Captcha Handling Guide
This document describes how to handle captcha-related logic in Tencent Cloud's identity authentication, including trigger conditions, error handling, and the complete implementation process.
Trigger Conditions
Captcha will be required to be entered under the following circumstances:
- After 5 failed username and password login attempts
- When sending SMS or email verification codes reaches the rate limit
Error Information
When a captcha is required, the API will return the corresponding error message:
error == captcha_required: Indicates that the request has triggered captcha-related logic and requires machine verificationerror == captcha_invalid: Indicates that the captcha is invalid and needs to be re-obtained.
After the captcha process is completed, if the business interface returns error equal to captcha_required, it indicates that the request requires the captcha_token parameter, and locally unexpired captcha should be used as much as possible. When error equals captcha_invalid, it indicates that the captcha is invalid and needs to be re-obtained. Within the same verification process, captcha_invalid can be attempted at most once.
// Example of error message:
{
data: {
error: "captcha_required",
error_code: 4001,
error_description: "captcha_token required"
}
}
Process Flow
Complete Process Flow
The complete process for captcha handling is as follows:
- User attempts to log in or send a verification code
- If a captcha requirement is triggered, the SDK throws a
captcha_requirederror - Write an SDK adapter to catch errors and trigger
openURIWithCallback - In the
openURIWithCallbackmethod, obtain the captcha parameters and send them to the frontend for display viaEVENT_BUS. - The frontend displays the captcha image and waits for user input
- User enters the captcha and submits it
- The system verifies and returns the result
- Determine whether to retry the original operation based on the verification result
For the SDK adapter in Step 3 and the openURIWithCallback method, refer to the Adapter Guide
Adapter Implementation
function genAdapter(options) {
const adapter: SDKAdapterInterface = {
captchaOptions: {
openURIWithCallback: async (url: string) => {
// Parse the captcha parameters in the URL.
const { captchaData, state, token } = cloudbase.parseCaptcha(url);
// Send the captcha data via EVENT_BUS for frontend caching and display
options.EVENT_BUS.emit("CAPTCHA_DATA_CHANGE", {
captchaData, // Base64-encoded captcha image
state, // captcha status flag
token, // captcha token
});
// Listen for the captcha verification result
return new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log("Waiting for the captcha verification result...");
options.EVENT_BUS.once("RESOLVE_CAPTCHA_DATA", (res) => {
// Verification result of auth.verifyCaptchaData
resolve(res);
});
});
},
},
};
return adapter;
}
Initialize the SDK
import cloudbase from '@cloudbase/js-sdk'
// Create an event bus instance. For specific EventBus implementations, refer to online samples.
const EVENT_BUS = new EventBus();
// Configure and use the adapter to inject EVENT_BUS into genAdapter
cloudbase.useAdapters(adapter, { EVENT_BUS });
const app = cloudbase.init({
env: 'Environment ID',
appSign: 'Application Identifier',
appSecret: {
appAccessKeyId: 'Application Credential Version Number',
appAccessKey: 'Application Credential'
}
});
const auth = app.auth();
Verification Code Page Implementation
// Store the current captcha status
let captchaState = {
captchaData: "", // Base64-encoded captcha image
state: "", // captcha status flag
token: "", // captcha token
};
// Listen for captcha data changes
EVENT_BUS.on("CAPTCHA_DATA_CHANGE", ({ captchaData, state, token }) => {
console.log("Received captcha data", { captchaData, state, token });
// Update local captcha status
captchaState = { captchaData, state, token };
// Display the captcha image in the page, for example, using an img tag in a Web environment
const captchaImage = document.getElementById('captcha-image');
if (captchaImage) {
captchaImage.src = captchaData;
}
});
// Called when the user clicks to refresh the captcha
const refreshCaptcha = async () => {
try {
// Obtain the latest captcha information
const result = await auth.createCaptchaData({
state: captchaState.state
});
// Update local captcha status
captchaState = {
...captchaState,
captchaData: result.data,
token: result.token,
};
// Update the displayed captcha image
const captchaImage = document.getElementById('captcha-image');
if (captchaImage) {
captchaImage.src = result.data;
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to refresh the captcha", error);
}
};
// Called when the user submits the captcha
const verifyCaptchaData = async (userCaptcha) => {
try {
// Verify the Captcha.
const verifyResult = await auth.verifyCaptchaData({
token: captchaState.token,
key: userCaptcha
});
// Notify the adapter of the verification result
EVENT_BUS.emit("RESOLVE_CAPTCHA_DATA", verifyResult);
console.log("Captcha verification successful");
} catch (error) {
console.error("Captcha verification failed", error);
// When verification fails, you can choose to refresh the captcha
await refreshCaptcha();
}
};
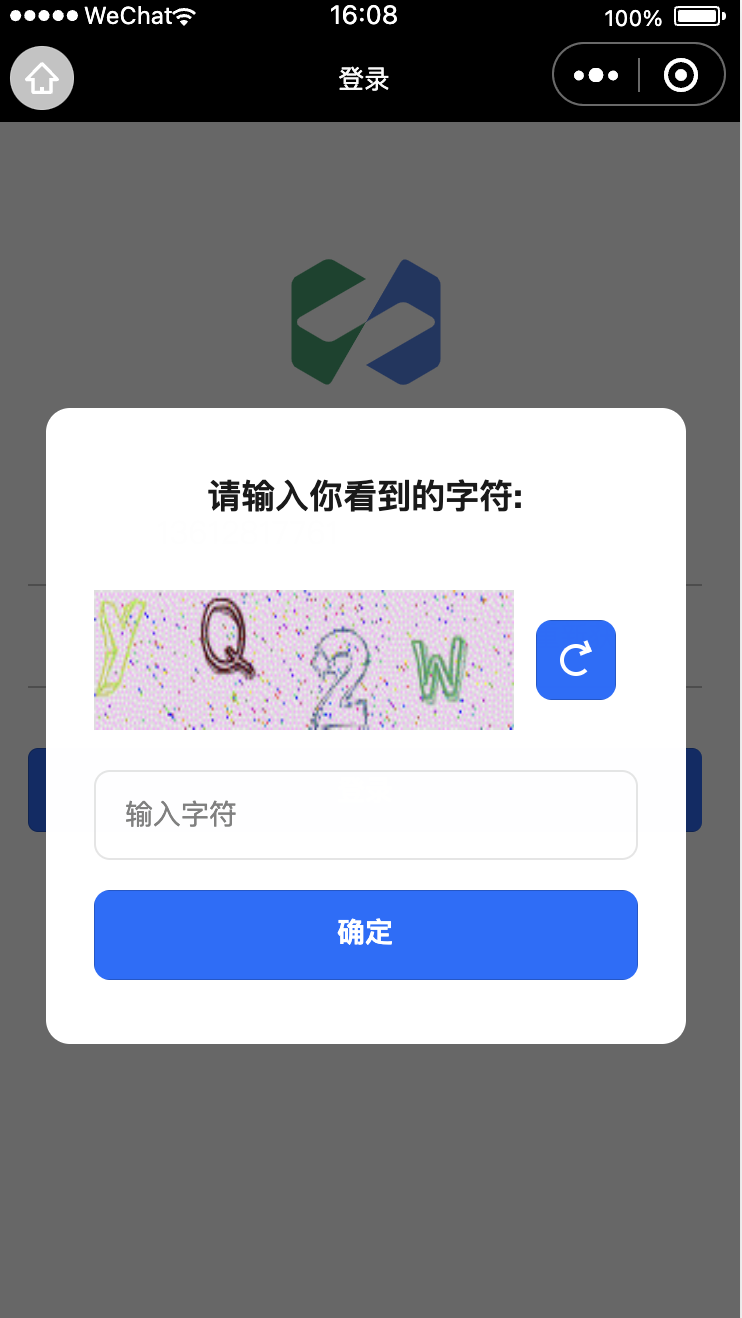
Captcha Display Effect
Sample code address: Sample Code
Related APIs
auth.createCaptchaData(options)- create captcha dataauth.verifyCaptchaData(options)- verify captchacloudbase.parseCaptcha(url)- Parse captcha URL parameters
Notes
- The captcha is time-sensitive; it is recommended to use it promptly after obtaining it.
- Within the same verification process, captcha verification can be retried at most once upon failure.
- It is recommended to provide a feature for refreshing the captcha after verification failure.
- Ensure the proper initialization of the event bus and event listening.