Log Search
Cloud Development log search feature helps you quickly locate and analyze issues during application runtime. It supports multiple search methods, including full-text search, key-value search, and fuzzy matching, enabling you to efficiently find specific log information.
Activate the search feature
- Log in to Cloud Development Platform/Log Monitoring
- Once activated, you can start using various search features.
Log Format
The log printing format automatically includes system default fields, which are as follows:
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| level | string | Required | Log level (log/info/warn/error) |
| requestId | string | Required | Request ID |
| module | string | Required | Module name |
| resourceName | string | Required | Resource name |
| errorCode | string | Required | Error code |
| errorMessage | string | Required | Error message |
| request | string | Required | Request parameters |
| response | string | Required | Response parameters |
| msg | string | Optional | Brief log content |
| user | string | Required | User identifier |
| src | string | Required | Source: system/app |
| startTime | string | Required | Request start time |
| timeCost | string | Required | Request duration |
| service | string | Required | Service invocation |
Cloud Function
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| function_name | string | Required | Function name |
| request_id | string | Required | Request ID |
| qualifier | string | Required | Version |
- If a user custom-prints log object content, custom log fields will be added and a key-value index will be created.
- If user-defined log fields contain system default fields, the custom log content will take precedence during log search.
- Restrict user-defined log fields from containing the following keywords:
"__FILENAME__","__TIMESTAMP__","__LOGSETID__","__TOPICID__".
Detailed Explanation of Search Methods
1. Full-text search
Full-text search is the most commonly used log lookup method. The system automatically splits log content into multiple terms using delimiters, allowing you to input keywords for exact or fuzzy matching.
Usage Scenarios:
- Search for logs containing specific error messages
- Search for logs containing a specific function name or variable name
- Locate operation records containing a specific user ID
Example:
polls # Search for all logs containing "polls"
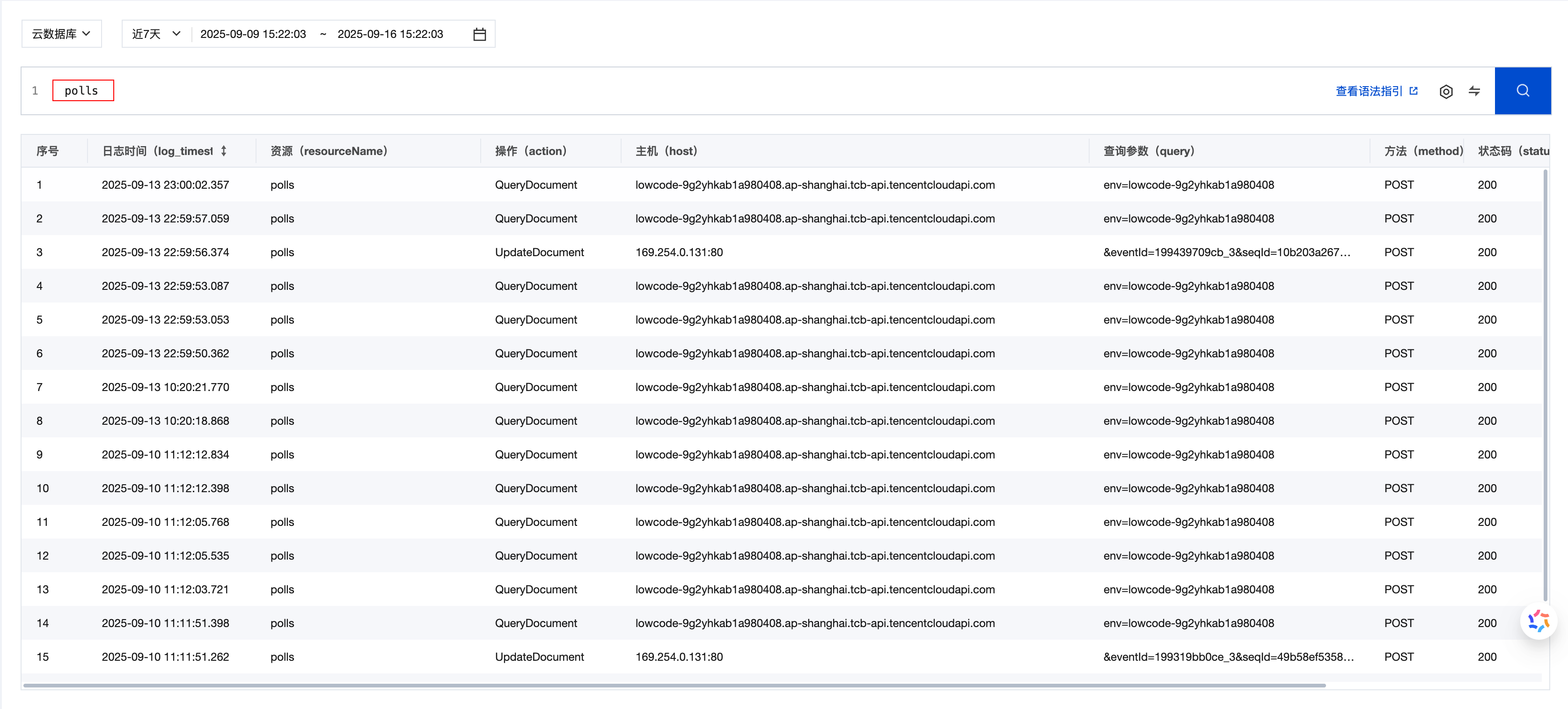
2. Key-value Search
Key-value search allows you to perform precise lookups based on structured fields in logs. Log content is stored in JSON format, and you can use the key:value format to search for specific field contents.
Common Fields:
level: Log level (error, warn, info, debug)source: Log source (function, database, storage, etc.)functionName: cloud function namerequestId: Request IDuserId: User ID
Usage Scenarios:
- Search for logs of a specific level:
level:error - Search for logs of a specific function:
functionName:user-login - Search for operations of a specific user:
userId:123456
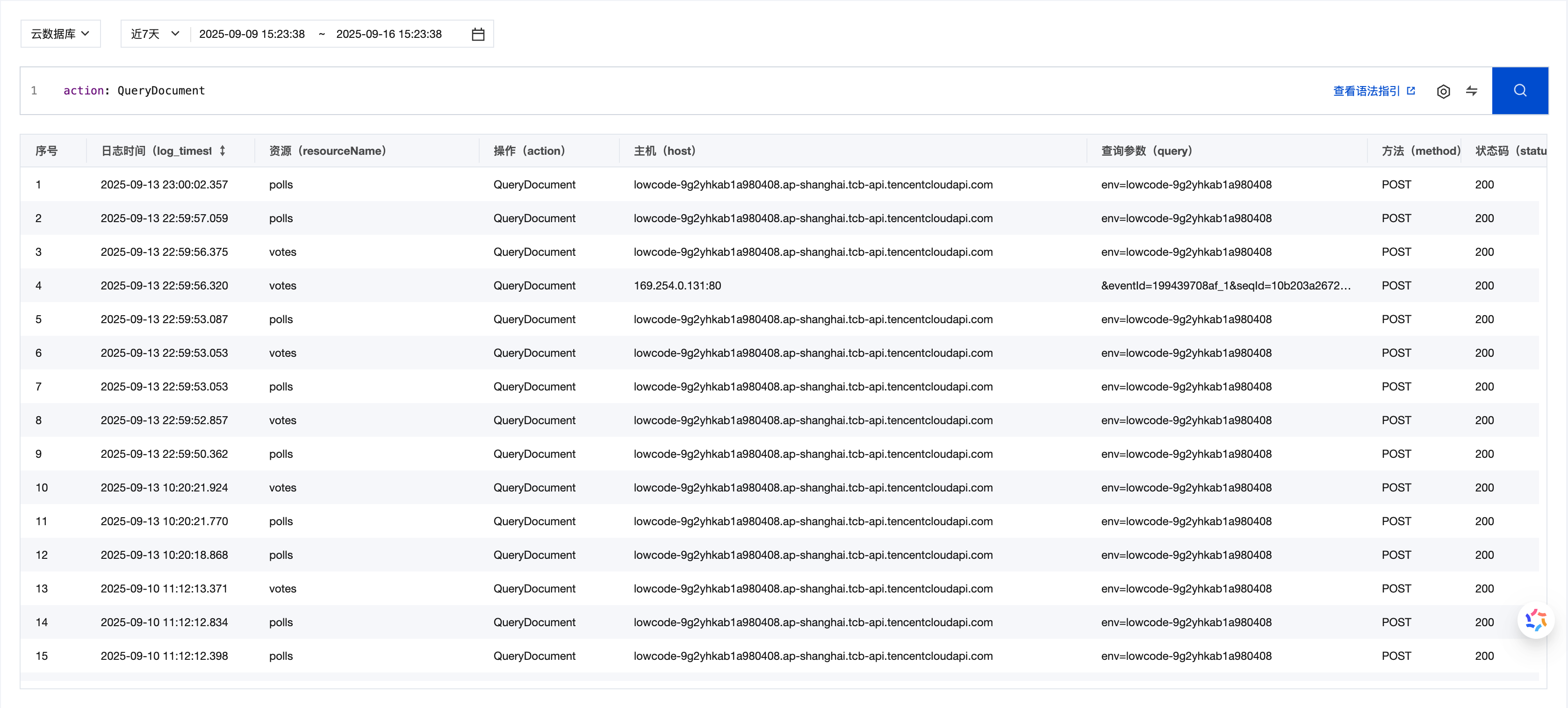
Example:
action: QueryDocument # Search for all logs where action is 'QueryDocument'
3. Fuzzy Keyword Search
Fuzzy search uses wildcards to match uncertain characters and is suitable for scenarios where partial information is known.
Wildcard Description
| Wildcard | Description | Example | Matching Results |
|---|---|---|---|
* | Matches zero or more arbitrary characters (not supported at the beginning) | abc* | abc, abcd, abcdef |
? | Matches any single character | ab?c | abdc, abec, ab1c |
Use Cases
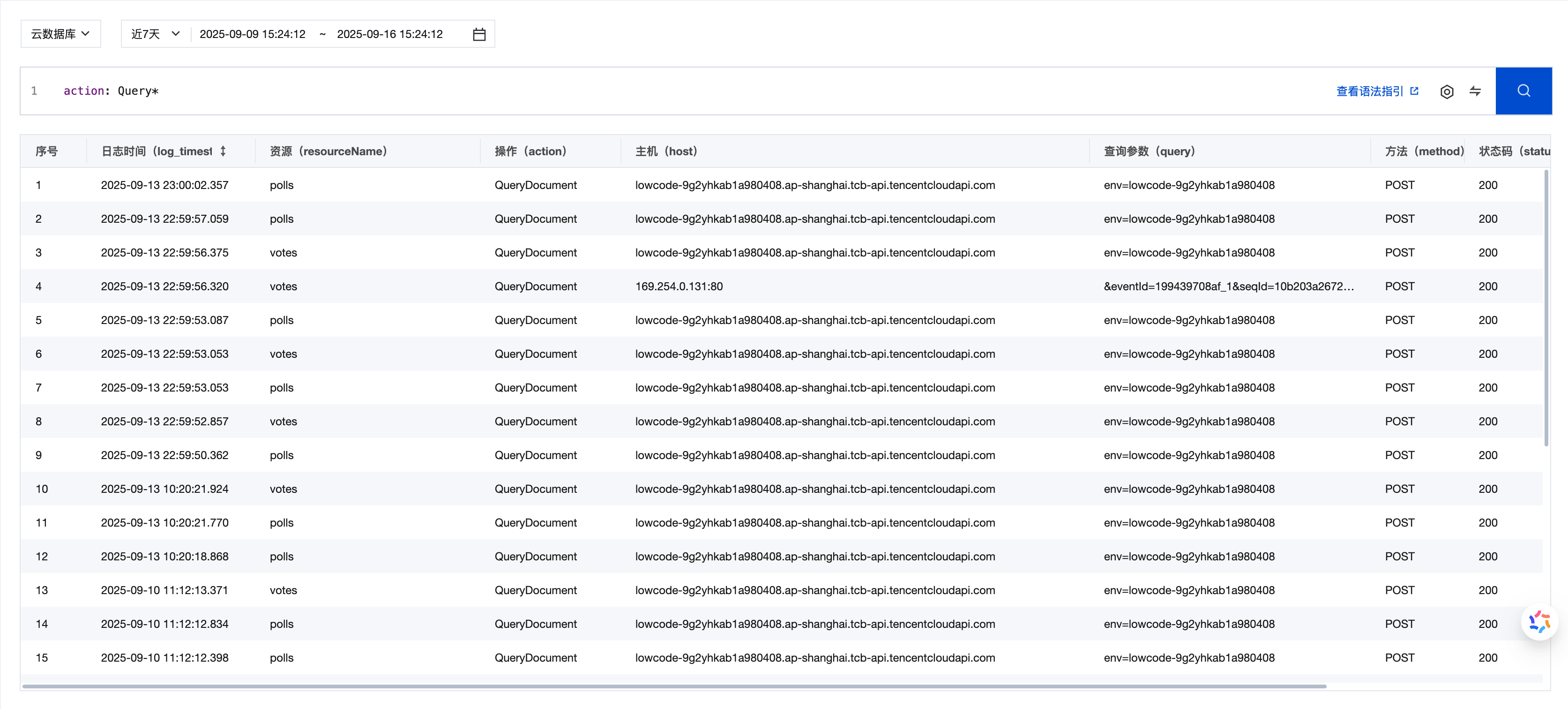
Multi-Version Function Lookup:
action: Query* # Search for all logs where actions start with 'Query'
Advanced Query Syntax
Logical Operators
| Operator | Syntax | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| AND | A and B or A B | Returns logs containing both A and B | error and timeout |
| OR | A or B | Returns logs containing A or B | error or warning |
| NOT | not B | Returns logs that do not contain B | not debug |
| MINUS | A not B | Returns logs that contain A but not B | error not timeout |
Special Characters Handling
| Syntax | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
'text' | Text within single quotes is treated as literal characters | 'and' finds logs containing "and" |
"text" | Text within double quotes is treated as literal characters. | "error:404" finds logs containing "error:404" |
\ | Escape character that escapes special symbols | \: represents the colon character itself |
Key-value Pair Query
key:value # 基本键值对查询: key:value # Basic key-value pair query
"error level":high # Keys containing spaces need to be enclosed in quotes
functionName:"user login" # 包含空格的值需要用引号: functionName:"user login" # Values containing spaces need to be enclosed in quotes
Composite Query Example
Troubleshooting
level:error and functionName:user-login # 查找user-login函数的错误日志: level:error and functionName:user-login # Search for error logs of the user-login function.
level:error and not timeout # 查找非超时的错误日志: level:error and not timeout # Search for error logs that are not timeouts.
Performance Analysis
duration:>5000 # 查找执行时间超过5秒的日志: duration:>5000 # Search for logs with execution time exceeding 5 seconds
level:warn or level:error # 查找警告和错误级别的日志: level:warn or level:error # Search for logs at warning and error levels
User Behavior Tracking
userId:123456 and (login or logout) # 查找特定用户的登录登出日志: userId:123456 and (login or logout) # Search for login or logout logs of the specific user
requestId:req-* and level:info # 查找特定请求的信息日志: requestId:req-* and level:info # Search for information logs of specific requests
Practical Search Scenarios
1. Troubleshooting
# Search for recent error logs
level:error
# Search for timeout errors of specific functions
functionName:payment-process and timeout
# Troubleshoot database connection issues
source:database and (connection or timeout)
2. Performance Monitoring
# Search for Slow Queries
duration:>3000
# Search for abnormal memory usage
memory:>512 or "out of memory"
# Search for High-Frequency Invocations
requestCount:>100
3. User Behavior Analysis
# Search for all operations of a specific user
userId:user123456
# Search for Login-Related Logs
action:login or action:logout
# Search for API Call Records
path:/api/* and method:POST