User Guide
Service Management
Create Service
To create a service through the AnyService console, you need to configure the following basic information:
Basic Configuration
| Item | Description | Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Service Name | Display Name | For easy identification and management |
| Service Identifier | The unique identifier of the service | Only letters, digits, and underscores are allowed. Must be unique within the environment. |
| Remarks | Service description | Optional, used to record the service purpose |
| Origin Type | Access method for backend services | Public network access origin or Tencent Cloud resources |
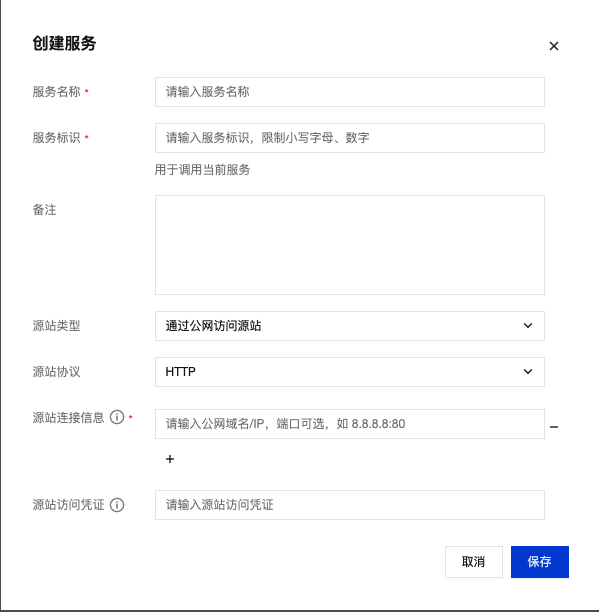
Public Network Access Origin Configuration
When you choose to access the origin via public network, you need to configure the following:
| Item | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Origin Protocol | HTTP or HTTPS | Default ports: HTTP(80), HTTPS(443) |
| Origin Connection Information | IP Address or Domain Name | 139.186.239.126 or tcb.tencentcloudapi.com:8080 |
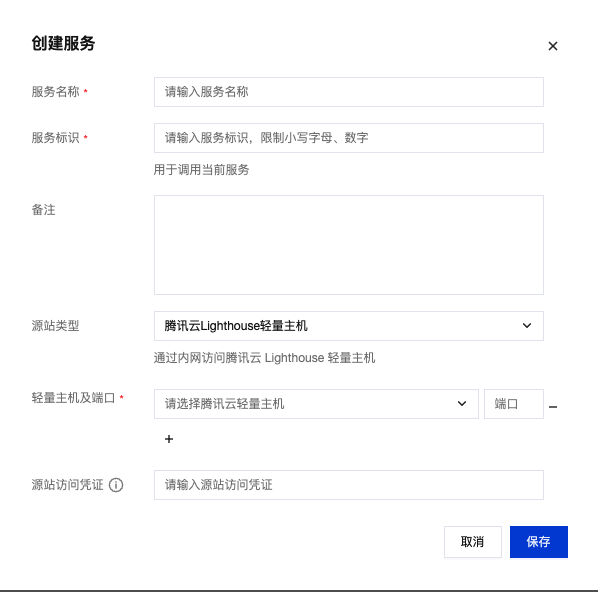
Tencent Cloud Resource Configuration
When you choose to connect to Tencent Cloud resources, you need to configure the following:
| Item | Description | Supported Range |
|---|---|---|
| Resource | Select specific cloud resource instances | CVM, CLB, Lighthouse in Shanghai region |
| Port | Service listening port | 1-65535 |
Security Configuration (Optional)
| Item | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Origin Access Credentials | Basic Auth authentication information | Complies with the Authorization Basic specification |
How it works: Once configured, each request adds an x-anyservice-authorization field in the Header, which the origin server can use for authentication or request source identification.
⚠️ Security Notice: When using the HTTP protocol, access credentials will be transmitted in plain text. It is recommended to use HTTPS in production environments.
Managing Services
In the service list, you can view and manage created services:
| Operation | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| View Details | View the service's configuration information and running status | - |
| Edit Service | Modify all configurations except the identifier | Service identifier cannot be modified |
| Delete Service | Permanently delete the service and its configurations | Ensure no code dependencies before deletion |
⚠️ Important Notice: Modifying or deleting services may affect applications that are using the service. Please carefully assess the impact scope before performing these operations.
Service Invocation
Invoking in Mini Programs
1. Initialize the CloudBase environment
Call the initialization once during the Mini Program loading phase; it only needs to be executed once globally:
// app.js - Global Initialization
App({
async onLaunch() {
// Initialize the CloudBase environment
wx.cloud.init({
env: "your-env-id" // Replace with your environment ID
})
}
})
2. Invoke the AnyService Service
Use the wx.cloud.callContainer method to invoke the AnyService service:
// Invoke Example
const callAnyService = async () => {
try {
const res = await wx.cloud.callContainer({
path: '/api/users', // Backend API path
method: 'POST', // HTTP method
header: {
"X-WX-SERVICE": "tcbanyservice", // Fixed value
"X-AnyService-Name": "my-service", // Your service identifier
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
data: {
name: 'Zhang San',
email: 'zhangsan@example.com'
}
// dataType: 'text' // Optional: Use when you do not want the SDK to automatically parse JSON
})
console.log('Call succeeded:', res.data)
return res.data
} catch (error) {
console.error('Call failed:', error)
throw error
}
}
Key Parameter Description
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
X-WX-SERVICE | tcbanyservice | Fixed value that identifies the AnyService call |
X-AnyService-Name | Your service identifier | Identifier set when creating the service |
path | /api/path | Backend API path, starting from the root directory |
method | GET/POST/PUT/DELETE | HTTP request method |
dataType | json (default) / text | Response data parsing method |
Error Handling and Best Practices
Common Error Handling
const callAnyService = async (path, data = {}) => {
try {
const res = await wx.cloud.callContainer({
path,
method: 'POST',
header: {
"X-WX-SERVICE": "tcbanyservice",
"X-AnyService-Name": "my-service",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
data,
timeout: 10000 // Set the timeout
})
return res.data
} catch (error) {
// Handle different types of errors
if (error.errCode === -1) {
console.error('Network request failed:', error.errMsg)
wx.showToast({ title: 'Network connection failed', icon: 'none' })
} else if (error.errCode === 40001) {
console.error('Service not found:', error.errMsg)
wx.showToast({ title: 'Service temporarily unavailable', icon: 'none' })
} else {
console.error('Call failed:', error)
wx.showToast({ title: 'Request failed, please try again', icon: 'none' })
}
throw error
}
}
Best Practice Recommendations
- Request Encapsulation: It is recommended to encapsulate AnyService calls into a generic function.
- Error Handling: Provide corresponding user prompts for different error types.
- Timeout Settings: Set a reasonable timeout period for network requests.
- State Management: Display loading status during the call process.
- Retry Mechanism: Retry logic can be implemented for transient errors.
📝 Note: Other parameters are consistent with wx.request.
Request and Response Data
Request Header
When calling services through the SDK, the system automatically carries Mini Program-related information in the HTTP Header. The backend can parse these headers to obtain user and environment information:
| Header Field | Meaning | Description |
|---|---|---|
X-WX-OPENID | Mini Program user openid | Unique user identifier |
X-WX-APPID | Mini Program AppID | Mini Program application identifier |
X-WX-UNIONID | Mini Program user unionid | Cross-application user identifier (subject to acquisition conditions) |
X-WX-FROM-OPENID | User openid in resource reuse scenarios | Original user identifier during resource reuse |
X-WX-FROM-APPID | Mini Program AppID in resource reuse scenarios | Original application identifier during resource reuse |
X-WX-FROM-UNIONID | User unionid in resource reuse scenarios | Original user cross-application identifier during resource reuse |
X-WX-ENV | CloudBase environment ID | The CloudBase environment where the current call is located |
X-WX-SOURCE | Call source | The source type that triggered this call |
X-WX-PLATFORM | Calling platform | Platform information that initiated the call |
X-Forwarded-For | Client IP address | Supports IPv4 and IPv6 |
X-AnyService-Name | AnyService service identifier | Service identifier for the current call |
Response Header
AnyService adds the following Header fields in the response for debugging and monitoring:
| Header Field | Meaning | Description |
|---|---|---|
X-Cloudbase-Request-Id | CloudBase request ID | Used for issue tracking and log queries |
X-Cloudbase-Upstream-Status-Code | Upstream response status code | The actual HTTP status code returned by the backend service |
X-Cloudbase-Upstream-Timecost | Upstream response time | Time taken by the backend service to process the request (in milliseconds) |
X-Cloudbase-Upstream-Type | Upstream service type | Type identifier of the backend service |