SDK File Management
CloudBase cloud storage provides comprehensive file management features, including uploading, downloading, deleting, copying files, and obtaining temporary links. This article details how to use these features.
| SDK Type | Applicable Platform |
|---|---|
| Mini Program SDK | Mini Program |
| JS SDK | Web browser |
| Node SDK | Node.js environment |
File Upload
You can upload any number and format of files to CloudBase cloud storage, and customize the paths and names of files and directories.
By default, only users who have passed CloudBase authentication can upload to / delete from cloud storage space. Therefore, users must first complete log in authentication before uploading files.
You can also use Custom Security Rules to set more relaxed or stricter read/write permissions for cloud storage.
Using the SDK, you can upload files to cloud storage space and obtain the globally unique identifier fileID for each file.
- JS SDK
- Mini Program SDK
- Node SDK
import tcb from "@cloudbase/js-sdk";
const app = tcb.init({
env: "your-env-id",
});
app
.uploadFile({
// Path of cloud storage.
cloudPath: "dirname/filename",
// File to be uploaded. File type.
filePath: document.getElementById("file").files[0],
})
.then((res) => {
// Return the file ID.
console.log(res.fileID);
});
wx.cloud
.uploadFile({
cloudPath: "example.png", // Path of uploading files to the cloud.
filePath: "", // Mini Program temporary file path, need to obtain using the Mini Program related APIs
})
.then((res) => {
// Return the file ID.
console.log(res.fileID);
});
const tcb = require("@cloudbase/node-sdk");
const fs = require("fs");
const app = tcb.init();
app
.uploadFile({
cloudPath: "path/test.jpg",
fileContent: fs.createReadStream("test.jpg"),
})
.then((res) => {
// Return the file ID.
console.log(res.fileID);
});
- When uploading, the file name must comply with file naming conventions;
- cloudPath is the path relative to the root directory of the cloud storage file or folder, in the form of directory/filename. The cloudPath should not start with
/; - If uploading a file to the same path, it will overwrite the existing file. By default, User A is not allowed to overwrite files uploaded by User B.
Download Files
By default, files in CloudBase cloud storage are publicly readable to all users.
You can also use Custom Security Rules to set more relaxed or stricter read/write permissions for cloud storage.
Using the SDK, you can download files from the cloud storage space. Pass the globally unique fileID of the cloud storage file when calling.
- JS SDK
- WeChat Mini Program SDK
- Node SDK
import tcb from "@cloudbase/js-sdk";
const app = tcb.init({
env: "your-env-id",
});
app
.downloadFile({
fileID: "cloud://a/b/c",
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res);
});
wx.cloud
.downloadFile({
fileID: "cloud://a/b/c", // File ID
})
.then((res) => {
// Return a temporary file path.
console.log(res.tempFilePath);
});
const tcb = require("@cloudbase/node-sdk");
const app = tcb.init({
env: "your-env-id",
});
app
.downloadFile({
fileID: "cloud://a/b/c",
})
.then((res) => {
// fileContent is of type Buffer.
console.log(res.fileContent);
});
You can use the file's download URL or obtain a temporary file link to directly download files from cloud storage in a browser, or use cloud storage as image hosting.
Deleting Files
By default, only users who have passed CloudBase Authentication can upload/delete files in the cloud storage space. Therefore, when deleting files on the client-side, users must first undergo login authentication.
- A single call can delete up to 50 files; if more, batch processing is required.
- By default, only the uploader/creator of the file and administrators have permission to delete the corresponding file; User A is not allowed to delete files belonging to User B.
- You can also use Custom Security Rules to set more lenient or stricter read/write permissions for cloud storage.
Using the SDK to call the deleteFile to delete one or multiple specified files in the cloud storage space.
- Web
- WeChat Mini Program
- Node.js
- HTTP API
import tcb from "@cloudbase/js-sdk";
const app = tcb.init({
env: "your-env-id",
});
const auth = app.auth({
persistence: "local", // remains valid for 30 days before the user explicitly logs out or changes the password
});
app
.deleteFile({
fileList: ["cloud://a/b/c", "cloud://d/e/f"],
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res.fileList);
});
wx.cloud
.deleteFile({
fileList: ["cloud://a/b/c", "cloud://d/e/f"],
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res.fileList);
});
const tcb = require("@cloudbase/node-sdk");
const app = tcb.init();
app
.deleteFile({
fileList: ["cloud://a/b/c", "cloud://d/e/f"],
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res.fileList);
});
curl -L 'https://your-envId.api.tcloudbasegateway.com/v1/storages/delete-objects' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <TOKEN>' \
-d '[
{
"cloudObjectId": "cloud://your-envId.bucket/not-exist"
},
{
"cloudObjectId": "cloud://your-envId.bucket/file.jpg"
}
]'
Copying Files
You can use the Node SDK and Open API to copy files in the cloud storage space to a specified path. By setting parameters, you can achieve the effect of moving files. This API supports batch copying. API documentation reference:
- The destination file path cannot be the same as the source file path
- Renaming during the copy operation is not supported, that is, the file name must remain consistent before and after copying
- The execution of the copy operation is affected by bucket permissions, source file and path permissions, and destination file and path permissions. Performing the copy operation does not change the original file permissions.
- The number of files in a single operation cannot exceed 50; for more, batch processing is required.
const tcb = require("@cloudbase/node-sdk");
const app = tcb.init({
env: "xxx", // Enter your environment ID
});
const path = "a.png"; // Enter the source file path
const fileList = [
{
srcPath: path,
dstPath: `dst/${path}`, // Enter the destination file path
removeOriginal: true, // Delete the source file after copying, equivalent to moving the file
},
];
const result = await app.copyFile({
fileList,
});
Obtain Temporary Link
You can use the fileID to retrieve an https link for a specific file in cloud storage space (cloud storage provides free CDN domains).
- JS SDK
- WeChat Mini Program SDK
- Node SDK
import tcb from "@cloudbase/js-sdk";
const app = tcb.init({
env: "your-env-id",
});
const auth = app.auth({
persistence: "local", // remains valid for 30 days before the user explicitly logs out or changes the password
});
app
.getTempFileURL({
fileList: ["cloud://a/b/c", "cloud://d/e/f"],
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res.fileList);
});
wx.cloud
.getTempFileURL({
fileList: ["cloud://a/b/c", "cloud://d/e/f"],
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res.fileList);
});
const tcb = require("@cloudbase/node-sdk");
const app = tcb.init();
app
.getTempFileURL({
fileList: ["cloud://a/b/c", "cloud://d/e/f"],
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res.fileList);
});
- The obtained https links for files with public read permissions do not expire; for example, the default permission is public read, and the obtained links are permanently valid;
- The obtained https links for files with private read permissions are temporary; for example, you can set file permissions to be readable only by the file uploader or administrators by combining user authentication and security rules. In this case, only users authenticated by CloudBase have permission to retrieve temporary links;
- The validity period can be dynamically set; requests for temporary links will be denied after expiration, ensuring file security;
- You can retrieve up to 50 at a time; batch processing is required for more.
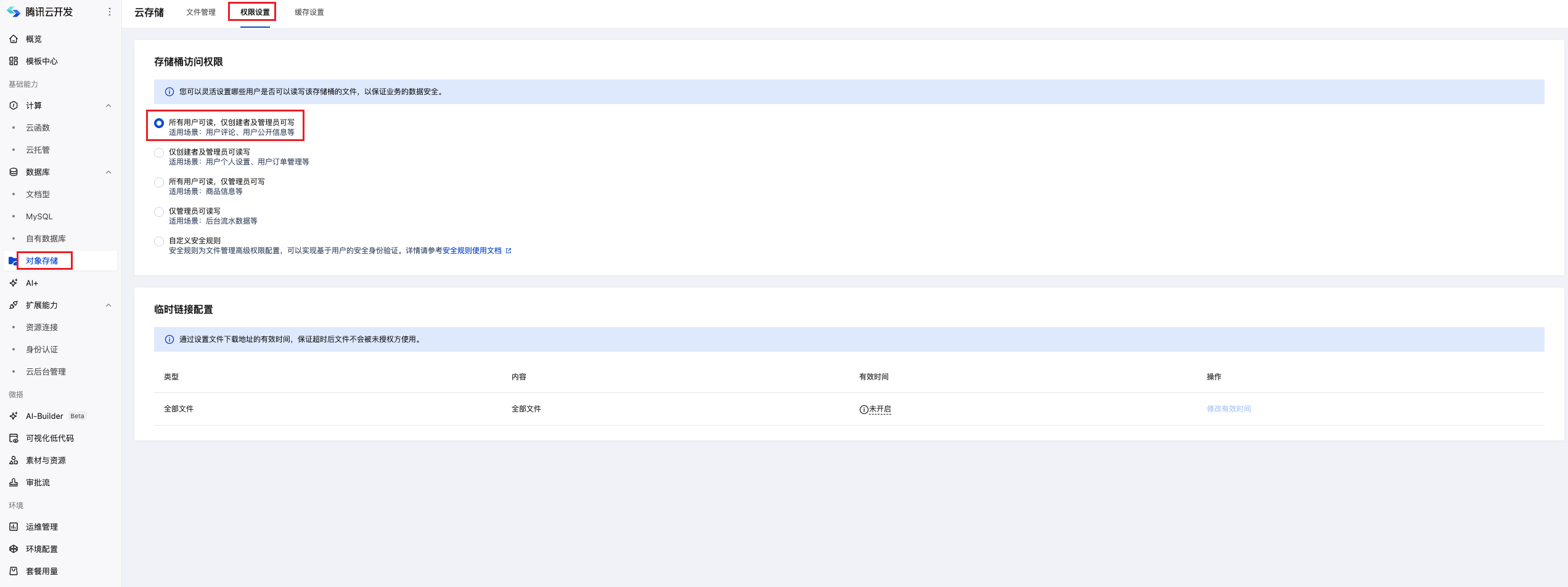
Setting Public Read Steps
Go to Cloud Development Platform - Cloud Storage - Permission Settings
Filename Naming Restrictions
When using CloudBase cloud storage, file names must comply with the following rules:
- It cannot be empty
- Cannot start with /
- Cannot contain consecutive /
- The encoded length can be up to 850 bytes
- It is recommended to use uppercase/lowercase letters, digits, and the symbols -, !, _, ., * and their combinations.
- Does not support the ASCII control characters: up arrow (↑), down arrow (↓), right arrow (→), left arrow (←), corresponding to CAN(24), EM(25), SUB(26), ESC(27).
- If a file or folder name uploaded by a user contains Chinese characters, the Chinese characters will be converted to percent-encoding according to URL Encode rules when accessing or requesting that file or folder.
- Special characters not recommended for use: ` ^ " \ { } [ ] ~ % # \ > < and ASCII 128-255 decimal.
- Special characters that may require special handling before use: , : ; = & \$ @ + ? (space) and ASCII character range: 00-1F hex (0-31 decimal) and 7F (127 decimal).