Common Data Model FAQs
Data Model Basic Capabilities Overview
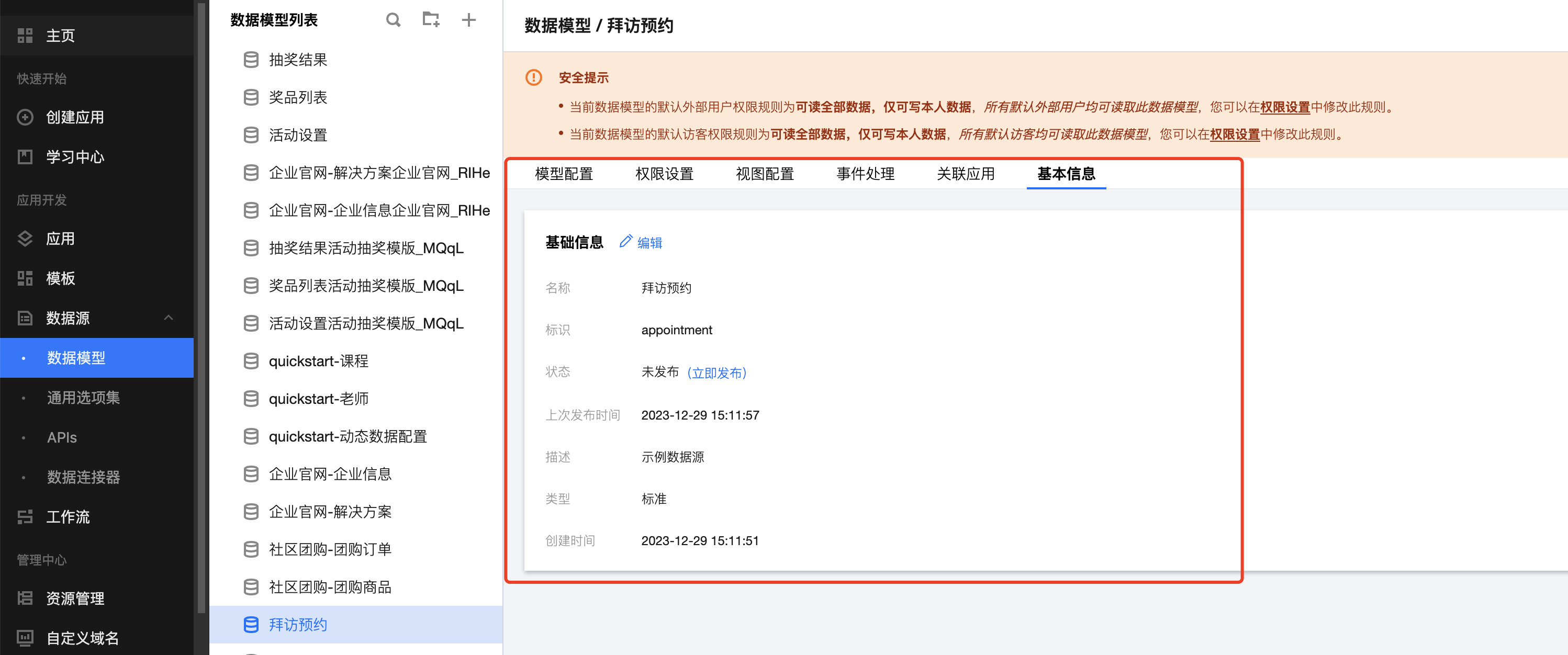
Name
The data model name is a Chinese name provided to developers, which need not be unique within the environment and is primarily used to facilitate developer identification of their own data models.
Identifier
The data model identifier is used to denote a unique English ID within the current environment. It is utilized across multiple modules such as the editor, OPENAPI, and APIS.
Status
Preview and Production
A data model is associated with two underlying physical tables: the preview table and the production table. The preview table is used for development and debugging, while the production table contains actual production data.
Why Release?
The underlying implementation of the data model is divided into two states: preview and release. These two states are physically isolated, meaning data between the two states will not be shared. Preview Status primarily allows developers to perform rapid development, quickly adjust component styles, and conduct interface testing related to data. Production Status requires publishing the data source. At this stage, the basic development is considered complete, requiring only minor adjustments before going live. Data will be written to the production environment and go through the full process in the WeDa feature module.
Data Model Client Capabilities
The underlying implementation of the data model is divided into: Document Database, Mysql. Because of the implementation of two database capabilities, WeDa API differs.
MongoDB has weaker association capabilities but excels in array and object queries. Mysql has strong association capabilities.
Data Model HTTP-API
Data Model Underlying Database
The underlying data model database enabled by default in WeDa is a shared MongoDB instance, suitable for small to medium-scale businesses with low concurrency requirements. Higher-tier plans can enable dedicated Mysql databases, suitable for medium to large scale businesses with high concurrency requirements.
Slow Queries on Data Models
Because of the implementation of two database capabilities, the WeDa API differs. As the business scales up and the data volume increases, query speed will become significantly slower. At this point, it is recommended that developers create indexes.
Document Database
Document Database essentially relies on CloudBase's database. You need to first locate the database.
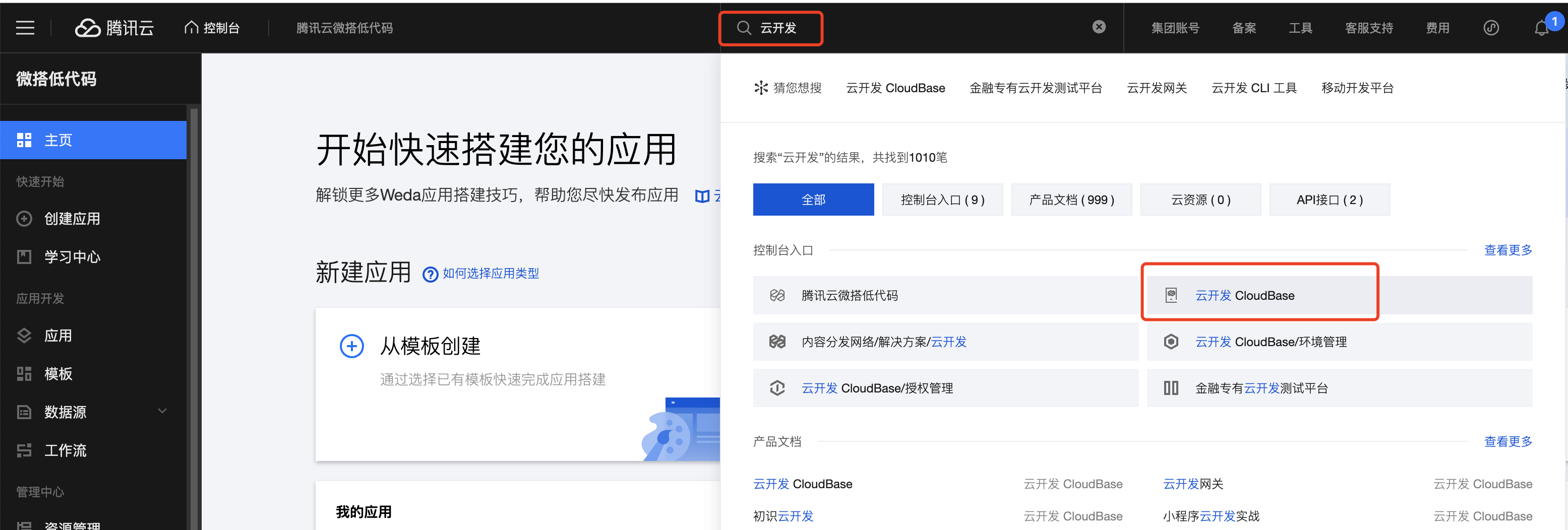
Return to the old console.
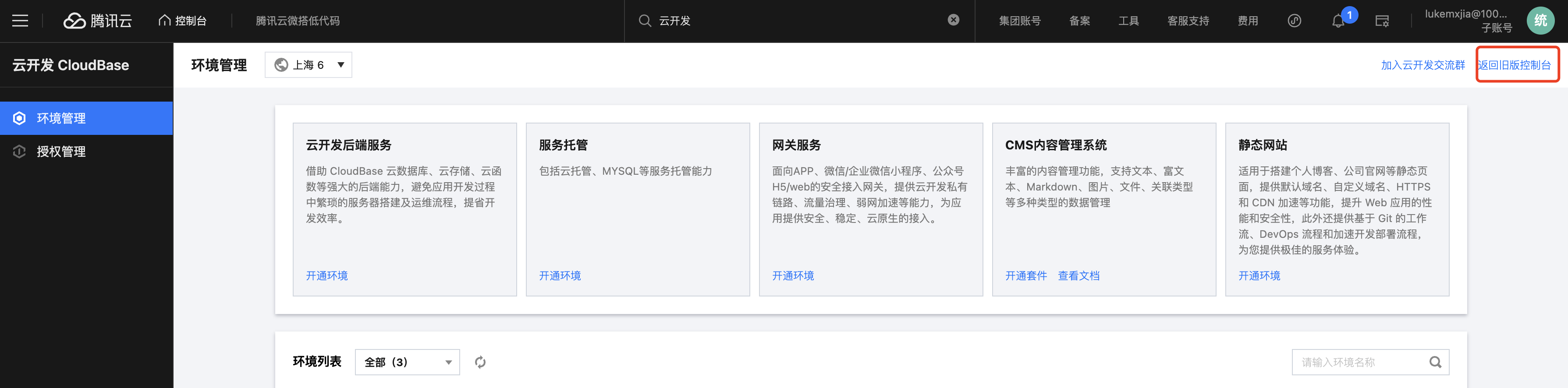
You can locate your environment based on the environment id.
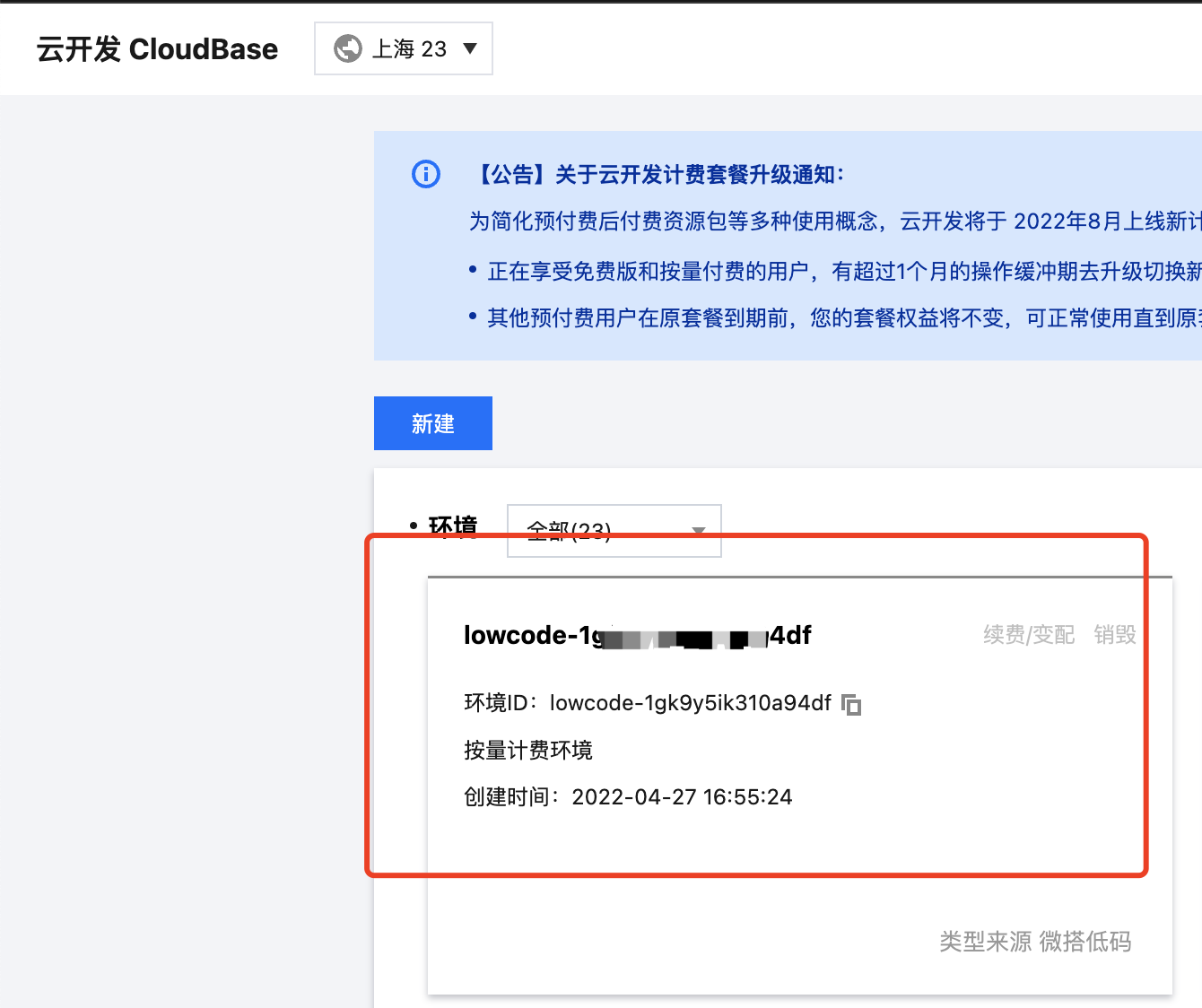
Find the database
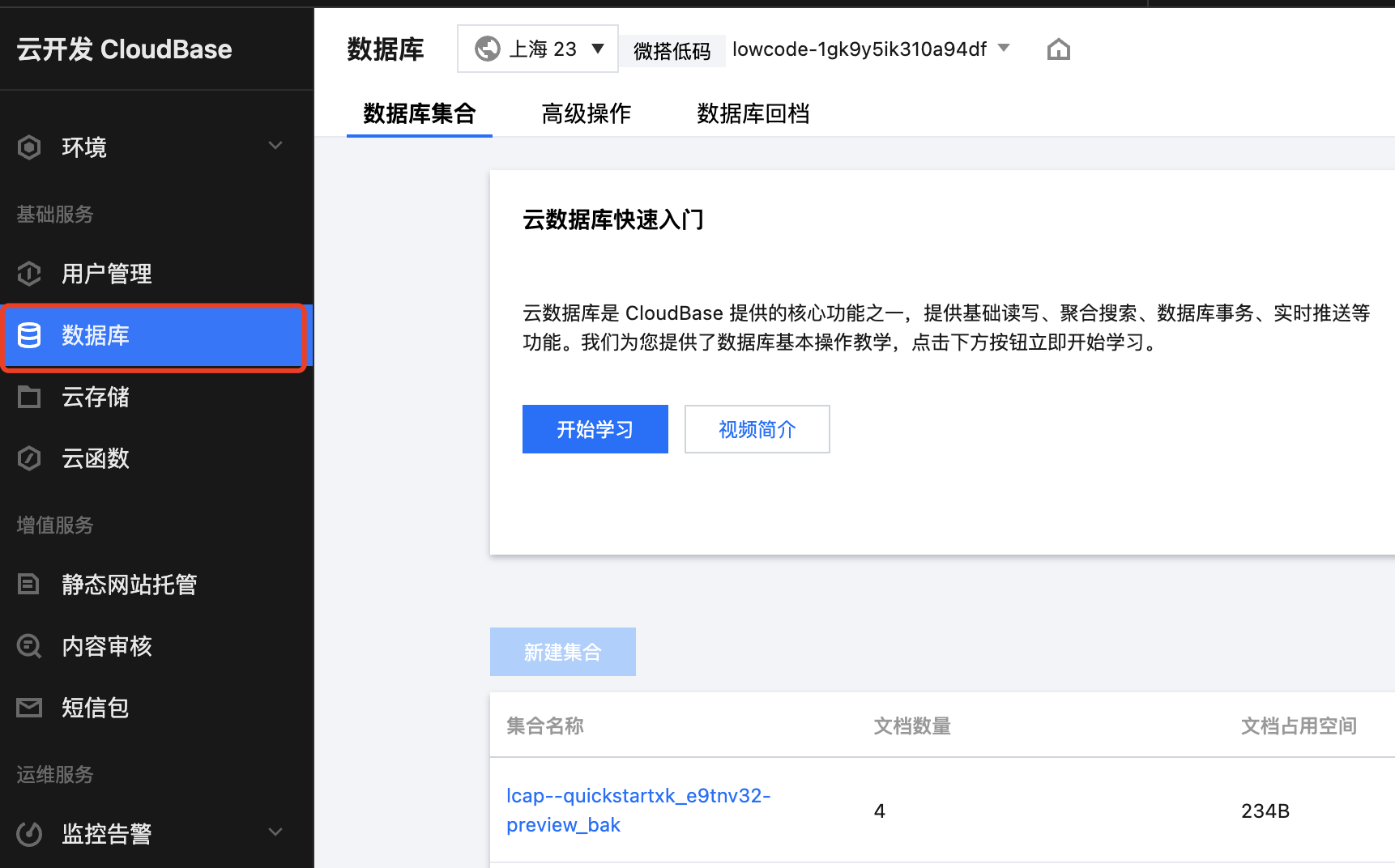
Create the required indexes based on the data model identifier.
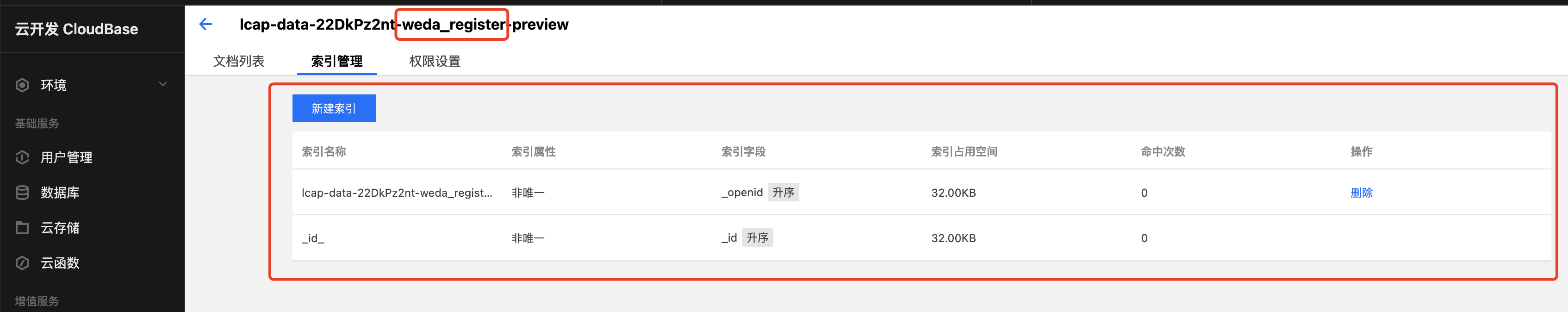
lcap-dataxxx-xxx-preview is the preview table. lcap-dataxxx-xxx is the official table.
!!! Note This operation involves the underlying database. Any addition, deletion, query, or modification of table data will affect WeDa features. Do not delete any table starting with lcap, otherwise it will cause the WeDa data model to become unavailable.
Mysql Database
Scaling out clusters is a common means of resource configuration. Ops personnel can dynamically adjust the node capacity in real time via the Tencent Cloud console or APIs.
How to Clear WeDa Model Data
Document Database
Find your database.
Write code through the console to clean up your data tables.
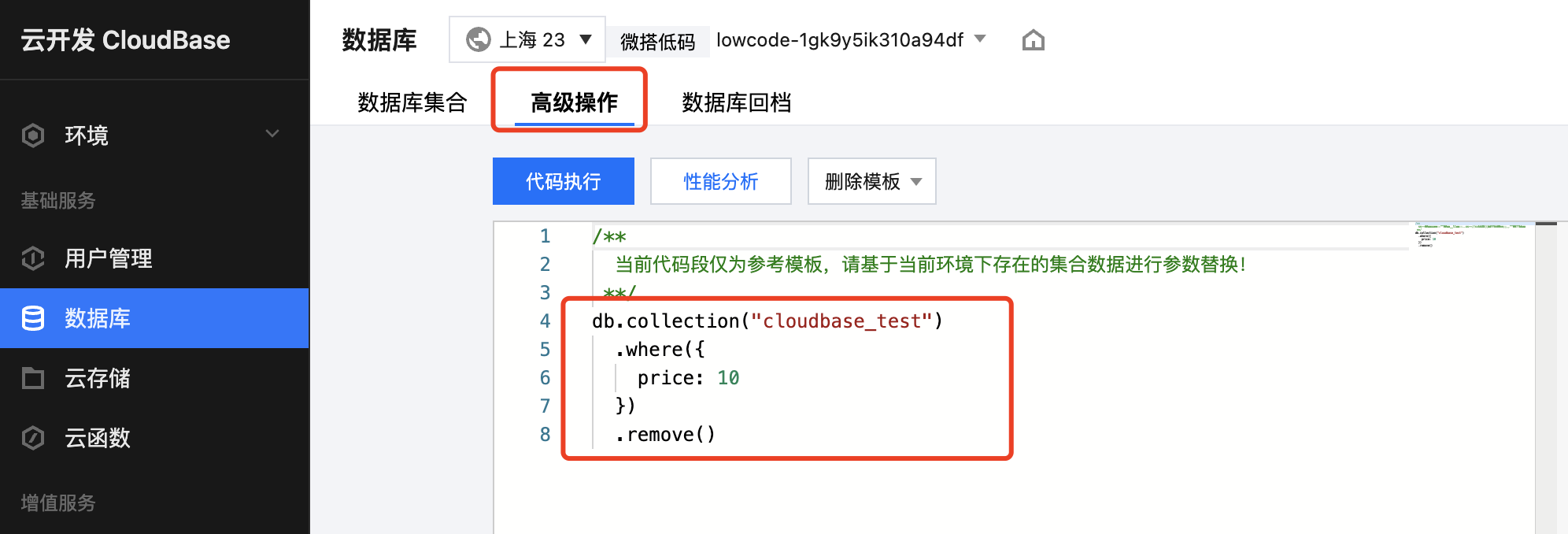
For how to write code, please refer to Database Deletion Reference
Mysql Database
Scaling out clusters is a common means of resource configuration. Ops personnel can dynamically adjust the node capacity in real time via the Tencent Cloud console or APIs.