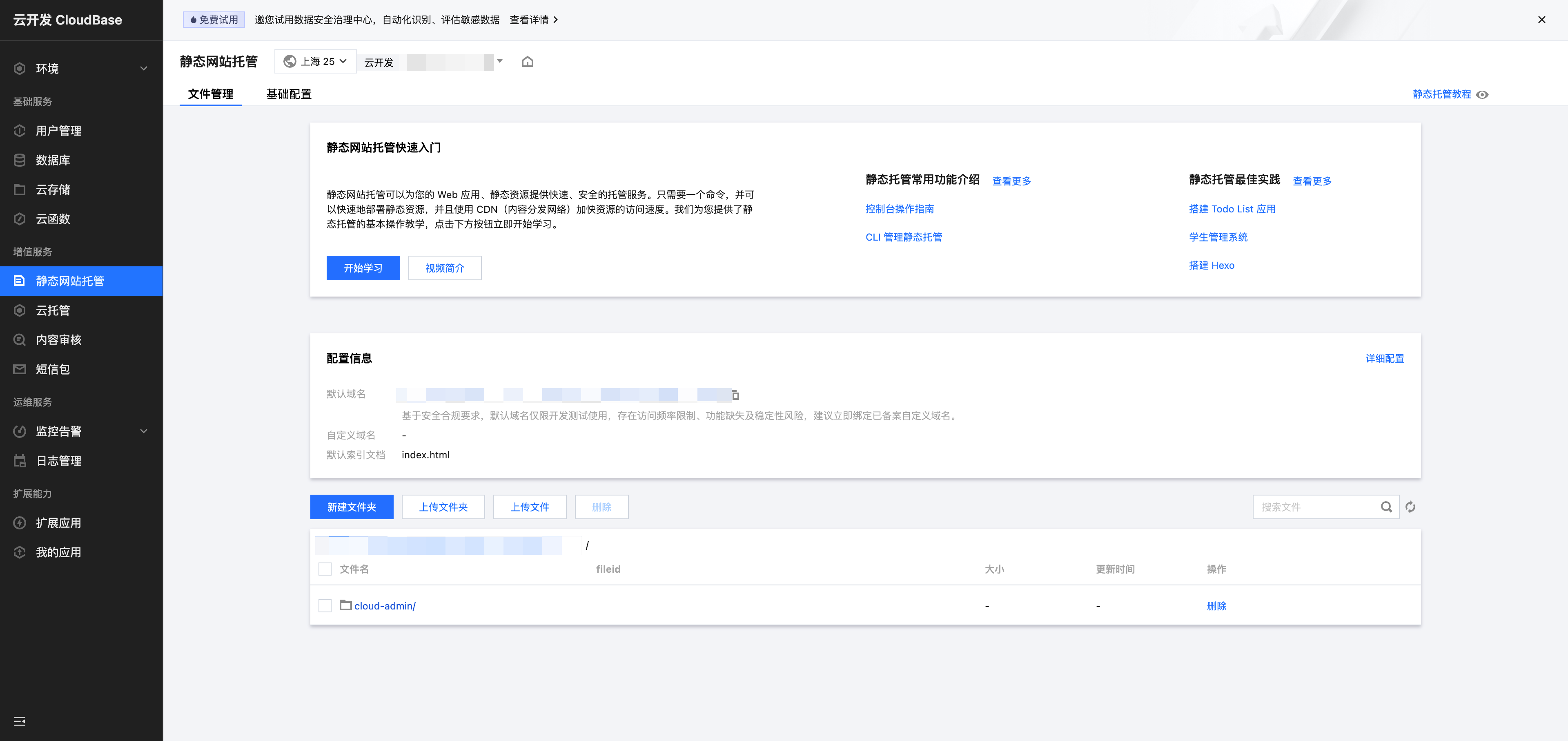
Basic Operations
In the Static Website Hosting console, you can perform the following operations:
- File Management: Upload, download, and delete files
- Folder Management: Create and delete folders
- Batch Operations: Supports batch upload and deletion
- Online Editing: Supports online editing of text files
File Naming Specifications
- File and folder names only support digits and combinations of Chinese/English characters.
- The name length is limited to 255 characters.
- It is recommended to use meaningful names to facilitate management and maintenance.
Service Status
Static hosting service does not require manual starting and stopping:
- The service runs automatically when there are files in the hosted space.
- The service is automatically paused when the hosted space is empty.
- No charges are incurred in the paused state.
Domain Name Management
Default Domain Name
CloudBase provides a default domain for each static hosting service with the following features:
- Free to Use: Accessible without additional configuration
- Test Purposes: Suitable for use during development and testing phases
- Access Restrictions: Access frequency limits exist, and access is temporarily unavailable when limits are exceeded.
Custom Domain
It is recommended to configure a custom domain for better access experience and brand presentation.
- No Access Restrictions: Not subject to the frequency limits of the default domain
- Brand Presentation: Enhance brand image by using your own domain
- SEO-Friendly: Beneficial for search engine optimization
It is recommended to configure a custom domain for production environments. For detailed configuration methods, please refer to Configure Custom Domain.
Indexed Documents Configuration
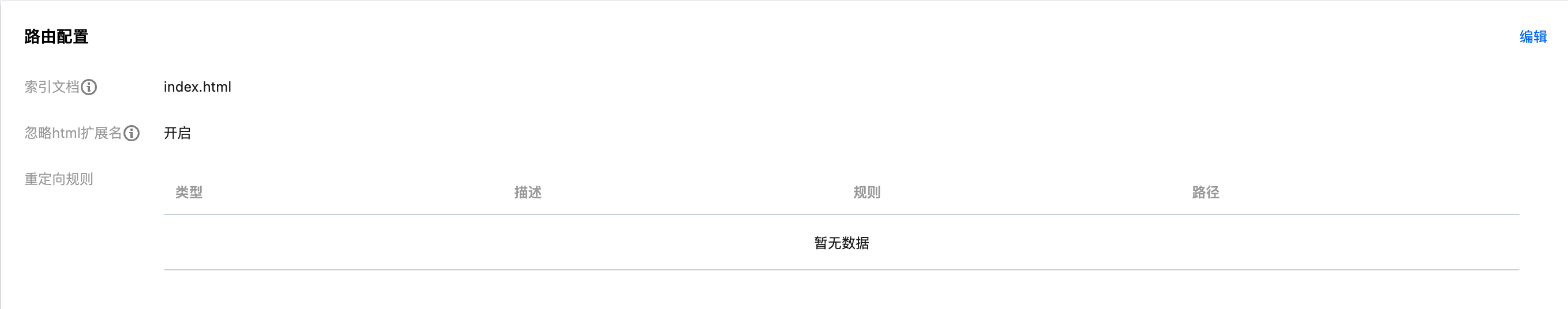
Default Indexed Documents
- Default File:
index.html - Scope: Root directory and all subdirectories
- Access Behavior: The index document is automatically returned when accessing a directory.
Configuration Best Practices
- Place
index.htmlfiles in both the root directory and important subdirectories. - Ensure the indexed documents have complete content to provide a good user experience.
- You can add navigation links in the index document to facilitate user access to other pages.
Redirect Rules
Redirect Rules help you handle URL changes and error pages to enhance user experience.
Application Scenarios
- File Migration: URL redirection after file movement or renaming
- URL Simplification: Redirecting long URLs to short URLs
- Error Handling: Customize error pages such as 404
- SEO Optimization: Maintaining search engine rankings
Rule Types
1. Error Code Redirection
Redirect for HTTP error status codes (e.g., 404, 403):
- Supported Range: 4xx error codes
- Custom Pages: You can design user-friendly error pages
- User Guidance: Provide navigation and assistance information on error pages
2. Prefix Match Redirection
Redirect based on URL prefix:
- Flexible Matching: Supports prefix matching for files and folders
- Batch Redirection: One rule can handle multiple similar URLs
- Path Mapping: Map old paths to new paths
Example Scenario:
Old path: docs/guide.html
New path: documents/guide.html
Rule: docs/ → documents/
Configuration Precautions
- Priority: Redirect rules take precedence over index document configurations
- Path Format: For the replacement path, only the relative path needs to be filled in, without including the domain name
- Testing and Verification: After configuration, thoroughly test to ensure redirects work properly
Cache Configuration
Reasonable cache configuration can significantly improve website access speed and reduce bandwidth consumption.
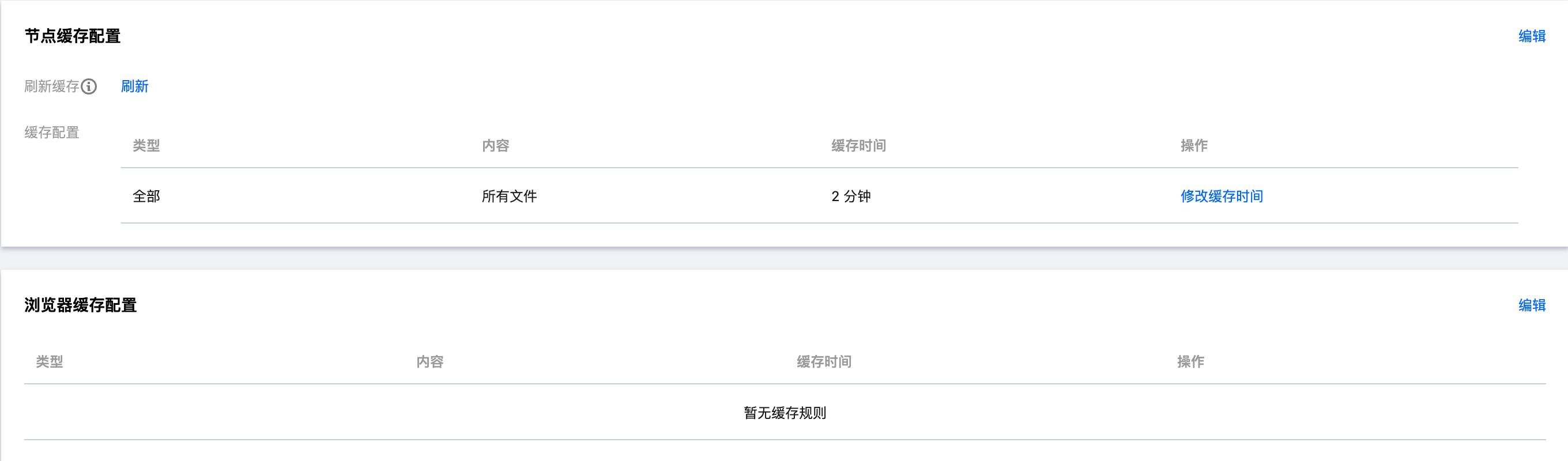
Cache Types
CloudBase Static Hosting supports two-level caching:
- Browser Caching: Resources are cached in the user's browser
- Node Caching: Resources are cached in CDN nodes
Configuration Method
It supports multiple cache configuration methods:
- File Extension: such as
.jpg,.png,.css,.js - Directory: such as
/static,/assets,/images - File Path: such as
/static/*.js,/css/main.css
Cache Policy Recommendations
| Resource Type | Recommended Cache Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Image files | 30 days | Images typically do not change frequently |
| CSS/JS files | 7 days | Style and script files are relatively stable |
| HTML files | 1 hour | Page content may be updated frequently |
| Font files | 30 days | Font files rarely change |
- Cache duration is set via
Cache-Control: max-age=<seconds> - Uploading files via the console will automatically refresh the CDN cache.
- When a user accesses a resource, the system prioritizes browser cache, followed by node cache.
Security Configuration
CloudBase Static Hosting provides multi-layered security defenses to protect your resources against malicious access.

Hotlink Protection Configuration
Prevent resource theft through Referer checks:
Blocklist Mode
- Feature: Deny access requests from specified domains.
- Applicable Scenario: Protection against known malicious domains
- Configuration method: Add the list of domains to be denied.
Allowlist Mode
- Feature: Only allow access requests from specified domains.
- Applicable Scenario: Strict control of access sources
- Configuration method: Add the list of domains allowed to access.
CloudBase determines the request source by checking the Referer field in the HTTP request header. Illegal requests will be returned with a 403 status code.
IP Access Control
IP Allowlist and Blocklist
Supported Formats:
- IPv4 address:
192.168.1.1 - IPv4 network segment:
192.168.1.0/24,10.0.0.0/8 - IPv6 address: Full IPv6 address format
Configuration Mode:
- Blocklist: Block access from specified IPs or network segments.
- Allowlist: Only allow access from specified IPs or network segments.
IP Access Frequency Limit
- Feature: Limit the access frequency of a single IP
- Protective effect: Can defend against some CC attacks.
- Configuration suggestions: Set the rate limiting threshold appropriately based on business requirements.
IP Access Frequency Limit may affect normal user access. Please configure cautiously based on actual business conditions. It is recommended to first verify the configuration effect in a test environment.