Basic Permissions
CloudBase provides a multi-layered storage permission management mechanism to ensure file security while meeting permission control needs for different business scenarios.
Cloud storage uses the _openid field as the basis for determining file ownership during read and write operations.
Permission Management System
CloudBase cloud storage permission management consists of two levels:
| Permission Type | Control Granularity | Use Case | Configuration Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Permission Control | Collection Level | Simple permission needs | Low |
| Security Rules | Document Level | Complex business logic | High |
Basic Permission Control
Configuration Method
On the CloudBase Console/Cloud Storage/Permission Settings page, set the corresponding permissions for cloud storage:
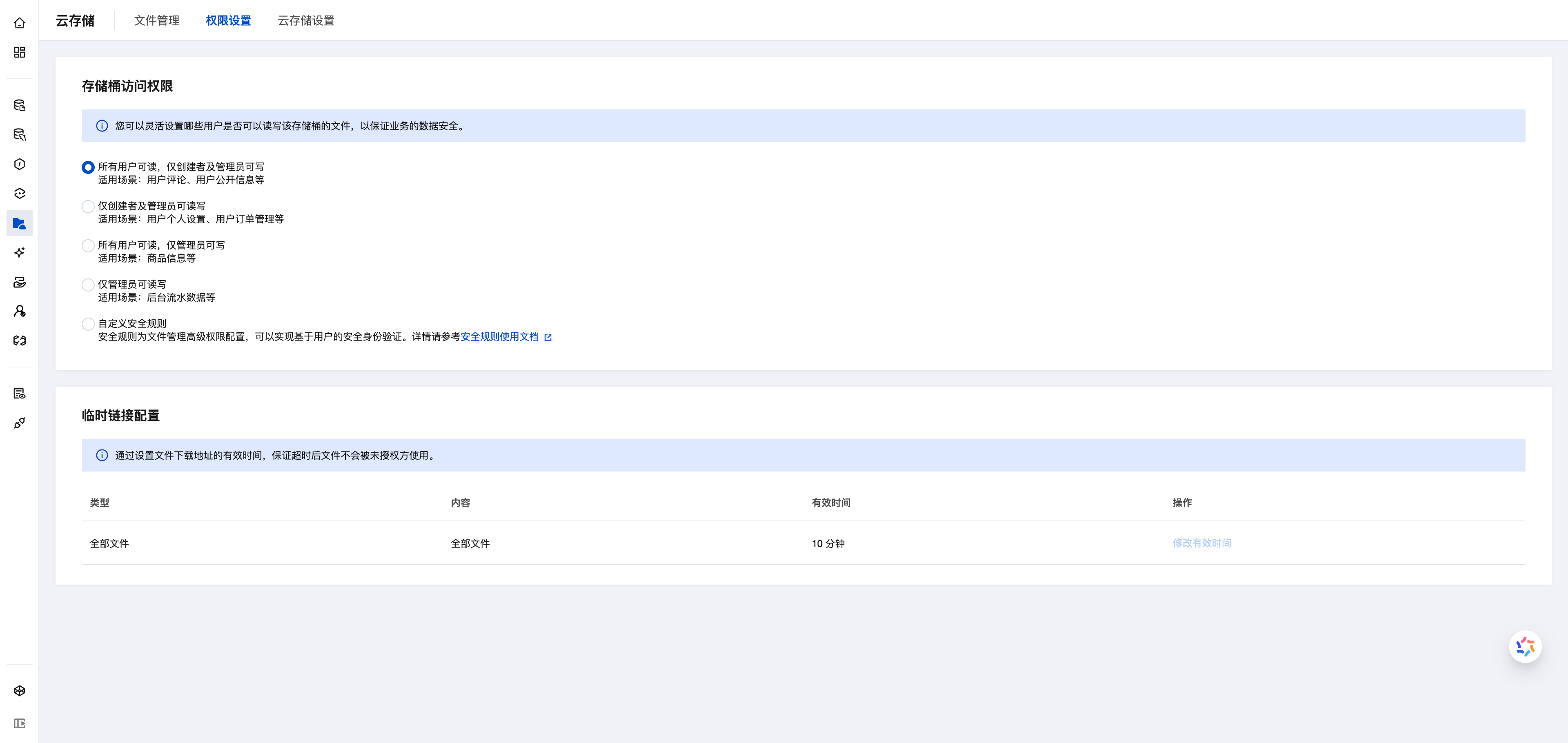
Permission Options
Basic permission control provides four preset permission types, choose based on user identity and file characteristics:
1. All Users Can Read, Only Creator and Admin Can Write (Public Read-Write)
Permission Description:
- ✅ Read: Everyone (including unauthenticated users) can access files
- 🔒 Write: Only the file creator and administrators can modify/delete
Use Cases:
- User avatars, user-published public content
- User comments, forum posts
- Socially shared images and videos
Usage Recommendations:
- ✅ Suitable for content display applications (blogs, forums, social apps)
- ✅ Files can be displayed directly in browsers/mini-programs via URL
- ⚠️ Anyone can access the files, be careful not to upload sensitive information
Typical Example:
// After users upload avatars, other users can directly access the avatar URL
<img src="https://xxx.tcb.qcloud.la/avatar/user123.jpg" />
2. Only Creator and Admin Can Read-Write (Private Read-Write)
Permission Description:
- 🔒 Read: Only the file creator and administrators can access
- 🔒 Write: Only the file creator and administrators can modify/delete
Use Cases:
- User personal data, ID card photos
- User order files, payment receipts
- Private albums, personal documents
Usage Recommendations:
- ✅ Suitable for personal information management and privacy protection
- ⚠️ Important: With this permission, file URLs cannot be used directly in frontend
- ⚠️ If you directly reference image URLs in web pages/mini-programs, it will cause images to not display (403 permission error)
Access Method:
You need to use temporary access links or access files through SDK:
// ❌ Wrong: Using file URL directly will cause 403 error
<img src="https://xxx.tcb.qcloud.la/private/photo.jpg" /> // Image won't display
// ✅ Correct: Use SDK to get temporary access link
const result = await app.getTempFileURL({
fileList: ['cloud://xxx.png']
});
const tempURL = result.fileList[0].tempFileURL; // Valid for 2 hours
<img src={tempURL} />
3. All Users Can Read, Only Admin Can Write (Public Read-Only)
Permission Description:
- ✅ Read: Everyone (including unauthenticated users) can access files
- 🔒 Write: Only administrators can upload/modify/delete files
Use Cases:
- Product images, carousel images, event posters
- Static resources (logos, icons, background images)
- Announcement files, downloadable resources
Usage Recommendations:
- ✅ Suitable for read-only configuration and reference data
- ✅ Files can be displayed directly in browsers/mini-programs via URL
- ✅ Prevents regular users from accidentally deleting or tampering with important files
Typical Example:
// Product images can be directly referenced anywhere
<img src="https://xxx.tcb.qcloud.la/products/iphone.jpg" />
4. Only Admin Can Read-Write (Fully Private)
Permission Description:
- 🔒 Read: Only administrators can access
- 🔒 Write: Only administrators can upload/modify/delete
Use Cases:
- Backend log files, system backups
- Sensitive data export files
- Financial reports, internal documents
Usage Recommendations:
- ✅ Suitable for sensitive data that requires server-side processing
- ⚠️ Frontend applications cannot access these files at all
- ⚠️ Can only be accessed through cloud functions (admin privileges)
Access Method:
Can only be accessed in cloud functions with admin privileges:
// Use admin privileges in cloud functions
const cloud = require('@cloudbase/node-sdk');
const app = cloud.init({ env: cloud.SYMBOL_CURRENT_ENV });
app.auth().getLoginState(); // Cloud functions have admin privileges by default
const result = await app.downloadFile({
fileID: 'cloud://xxx.pdf'
});
Permission Selection Flowchart
Permission Comparison Quick Reference
| Permission Type | Anonymous Access | Regular User Read | Creator Read | Admin Read | Regular User Write | Creator Write | Admin Write | Direct URL Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Read-Write | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ Yes |
| Private Read-Write | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ Need temp link |
| Public Read-Only | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ Yes |
| Fully Private | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ Not at all |
⚠️ Common Issues
Issue 1: Images/Files Cannot Display in Frontend (403 Error)
Cause: File has private read permission set ("Only creator and admin can read-write" or "Only admin can read-write")
Solutions:
- Solution A (Recommended): Switch to public read permission ("All users can read, only creator and admin can write")
- Solution B: Use temporary access links
Issue 2: Users Cannot Upload Files
Cause: File has "Only admin can write" permission set
Solutions:
- Switch to "All users can read, only creator and admin can write" permission
- Or use admin privileges in cloud functions to upload
Issue 3: How to Switch Permissions?
Steps:
- Log in to CloudBase Console/Cloud Storage/Permission Settings
- Select the new permission type
- Click "Save"
- ⚠️ Permission changes take effect immediately and may affect access to existing files
Security Rules
Security rules are document-level permission control capabilities provided by CloudBase database, offering greater flexibility and precision compared to basic permission control.
For details, please refer to Cloud Storage Security Rules