Integrate WeDa into existing project
In custom-developed applications, WeDa provides developers with the following two capabilities:
- Provides the feature of downloading corresponding code as a component library, enabling developers to use pages or components developed with WeDa in existing Mini Programs or react projects.
- Provides the corresponding SDK for developers to integrate with WeDa's user management system, utilize WeDa services (login authentication, cloud functions, cloud storage, database, etc.), and facilitate user information management.
If developers only need to use WeDa's user management system or services, please jump to Access WeDa Services.
1. Download and use WeDa block components
1.1 Developing Block Components
WeDa supports Custom Blocks. Blocks can be used within WeDa or downloaded as code packages for developers to use as Mini Program components in existing Mini Programs. Developers can also choose to use Mini Program components in subpackages. Additionally, blocks support being downloaded and used as components in react projects.
It is recommended that developers using blocks for the first time read Custom Blocks to understand the basic concepts of WeDa Blocks.
1.1.1 Block Parameter Passing
If developers do not need to pass parameters or callbacks, please jump to Save Block.
Blocks can save all content under a single container or component. When saving a block, developers need to specify the parameters the block needs to receive in Dynamic Item Configuration. When downloaded as a component code package, all parameters of the component will be bound to this root container element.
The Dynamic Item Configuration when saving the block will determine the parameter passing when the block is downloaded and used as a component.
When configuring dynamic item settings upon clicking the save popup, you can define block parameters. For details, refer to Block Dynamic Item Configuration.
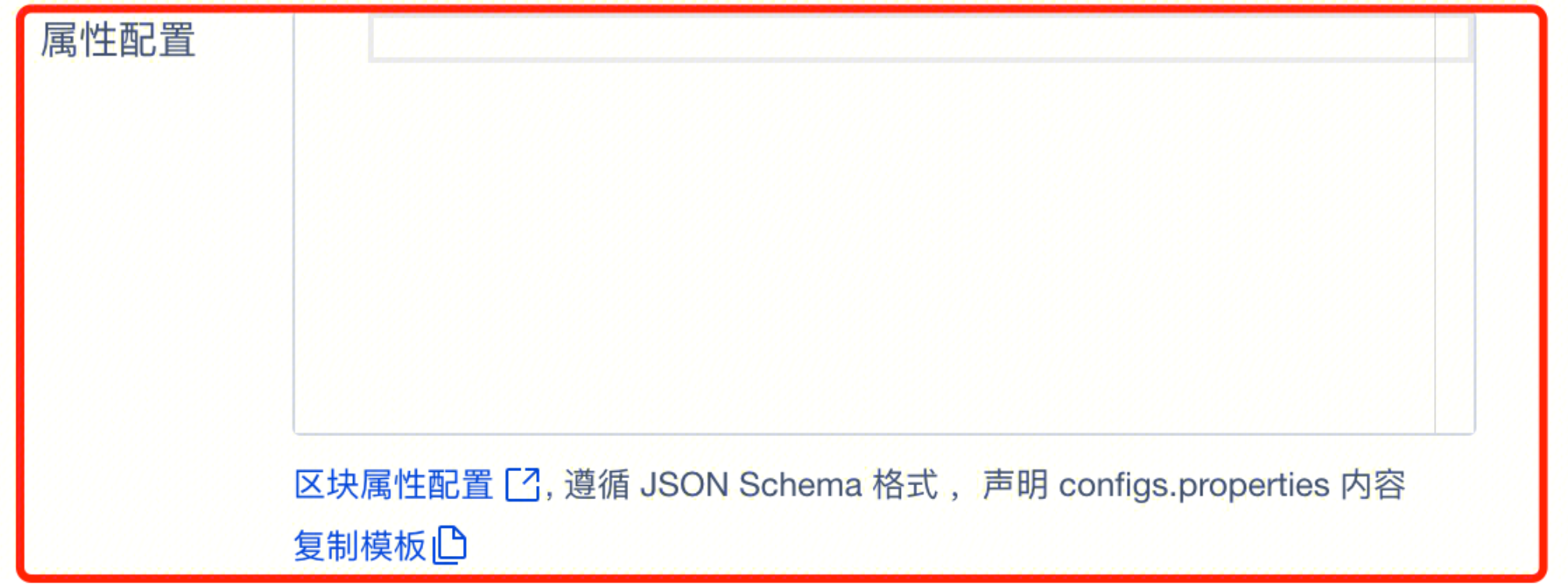 Complete example content is as follows:
Complete example content is as follows:{
"configs": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"messgae": {
"type": "string",
"default": "This is the property value",
"required": true
},
"callbackObj":{
"type": "object"
}
}
}
}
Developers can configure parameters in properties such as message or callbackObj format. The passed parameters will be bound to the block's root container. Within the block, developers can retrieve the required passed parameters or execute the corresponding callback functions from the root container's data.
Note that blocks do not support directly passing functions. The recommended approach is to encapsulate function callbacks within an object such as callbackObj for invocation.
Example method: $w['rootElement'].data.callbackObj.callbackFunction
1.1.2 Block: How to Use Parameters
Due to the characteristics of blocks, WeDa recommends that developers determine the root element when developing blocks, and perform parameter access and callback invocation based on the root element ID.
Parameter Access
Developers can directly access the data attribute on the root element in $w to obtain parameters. Example code:
// $w.[rootElement].data.[parameter]
$w.container1.data.message;
Callback Invocation
Developers may need to invoke functions from existing projects within blocks or use callback functions to obtain values within WeDa. The recommended solution is to create new JavaScript methods.
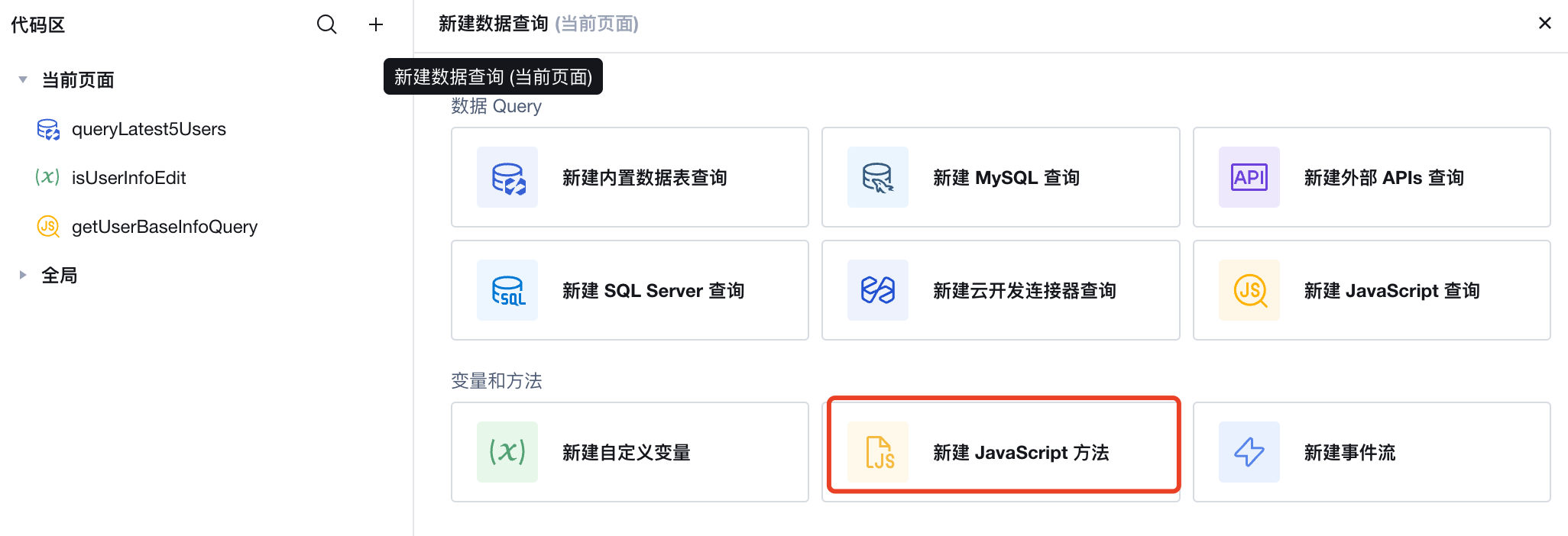
// $w.[rootElement].data.[callbackObj].[callbackFunction]
export default function ({ event, data }) {
$w.container1.data.callbackObj.callback({ event, data });
}
After creating a new JavaScript method, developers can bind it to WeDa component events for invocation, such as obtaining the value of an Input component or handling trigger events from a Button component.
1.2 Saving Blocks
Select the root container of the block to be saved and save it as a block. Developers need to include all queries and functions used within the block in the saved items to ensure they function properly when reusing or downloading the block.
- Global variables and methods cannot be saved to blocks. Do not use them in blocks.
- If developers use WeDa services such as login authentication, cloud functions, cloud storage, or databases in blocks, please access WeDa services. If not used, this step is not required.
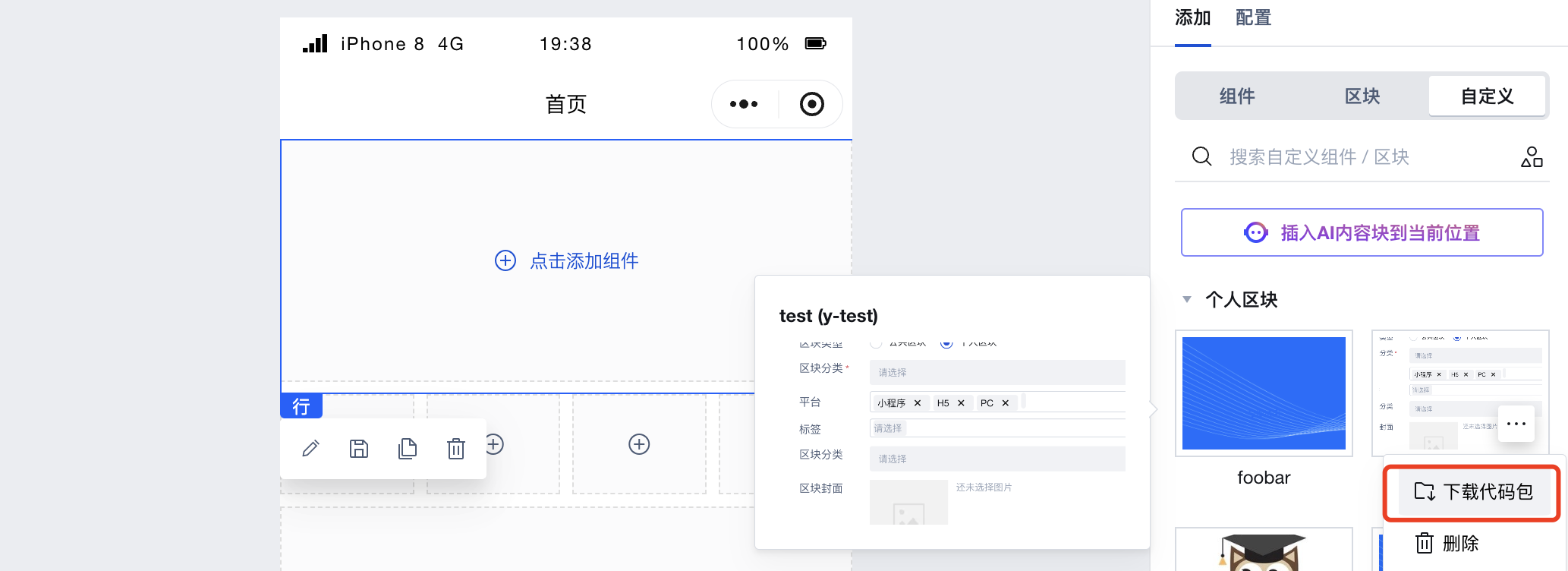
1.3 Downloading Blocks
After saving the block, developers can download it under 'Add-Custom-Custom Blocks' and incorporate it as a component in existing projects by following the pop-up instructions.
The block is downloaded as a Web code package and requires the corresponding react version.
"react": "^16.14.0",
"react-dom": "^16.14.0"
2. Accessing WeDa Services
Developers need to use the corresponding SDK to integrate with WeDa when utilizing WeDa services in custom development or when using WeDa services in downloaded WeDa components and pages.
2.1 WeDa User Management Access Preparation
Before integration, developers need to install the corresponding npm package(s), as follows:
{
...,
"dependencies": {
"@cloudbase/js-sdk": "2.5.6-beta.1",
"@cloudbase/oauth": "0.1.1-alpha.5",
"@cloudbase/weda-client": "1.0.24",
"@cloudbase/weda-cloud-sdk": "1.0.57",
"mobx": "^5.15.4",
"lodash.get": "^4.4.2",
"lodash.set": "^4.3.2",
"miniprogram-gesture": "^1.0.6",
"miniprogram-api-promise": "^1.0.4"
},
...
}
2.2 Initialize the SDK
Before using, the SDK needs to be initialized by filling in the corresponding environment parameters, where the value of endpointType is determined by the application's development mode.
Generally, when developing in WeChat Cloud Development or WeDa scan code authorization mode, this parameter can be omitted.
If using WeDa Fully Managed Mode for development, the tcb-api must be passed.
// sdk initialization
import * as wedaClient from "@cloudbase/weda-client";
wedaClient.init({
/** Whether currently in production release mode */
isProd: true,
/** Low-code Application ID */
appId: "app-xxx",
/** Cloud Base environment ID */
envId: "lowcode-xxx",
/** Determine the call path, either tcb-api or not passed */
endpointType: "tcb-api",
appConfig: {
staticResourceDomain: "<Static hosting access domain for accessing material resources>",
},
});
2.3 Application Related Methods
Primarily used for SDK initialization, accessed via wedaClient.app
2.3.1 wedaClient.app.init
wedaClient.app.init(params: IMpInitParams): Promise<{ app: cloudbase.app.App; auth: cloudbase.auth.App }>
Feature Description
Initialize the application.
Input Parameters: IMpInitParams
| Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| isProd | boolean | Whether currently in production release mode |
| appId | string | Low-code Application ID |
| envId | string | Cloud Base environment ID |
| endpointType | string | Determine the call path, either tcb-api or empty |
Output Parameters
| Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| app | cloudbase.app.App | See details |
| auth | cloudbase.auth.App | See details |
2.4 User Management Related Methods
This section can basically refer to the WeDa Client Permissions API, used via wedaClient.auth
2.4.1 wedaClient.auth.currentUser
Feature Description
User information reference can refer to $w.auth.currentUser
2.4.2 wedaClient.auth.getAccessToken
Feature Description
Retrieve the accessToken of the current user. If the user is not logged in, it returns null.
Input Parameters: None
Output Parameters
| Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| accessToken | string | The current user's token information |
| env | string | The currently configured environment ID of the sdk |
Example
const token = await wedaClient.auth.getAccessToken();
console.log(token?.accessToken);
2.4.3 wedaClient.auth.getUserInfo
Feature Description
Obtain current logged-in user information by referring to $w.auth.getUserInfo
2.4.4 wedaClient.auth.loginScope
Feature Description
Obtain the user login permission scope by referring to $w.auth.loginScope
2.4.5 wedaClient.auth.signIn
wedaClient.app.signIn(params: IWebSiginParams | IMpSiginParams): Promise<void>
Feature Description
User login. Currently supports two types:
web login: supports username and password
Mini Program: supports phone number login
Input Parameters
IWebSiginParams
Input parameters used on the Web: currently supports login via phone number, email, or username and password.
| Value | Type | Description |
|---|
Obtain the user login permission scope by referring to $w.auth.loginScope | password | string | User password. Either password or verification_token must be provided. | | verification_token | string | Verification code token. Either password or verification_token must be provided. |
IMpSiginParams
Input parameters used in the Mini Program: currently supports login via phone number code.
| Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| encryptedPhoneCode | string | Dynamic token for phone number. For how to obtain, refer to WeChat documentation |
Output Parameters: None
Example
await wedaClient.auth.signIn({
username: "Username",
password: "Password",
});
2.4.6 wedaClient.auth.modifyCurrentUser
wedaClient.auth.modifyCurrentUser(params: IModifyCurrentUser): Promise<CurrentUserInfo>
Feature Description
Modifying User Information
Input Parameters
IModifyCurrentUser
| Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| userName | string | Username |
| nickName | string | User nickname |
| avatarUrl | string | Avatar |
| description | string | Description |
Output Parameters
Consistent with wedaClient.auth.currentUser
Example
const userInfo = await wedaClient.auth.modifyCurrentUser({
userName: "test",
});
2.4.7 wedaClient.auth.openIdLoginInWxApp
wedaClient.auth.openIdLoginInWxApp(): Promise<boolean>
Feature Description
openId silent login
Input Parameters
None
Output Parameters
| Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| result | boolean | Successful login |
Example
await wedaClient.auth.openIdLoginInWxApp();
console.log(wedaClient.auth.currentUser);