Provisioned Concurrency
Concurrency Overview
Concurrency is the number of requests that a cloud function processes simultaneously at a given moment. If other business services can support it, you can scale your cloud function from handling a few concurrent requests to tens of thousands with simple configuration.
Concurrency Working Mechanism
When a function is invoked, the cloud function allocates a concurrent instance to process the request or event. After the function code finishes running and returns, the instance handles other requests. If all instances are busy when a new request arrives, the cloud function allocates a new concurrent instance.
Cloud function follows the operational logic where one concurrent instance processes only one event at the same time, ensuring the efficiency and stability of processing each event.
Concurrency Calculation
Cloud function concurrency refers to the number of requests or invocations that the function code processes simultaneously. You can estimate it using the following formula:
Concurrency = Request rate × Function execution time = Requests per second × Average request duration
You can view the average request duration in the "Execution Time" section of the monitoring information. For example: If a business has a QPS of 2000 and the average request duration is 0.02s, the concurrency at any given moment is 2000qps × 0.02s = 40
Concurrent Instance Reuse and Reclamation
After a concurrent instance completes processing an event request, it is not immediately reclaimed but retained for a period to facilitate reuse. During this retention period, if new request events require processing, the system prioritizes using retained concurrent instances. This enables rapid event handling without needing to start new concurrent instances.
- After the retention period, if no requests require processing by that instance, the cloud function platform will reclaim it. For low-concurrency scenarios, no retention period is set; instead, the platform activates an intelligent reclamation mechanism for recycling.
- The concurrency retention duration is dynamically adjusted by the cloud function platform based on actual conditions. Therefore, in your function business code, you should not assume a specific retention time when programming.
Concurrency Scaling
If no concurrent instance of this version is available to handle the request when it arrives, the cloud function platform starts a new concurrent instance to process it. After initialization, the newly started concurrent instance can handle events. This is referred to as scaling out driven by elastic concurrency.
At the region level, the scaling out rate for elastic concurrency per account is limited by default to 500/minute, meaning that within one minute, a maximum of 500 new concurrent instances can be started. If the current limit is reached within one minute, no new concurrent instances can be started until the next minute. During this period, new scaling out requests will result in a scaling limit error (429 ResourceLimit).
For example, the default concurrency quota for an account in the Guangzhou region can support 1000 concurrent instances for 128MB functions. When a large number of requests arrive, in the first minute, it can scale from 0 concurrent instances to 500 concurrent instances. If there are still requests to be processed, in the second minute, it can scale from 500 concurrent instances to 1000 concurrent instances, until the concurrent instances can meet the demand of requests or reach the concurrency limit.
An elastic concurrency scaling out rate of 500/minute can meet the needs of most business scenarios. If your business encounters this scaling speed limit, you can choose to use pre-provisioned concurrency to pre-warm or purchase the reserved resource package to increase the elastic concurrency scaling out speed limit.
Provisioned Concurrency
Concurrent instances for elastic concurrency scaling on the cloud function platform need to undergo an initialization process, including runtime environment initialization and business code initialization. You can use the provisioned concurrency feature to pre-configure concurrent instances. After configuration, the cloud function platform will start launching concurrent instances and will not actively reclaim provisioned concurrency instances, ensuring as much as possible that a corresponding number of concurrent instances is maintained. If concurrent instances encounter errors such as code memory leaks, the cloud function platform will replace them with new instances.
Concurrency Service Commitment
Scaling Out Concurrency Limits
| Limit Type | Individual User | Enterprise User |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic Scaling Concurrency Limit | 500 concurrency/minute | 1000 concurrency/minute |
| Provisioned Scaling Concurrency Limit | 100 concurrency/minute | 100 concurrency/minute |
At the region level, the default elastic concurrency scaling out speed for Individual Users is limited to 500 concurrency/minute, while for Enterprise Users it is 1000 concurrency/minute. For example, if a customer requires 100k concurrency, at the maximum elastic scaling out speed, it would take 100k / 1000 = 100 minutes to complete the scaling operation. To increase quotas, you can purchase the reserved resource package.
Concurrency quota: Up to 256,000MB in a single environment.
Provisioned Concurrency
Provisioned Concurrency supports the pre-launch of concurrent instances according to configuration. The cloud function platform will not actively reclaim these instances and will strive to ensure a sufficient number of concurrent instances are available to handle requests. You can use this feature to set the provisioned concurrency quota for specific function versions. By configuring provisioned concurrency, computing resources can be prepared in advance, reducing latency caused by cold starts, runtime environment initialization, and business code initialization.
Provisioned Concurrency addresses the issue of concurrent instance initialization when requests arrive at the version level. When you configure Provisioned Concurrency for a function version, the following effects will occur:
- The cloud function platform immediately starts launching concurrent instances until the configured value is reached.
- The cloud function platform will not actively reclaim Provisioned Concurrency instances and will strive to maintain the number of provisioned concurrent instances.
- The startup speed of Provisioned Concurrency instances is separate from that of elastic invocation. The startup of Provisioned Concurrency does not consume the region-level elastic scaling speed of 500/minute. The cloud function platform adjusts the startup speed of Provisioned Concurrency based on your business needs, with a default of 100/minute.
- The cloud function platform will not actively reclaim Provisioned Concurrency instances, but instances may become unavailable due to issues such as process termination or memory overruns. When instances become unavailable, the platform will reclaim them while preparing new concurrent instances to maintain the configured provisioned concurrency level. During this process, there may be brief periods where the actual number of concurrent instances is lower than the provisioned amount. Unstarted concurrent instances will not be billed. You can monitor the startup status of provisioned concurrency in the "Concurrent Executions and Provisioned Concurrency" graph under the function's monitoring information.
- Provisioned Concurrency can only be configured on published versions, not on the $LATEST version. The $LATEST version is in an editable state, while Provisioned Concurrency requires launching concurrent instances before requests arrive. To ensure business stability and avoid version inconsistency issues caused by code and configuration edits, Provisioned Concurrency is only configurable on published versions. Published versions have immutable code and configurations, making them suitable for production environments.
Operation Steps
Adding Provisioned Concurrency
For published versions of the function, you can set the desired number of provisioned concurrency.
- Log in to the Cloud Development Console and select "Cloud Function" in the left navigation bar.
- On the "Function Services" list page, click Preset Management under the Operation column of the target function name to enter the "Provisioned Concurrency" page. As shown in the figure below:

- On the Cloud Function details page, click Provisioned Concurrency. As shown in the figure below:
- In the pop-up "Add Provisioned Concurrency" window, select the desired version and click Next. As shown in the figure below:
- After completing version selection, set the provisioned concurrency number and click Confirm to provision the instances. As shown in the figure below:
After configuration, you can view the status in "Provisioned Concurrency". The cloud function backend will take some time to complete the scaling of provisioned concurrency, displaying the number of prepared concurrent instances and completion status in the list.
Through Gradual Rollout, traffic is gradually shifted from the old version to the new version. If any issues are encountered, traffic is rolled back to the old version.
Updating Provisioned Concurrency
When the backend completes the scaling of provisioned concurrency, you can modify the concurrency number as needed.
- Log in to the Cloud Development Console and select "Cloud Function" in the left navigation bar.
- On the "Function Services" list page, click Preset Management under the Operation column of the target function name to enter the "Provisioned Concurrency" page. As shown in the figure below:

- On the "Provisioned Concurrency" page, select Configure on the right side of the row for the version to be updated. As shown in the figure below:
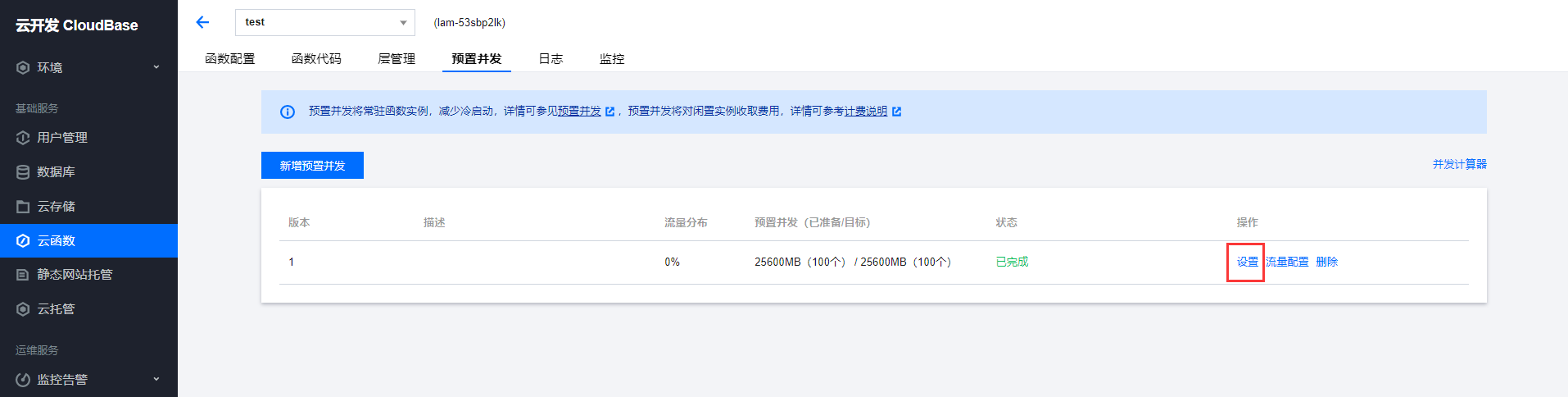
- In the pop-up "Set Provisioned Concurrency" window, update the setting value and click OK to complete the operation.
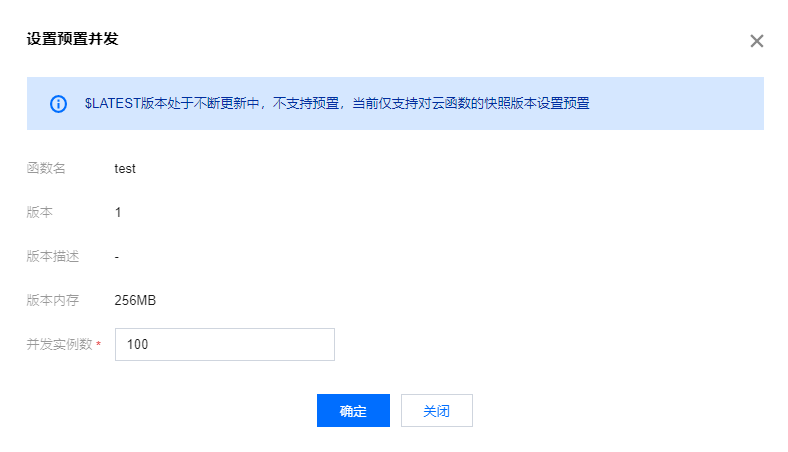
After the configuration is completed, the platform will complete the increase or decrease of concurrency again within a certain period based on your modifications.
Deleting Provisioned Concurrency
After traffic is fully switched to the new version and no abnormalities are observed for a period, delete the provisioned concurrency of the old version. Alternatively, when you no longer plan to use a specific provisioned concurrency configuration, you can delete it.
- Log in to the Cloud Development Console and select "Cloud Function" in the left navigation bar.
- On the "Function Services" list page, click Preset Management under the Operation column of the target function name to enter the "Provisioned Concurrency" page. As shown in the figure below:

- On the "Provisioned Concurrency" page, select Delete on the right side of the row for the version to be adjusted. As shown in the figure below:
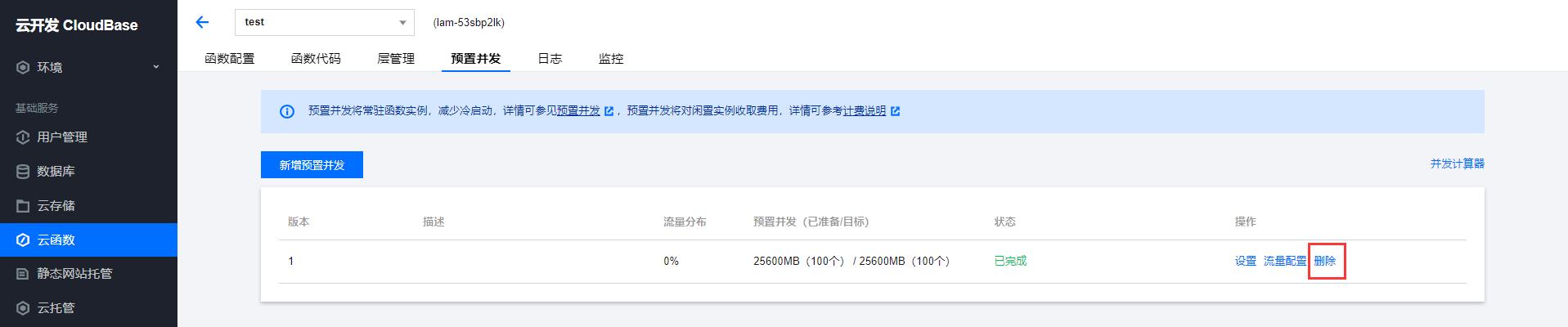
- In the pop-up "Delete Function Provisioned Concurrency Quota" window, click Confirm to complete the operation. As shown in the figure below:
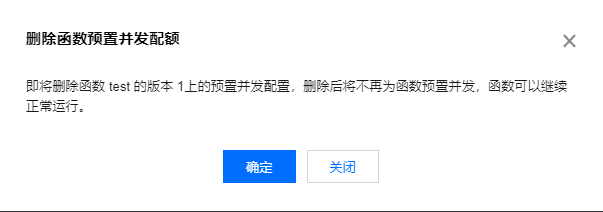
After the configuration is deleted, the platform will gradually reclaim the concurrent instances.
Best Practices
Concurrency is the number of requests that a cloud function processes simultaneously at a given moment. If other business services can support it, you can scale your cloud function from handling a few concurrent requests to tens of thousands with simple configuration.
Application Scenarios
High QPS with Short Execution Duration
Using cloud functions for simple data and file processing, such as cloud storage triggering cloud functions to report information or process files. In such scenarios, the runtime per request is short.
Practice Recommendations
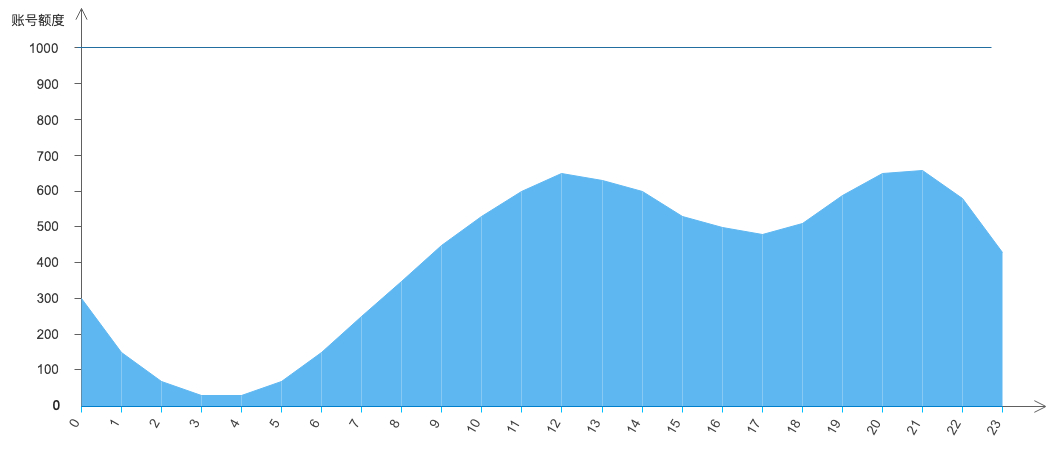
When multiple businesses under a single account simultaneously use cloud functions for support, the concurrency quotas of the cloud functions need to be dynamically scheduled on demand. For example, configure based on the characteristics of client-side businesses: client-side businesses experience peaks and valleys in user traffic; to ensure user experience, they require fast loading speeds and can tolerate a certain level of errors.
For the above business scenario, you can configure a certain amount of provisioned quota for the function. For example, set it at 60% of peak usage while not configuring a maximum dedicated quota for the function, ensuring full utilization of the total quota during traffic peaks. The cloud function quota changes are shown in the figure below: