Not Logged In
Authentication (v1) is no longer maintained. Please migrate to Authentication (v2).
CloudBase allows clients to access resources without logging in. Developers can restrict resource access permissions for unauthenticated users in conjunction with security rules.
Activation Process
Step 1: Enable Unauthenticated Access
Log in to the Cloud Development CloudBase Console, and in the Login Authorization section, enable or disable the Unauthenticated Access option.
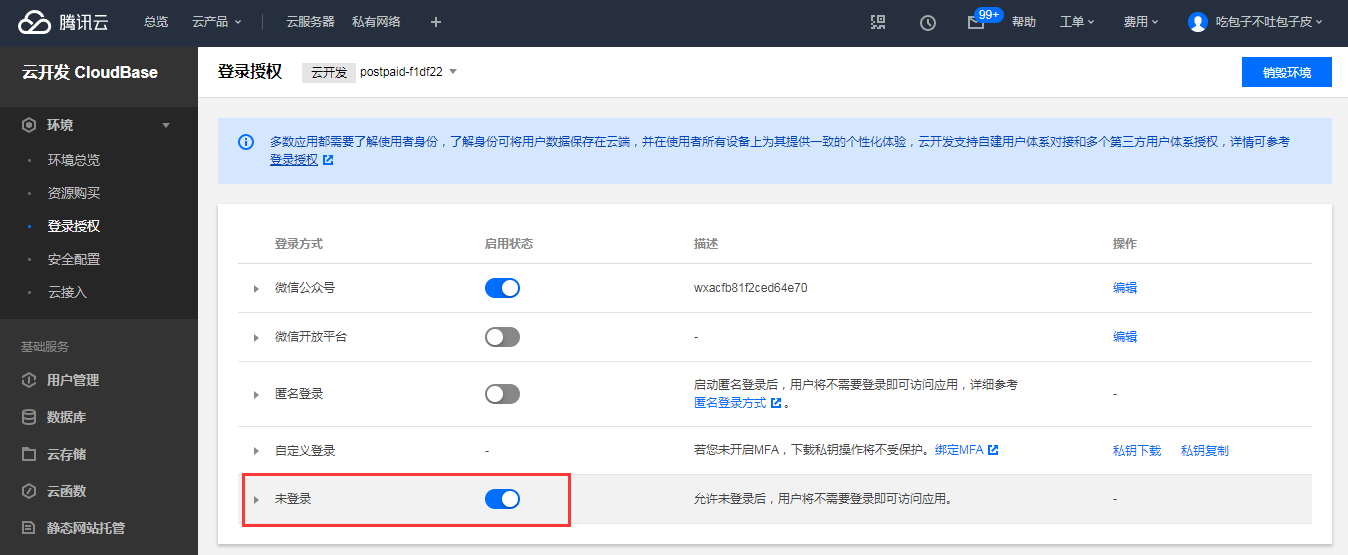
Step 2: Add Secure Domains (Optional)
Log in to the Cloud Development Platform, and on the Security Sources page under Secure Domains, add the domain to the list; otherwise, it will be identified as an illegal source.
Usage Process
Step 1: Set Up Custom Security Rules to Allow Unauthenticated Access
You need to use custom security rules to allow resource access in unauthenticated mode.
For security reasons, the four basic permission settings do not allow access by unauthenticated users.
For example, you can configure database permissions as follows:
{
"read": "doc._openid==auth.openid || auth == null"
}
Building upon the original private read rule doc._openid==auth.openid, it now allows all unauthenticated users to read resources. For details, see Writing Security Rules.
Step 2: Initialize the SDK and Initiate the Call
- Web
import cloudbase from '@cloudbase/js-sdk';
const app = cloudbase.init({
env: 'xxxx-yyy';
});
Once the SDK is initialized, you can normally initiate calls to cloud development resources.
- Starting from version 1.9.0, tcb-js-sdk supports calling resources in unauthenticated mode, while earlier versions require resource calls to be made within a valid login session;
- Data written in unauthenticated mode (database, cloud storage) will become ownerless data, meaning it will not automatically contain corresponding identity identifier fields.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Anonymous Login and not being logged in?
From the end user's perspective:
- There is no difference in the initial usage between Anonymous Login and not being logged in, as neither requires registration;
- In unauthenticated scenarios, private data cannot be generated. Data is shared among all unauthenticated users, and individual users lack distinguishing identifiers;
- Compared to Anonymous Login, unauthenticated mode cannot be upgraded to registered login, and data generated during unauthenticated sessions cannot be automatically migrated to registered user accounts.
From the application developer's perspective:
- The anonymous user generated by CloudBase Anonymous Login is essentially a valid user with a unique user ID, enabling the creation of private Database and Cloud Storage data for them, along with personalized access policies configured through Security Rules;
- Unauthenticated mode is purely stateless access; operations performed in this mode will not enter user tracking statistics;
- Under default permissions, unauthenticated users cannot access any CloudBase services or resources. Access to required resources must be allowed through security rules. Additionally, since the uniqueness of unauthenticated users cannot be determined, private data and personalized policies cannot be created within the developer's own service system.
Unauthenticated Access Enabled but Still Encountering Permission Errors
Since unauthenticated access is a low-security, public access mode, to ensure the security of developers' cloud resources, the system requires both enabling the unauthenticated access switch and explicitly allowing resource access for unauthenticated mode through security rules. Only when both conditions are met can cloud resources be truly accessed in unauthenticated mode. These two steps are independent yet indispensable.