Permission Configuration Guide
CloudBase provides a multi-level data permission management mechanism, ensuring data security while meeting the permission control requirements of different business scenarios.
📄 Page Permissions
Enter the app, click the "App Settings" button in the upper right corner to access the App Settings page.
When Application Access Rules selects Use Independent Hosted Login Page, page permissions can be configured.
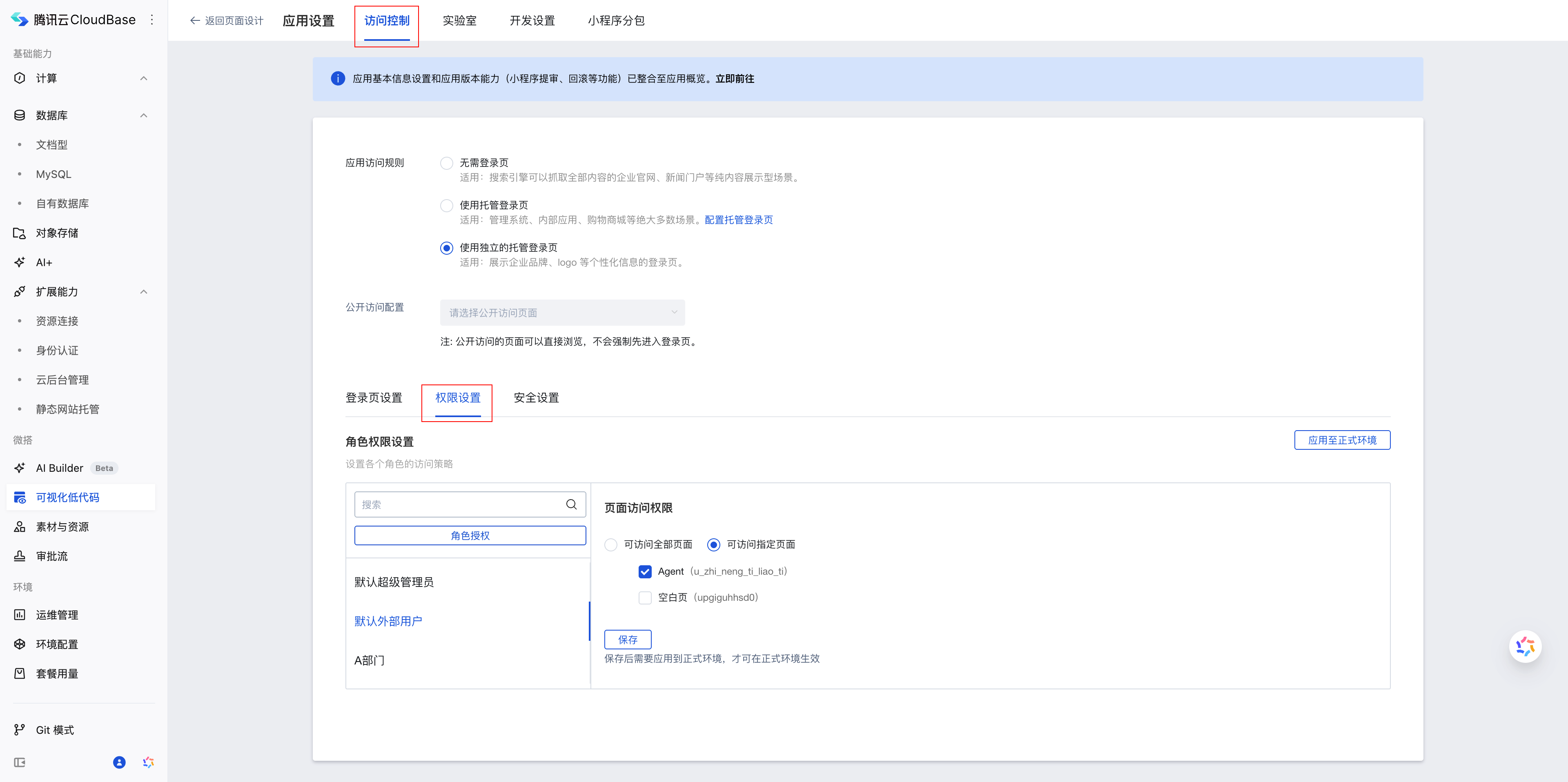
The role permissions configured here need to be set in conjunction with role management. The User => Role => Role Permissions relationship is as follows:
You can access the Role Management page from the Cloud Admin Console.
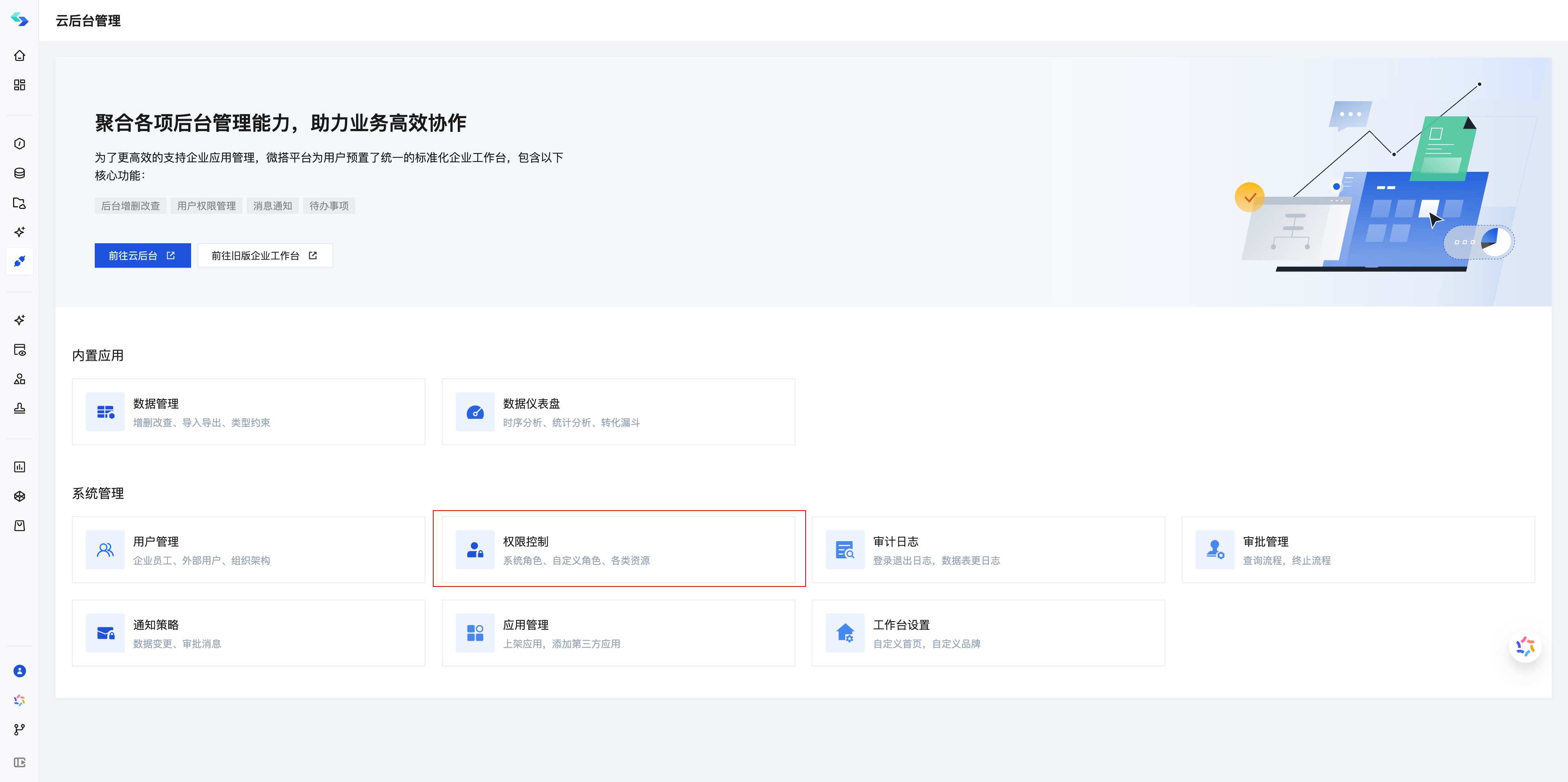
System roles are categorized as:
| Role Nickname | Description |
|---|---|
| Default Visitor Role | The "Default Visitor Role" is assigned by the system to anonymous users by default, and members cannot be added manually. |
| Default Super Administrator Role | The "Default Super Administrator Role" is a system-generated role with all permissions, and members can be added manually. |
| Default External User Role | The "Default External External User Role" is assigned by the system to external registered users by default, and members cannot be added manually. |
| Default Internal User Role | The "Default Internal User Role" is assigned by the system to internal organization members by default, and members cannot be added manually. |
You can choose to create "Custom Roles" to implement more granular permission control.
🎯 Data Permissions
CloudBase data permission management includes three levels:
| Permission Type | Control Granularity | Applicable Scenarios | Configuration Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Permission Control | Model Level | Simple Permission Requirements | Low |
| Role Permissions | User Level | Organizational Structure Permissions | Medium |
| Security Rule Permissions | Document Level | Complex Business Logic | High |
Permission Priority
Relationships between different permission types:
- Role Permissions and Basic Permissions are combined as a union to form the final permissions.
- Security Rule Permissions have the highest priority and override other permission settings.
- Choose the appropriate permission management method based on business complexity.
🔧 Basic Access Control
Features
Basic Permission Control is the simplest permission management method, suitable for most common business scenarios:
- Model-level Control: Apply uniform permissions to the entire data model.
- Predefined Permission Templates: Provide common permission configuration templates.
- Simple and Easy to Use: No need to write complex rule expressions.
Configuration Method
On the Data Model page in the CloudBase console, set corresponding permissions for each model:
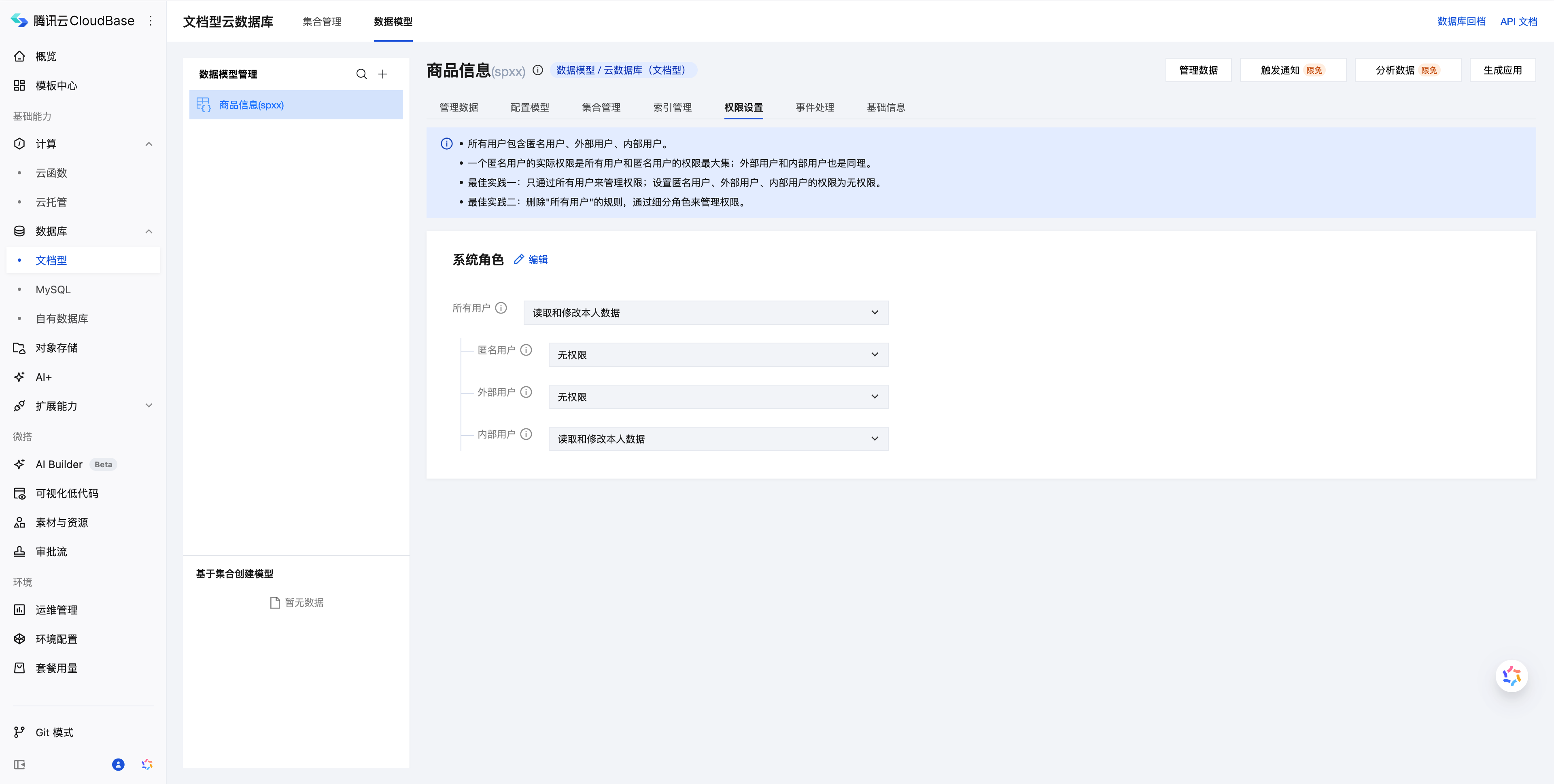
Permission Options
Based on the user's identity, select the corresponding permissions.
- All users include anonymous users, external users, and internal users.
- The actual permissions for an anonymous user are the maximum set of permissions from both "all users" and "anonymous users"; the same principle applies to external users and internal users.
- Best Practice 1: Manage permissions exclusively through "all users"; set permissions for anonymous users, external users, and internal users to no access.
- Best Practice 2: Delete the "all users" rules and manage permissions through granular roles.
| Permission Type | Applicable Scenarios |
|---|---|
| Read all data and modify own data | Public content, such as articles and products |
| Read and modify own data | Private data, such as user profiles |
| Read all data but cannot modify data | Configuration data, such as system settings |
| No access | Sensitive data, such as financial information |
👥 Custom Role Permission Control
Feature Overview
Role-based permissions are a permission management approach based on organizational structure, suitable for hierarchical permission control in enterprise-level applications. It complements Basic Permission Control, with the final permissions being the union of both.
Core Features:
- Support for Organizational Structure: Permission control based on departments and reporting relationships.
- Role Inheritance: Supports hierarchical inheritance of permissions.
- Flexible Combination: Combined with Basic Permissions as a union to provide more flexible permission configuration.
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Access Role Management
Access the Custom Roles Page to manage organizational structure and role definitions:
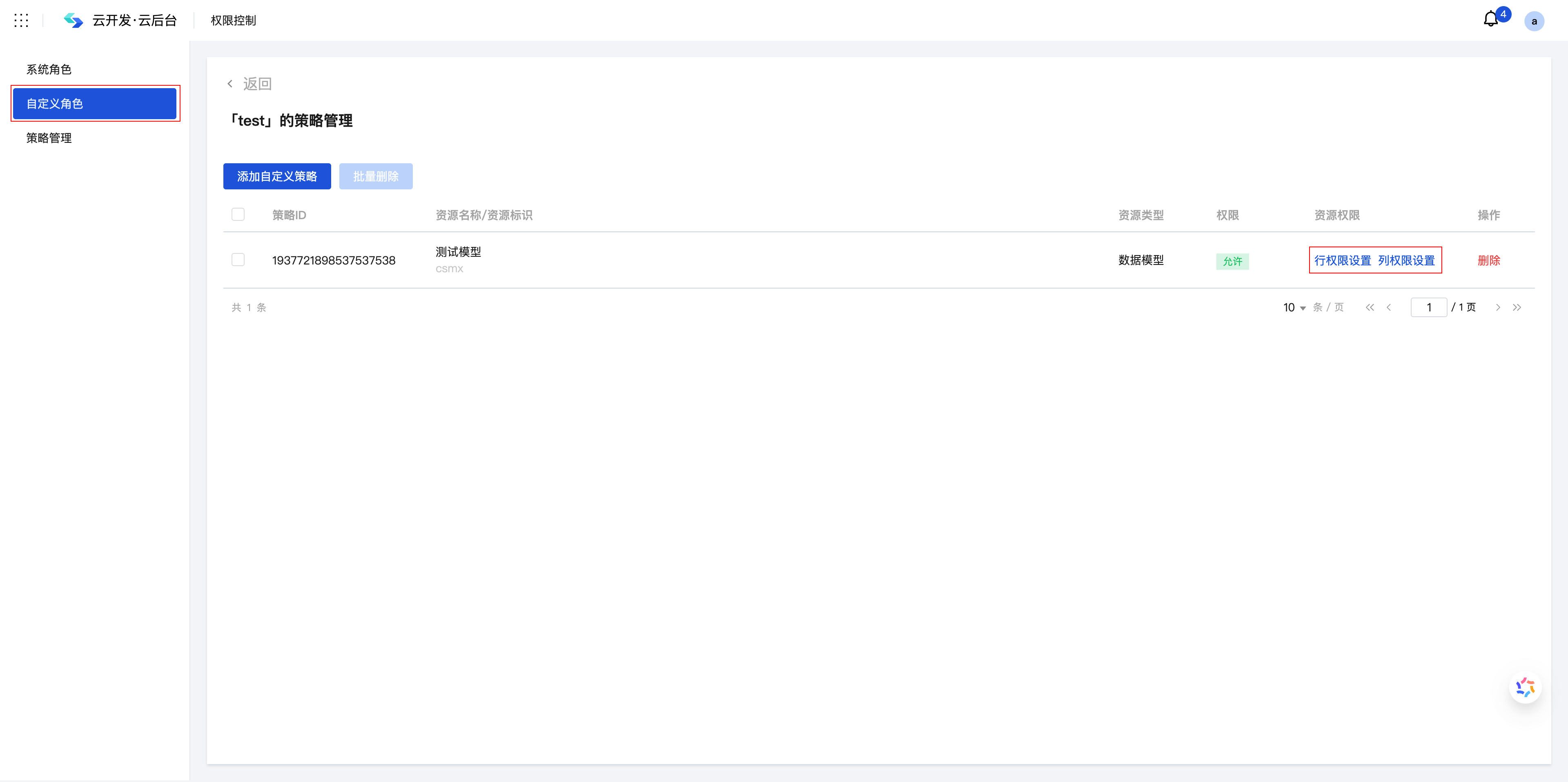
Step 2: Configure Row-level Permissions
Select the target role and click "Row Permission Settings" for detailed configuration:
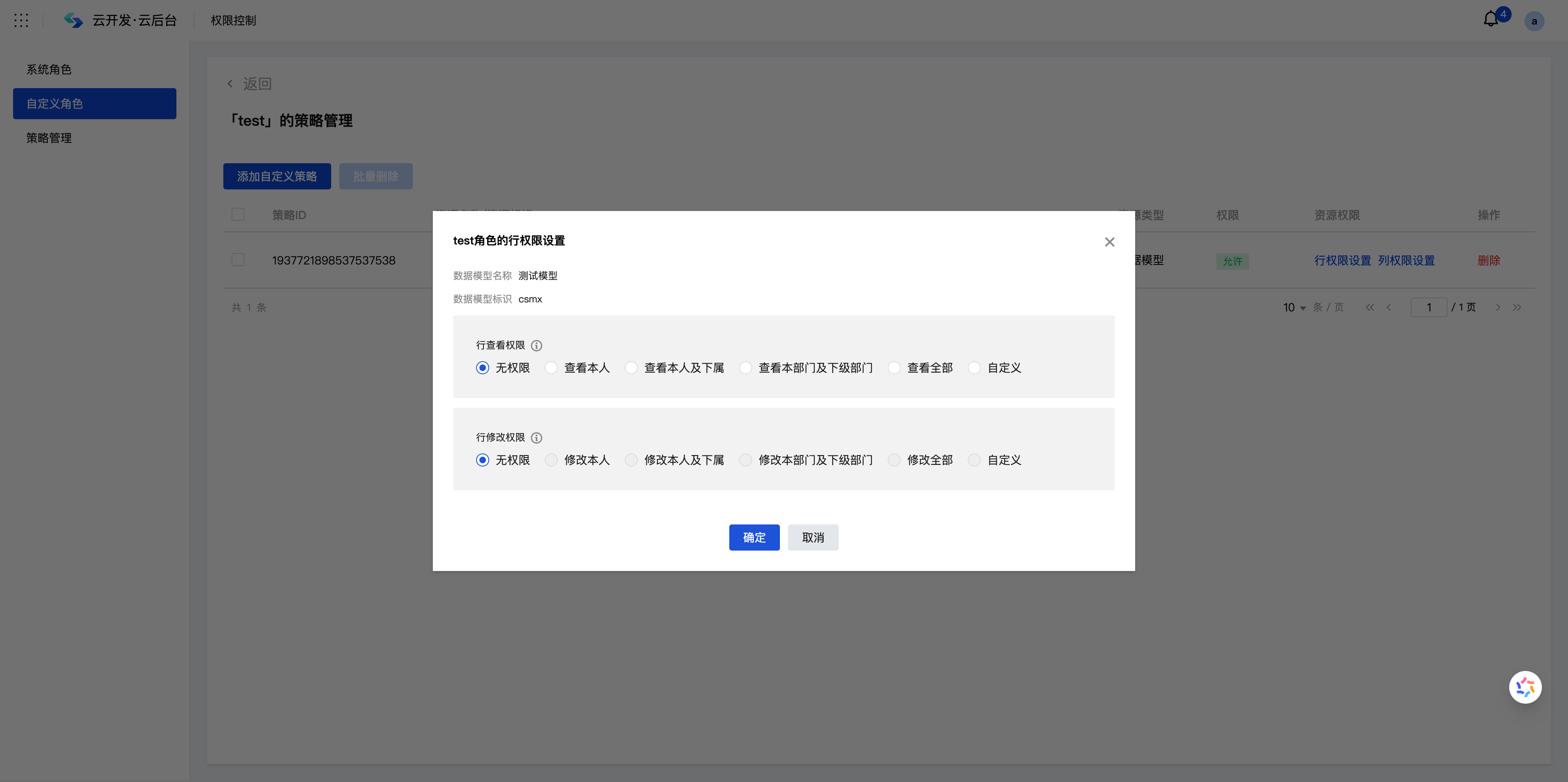
Permission Level Description
| Permission Level | Data Scope | Applicable Scenarios | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| View own | Data where the Owner field is set to self | Personal data management | Employees can only view their own attendance records |
| View Self and Subordinates | Data of self and subordinates | Team management | Supervisors can view work reports of team members |
| View Own Department and Sub-departments | Data of own department and sub-departments | Department management | Department managers view all projects within the department |
| View All | All data | System management | Administrators can view company-wide data |
Permission Combination Rules
Relationship Between Read and Write Permissions
⚠️ Important: Row modification permission automatically includes read permission, meaning that having modification permission implies having read permission.
Permissions Union Calculation
Basic Permissions + Role Permissions = Final Permissions
Example Scenario:
Basic Permissions: Readable and writable only by the creator and administrators
Role Permissions: View All + No Modification Permission
─────────────────────────────────
Final Permissions: Can view all data, but can only modify the data they created
🛡️ Security Rule Permissions
If the above two permission modes do not meet your requirements, you can use Security Rule Permissions for more granular permission control.
Please refer to the Custom Role Permission Control document.
Practical Application Cases
Case 1: Blog Permissions
Business Requirements:
- Can view everyone's blogs
- Can update their own blogs
Basic Permission Configuration
All users/Read all data, Modify own data
Case 2: Project Management System
Business Requirements:
- Project members can only view projects they participate in.
- Project managers can manage the projects under their responsibility.
- Department managers can view all projects within the department.
Basic Permission Configuration
All users/Read and modify own data
Role Permissions Configuration
| Role | Role Data Permissions | Row Modification Permissions | Final Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salesperson | View own | Self | Can only view and modify their own customers |
| Sales Supervisor | View Self and Subordinates | Self and subordinates | Can manage all customers of the team |
| Sales Director | View All | View All | Can manage all customers |
🎯 Permission Selection Guide
Select based on business complexity
| Business Scenario | Recommended Solution | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Application | Basic Permission Control | Simple configuration that meets basic requirements |
| Complex Business Logic | Security Rule Permissions | Flexible expressions that support complex judgments |
| Enterprise-level Application | Role Permissions + Basic Permissions | Supports organizational structure with clear permission hierarchy |
| High Security Requirements | Security Rules + Role Permissions | Multi-layered protection with fine-grained control |
Permission Configuration Recommendations
- Start simple: Begin with basic permissions and gradually upgrade as needed
- Layered Design: Basic permissions handle common logic, while security rules handle specific logic
- Test Verification: Thoroughly test various permission scenarios in the development environment
- Documentation: Thoroughly document the permission design rationale and configuration instructions
Through reasonable permission configuration, you can build a secure yet flexible data access control system that meets various complex business requirements.