RESTful API
Starting from CloudBase CMS version 2.3.0, it provides the capability to access content collection data via RESTful API.
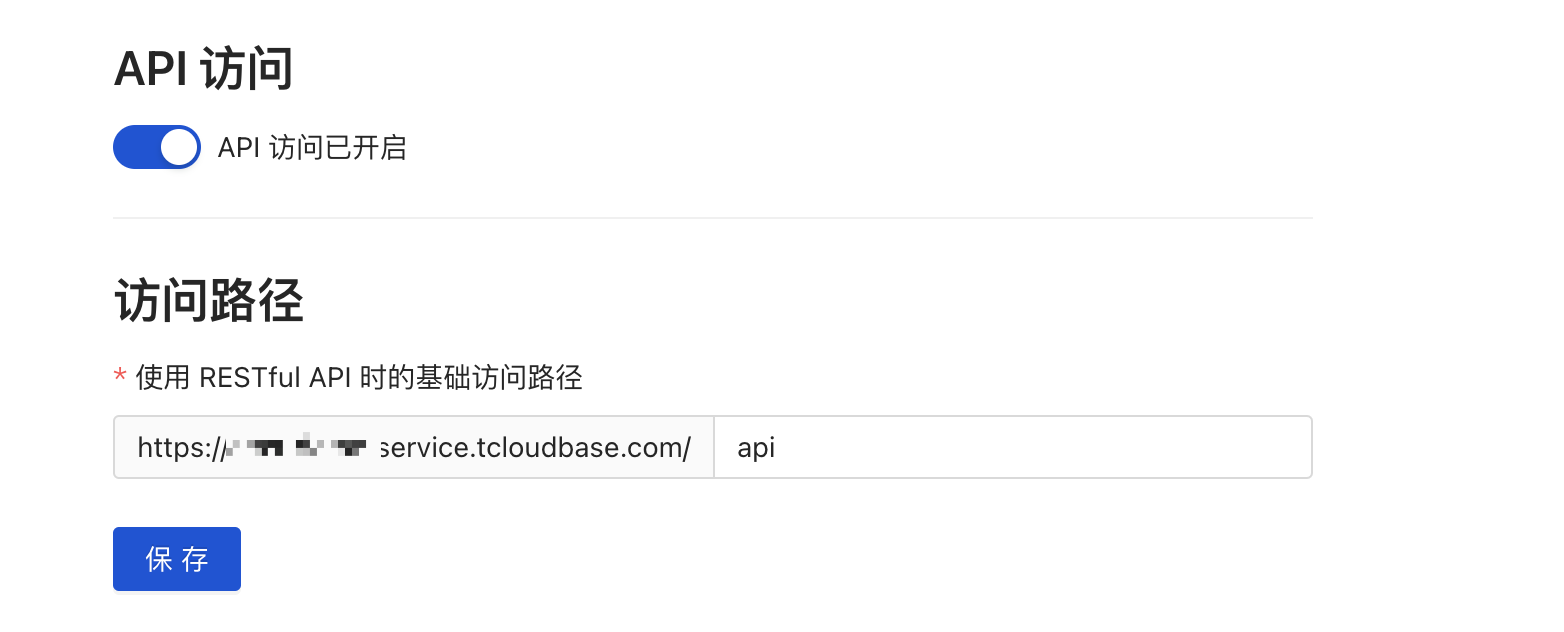
Enable RESTful API
By default, API access is disabled, rendering the RESTful API feature unavailable. To utilize RESTful APIs, you must enable API access in the project settings and configure an access path. Only then can you access RESTful APIs through the complete access path.
Access Permissions
By default, RESTful API cannot access any data. You need to configure the content that allows access/modification.
Allow access: Read content via RESTful API
Allow modification: Create and update content via RESTful API
Allow deletion: Delete content via RESTful API

Request Path
CloudBase CMS's RESTful API request path consists of three parts: deployment path + API version path + service path. For example
CMS service deployment path (the domain name below is an example; for the actual domain name, please check your HTTP Access Service default domain name)
https://xxxx.tcloudbase.com/api/
API Version Path
/v1.0
Service path, where collectionName is the database collection name
/{collectionName}
Then the request path to retrieve the document list for the database named goods is
GET https://xxx.tcloudbase.com/api/v1.0/goods
Notes
The body of all POST requests should be of type
application/json; other types are not allowedWhen querying data, a maximum of 100 records are returned per request by default.
Parameters passed in the request override the default behavior. For example, if a request specifies that a certain field should be included in the response, but in the model definition this field is hidden in the API return value, then following the above principle, this field will be present when data is returned.
By default, CloudBase CMS stores uploaded images and files in cloud storage and saves access links in the form of
cloudIdin the database. When retrieving data using the RESTful API, thecloudIdin the response is automatically converted to an HTTP link. This conversion only applies to directly recordedcloudId;cloudIdin associated documents will not be processed.When using the RESTful API to retrieve data, the associated fields in the response will be converted to the full value of the associated document. For example, when a product content model is associated with a tag content model (tag), the underlying database storage is as follows:
{
"_createTime": 1603183501849,
"_id": "112557505f8ea38e001e1fc210bd51ed",
"_updateTime": 1604541130908,
"name": "Apple",
"price": 6299,
"stock": 100000,
"tags": [
"b8df3bd65f681d43002b894d0bdce7ac"
]
}
The returned result is:
{
"_createTime": 1603183501849,
"_id": "112557505f8ea38e001e1fc210bd51ed",
"_updateTime": 1604541130908,
"name": "Apple",
"price": 6299,
"stock": 100000,
"tags": [
{
"_id": "b8df3bd65f681d43002b894d0bdce7ac",
"_createTime": 1603183501849,
"_updateTime": 1604541130908,
"name": "Fruit",
"count": 10
}
]
}
Common Parameters
When performing query operations, you can add the following Query parameters to the URL.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| limit | String | No | The number of documents returned by the query, with a maximum value of 1000 |
| skip | String | No | The number of documents to skip in the query |
| fields | String | No | JSON object string, e.g. { key1: 1, key2: 0 }, indicating to include the key1 field and exclude the key2 field |
| sort | String | No | JSON object string, e.g. { key1: 1, key2: -1 }, indicating sorting by key1 in ascending order and key2 in descending order |
like:
GET /{collectionName}/?limit=10&skip=0&fields={"name":1}&sort={"name":1}
Document List Retrieval
Retrieve document data from a collection based on simple sorting and grouping conditions.
Request Path
GET /{collectionName}/?limit={limit}&skip={skip}&fields={fields}&sort={sort}
Response Body
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| requestId | String | Request ID |
| data | Object | Result |
| code | String | Error code returned when an error occurs |
| message | String | Error message returned when an error occurs |
| total | Number | Total number of documents |
Response Example
{
"data": [
{
"_id": "ecdacfc05f3f28a800000bf51126de2f",
"name": "test",
"arr": ["sss", "sss", "ssss"],
"markdown": "markdown text",
"textarea": "ssssssssssssssssssssssssssssss",
"_createTime": 1597974695982,
"_updateTime": 1597974695982
}
],
"offset": 0,
"limit": 10,
"requestId": "1742eb3145c_11",
"total": 1
}
Document List Query
Retrieve the list of documents matching the query criteria
Request Path
POST /{collectionName}/find?limit={limit}&skip={skip}&fields={fields}&sort={sort}
Request Body
As shown below, query is the query condition and supports the use of Query Command
{
"query": {
"price": { "$ge": 100 }
}
}
Response
{
"data": [
{
"_id": "ecdacfc05f3f28a800000bf51126de2f",
"name": "test",
"arr": ["sss", "sss", "ssss"],
"markdown": "markdown text",
"textarea": "ssssssssssssssssssssssssssssss",
"_createTime": 1597974695982,
"_updateTime": 1597974695982
}
],
"requestId": "1742eb3145c_11",
"total": 1,
"offset": 0,
"limit": 10
}
Get a Single Document
Get the document by specified Id
Request Path
GET /{collectionName}/{docId}
Parameter Description
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| docId | String | Required | Content Document Id |
Response
{
"data": {
"_id": "ecdacfc05f3f28a800000bf51126de2f",
"name": "test",
"arr": ["sss", "sss", "ssss"],
"markdown": "markdown text",
"textarea": "ssssssssssssssssssssssssssssss",
"_createTime": 1597974695982,
"_updateTime": 1597974695982
},
"requestId": "175d6218c00_6"
}
Create a New Document
Create a new content document
Request Path
POST /{collectionName}
Request Body
The request body is as follows. data is an array consisting of new documents, supporting the creation of multiple documents at once.
{
"data": [
{
"name": "Product Name",
"price": 100
}
]
}
Response
{
"id": "b5416b755f476d450088360c0054b6fb",
"requestId": "1742f02d897_42"
}
Update a Single Document
When updating a document, the final result is a merge of the incoming data and the existing document content, where fields with the same name replace the original values.
Request Path
The docId` is the document that needs to be updated.
PATCH /{collectionName}/{docId}
Request Body
The request body is as follows. data is the content to be updated, and supports the use of Update Command.
{
"data": {
"name": "Product Name",
"price": 100
}
}
Response
{
"updated": 1,
"requestId": "1742ef4477b_12"
}
Batch Updating Documents
Batch update data that meets the query conditions to the specified content.
Request Path
PATCH /{collectionName}/
Request Body
query is the query condition, and data is the content to be updated. For example, update all entries where name is oldName to set name to newName. Additionally, query also supports Query Command.
{
"query": {
"name": "oldName"
},
"data": {
"name": "newName"
}
}
Response
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| updated | Number | Number of successfully updated documents |
| matched | Number | Number of matching documents |
| upsert_id | String | Present when inserting a new document during a replacement update; null otherwise |
{
"requestId": "2a3ec45e223a4",
"updated": 1,
"matched": 1,
"upsert_id": null
}
Replace a Single Document
Replace the specified document with new content; this operation only supports replacing a single document.
Request Path
The docId` is the document to be replaced.
PUT /{collectionName}/{docId}
Request Body
The request body is as follows. data is the content to be updated.
{
"data": {
"name": "Product Name",
"price": 100
}
}
Response
{
"updated": 1,
"upsertedId": null,
"requestId": "175d648919d_e"
}
Delete a Single Document
Delete the specified document of a content type within a project.
Request Path
The docIdis the_id` of the document to be deleted.
DELETE /{collectionName}/{docId}
Response
{
"deleted": 1,
"requestId": "175d649a89f_a"
}
Batch Deleting Documents
Batch delete content documents that match the query conditions.
Request Path
DELETE /{collectionName}/
Request Body
As shown below, query is the query condition and supports the use of Query Command
{
"query": {
"price": { "$gt": 100 }
}
}
Response
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| deleted | Number | Number of successfully deleted documents |
{
"requestId": "23f416d4f8722",
"deleted": 1
}
Query Command
Only some of the Commands are listed below. For all Commands, please refer to the Database SDK Documentation.
$eq
Means the field equals a specific value.
Syntax: { <field>: { $eq: <value> }}
{
"data": {
"name": {
"$eq": "cms"
}
}
}
$ne
Means the field equals a specific value.
Syntax: { <field>: { $ne: <value> }}
{
"data": {
"name": {
"$ne": "luke"
}
}
}
$gt
Means the field is greater than a specific value.
Syntax: { <field>: { $gt: <value> }}
{
"data": {
"age": {
"$gt": 18
}
}
}
$gte
Means the field is greater than or equal to a specific value.
Syntax: { <field>: { $gte: <value> }}
{
"data": {
"age": {
"$gte": 18
}
}
}
$lt
Means the field is less than a specific value.
Syntax: { <field>: { $lt: <value> }}
{
"data": {
"age": {
"$lt": 18
}
}
}
$lte
Means the field is less than or equal to a specific value.
Syntax: { <field>: { $lte: <value> }}
{
"data": {
"age": {
"$lte": 18
}
}
}
$in
The field value is within the given array.
Syntax: { <field>: { $in: [<value1>, <value2>, ... <valueN>] }}
{
"data": {
"category": {
"$in": ["science", "computer"]
}
}
}
$nin
The field value is not in the given array.
Syntax: { <field>: { $nin: [<value1>, <value2>, ... <valueN>] }}
{
"data": {
"category": {
"$nin": ["science", "computer"]
}
}
}
$and
Means that two or more specified conditions must be satisfied simultaneously.
Syntax: { $and: [{ <expression1> }, { <expression2> } , ... , { <expressionN> }] }
{
"data": {
"$and": [
{
"price": {
"$lt": 200
}
},
{
"price": {
"$gt": 100
}
}
]
}
}
$or
Means that at least one of the specified conditions must be satisfied.
Syntax: { $or: [{ <expression1> }, { <expression2> }, ... , { <expressionN> }] }
{
"data": {
"$or": [
{
"price": {
"$lt": 200
}
},
{
"price": {
"$gt": 100
}
}
]
}
}
$nor
Indicates the logical "none" relationship, meaning that all specified conditions must not be satisfied.
Syntax: { $nor: [{ <expression1> }, { <expression2> }, ... { <expressionN> }] }
{
"data": {
"$nor": [
{
"price": {
"$lt": 200
}
},
{
"price": {
"$gt": 100
}
}
]
}
}
Update Command
Only some of the Commands are listed below. For all Commands, please refer to the Database SDK Documentation.
$set
Used to set a field equal to a specified value, supporting access to array elements and embedded document fields using dot notation.
Syntax: { $set: { <field>: <value>, ... } }
{
"data": {
"$set": {
"text": "a",
"style.color": "red",
}
}
}
$inc
Used to increment a field by a specified value. This is an atomic operation.
Syntax: { $inc: { <field1>: <amount1≥, <field2>: <amount2>, ... }}
{
"data": {
"$inc": {
"price": 1000
}
}
}
$mul
Used to multiply a field by a specified value.
Syntax: { $mul: { <field>: <number1> }}
{
"data": {
"$mul": {
"price": 1.5
}
}
}
$unset
Used to indicate the removal of a field.
Syntax: { $unset: { <field1>: "" }}
{
"data": {
"$unset": {
"rating": ""
}
}
}
$push
Appends elements to the end of an array, supporting passing in either a single element or an array.
Syntax: { $push: { <field>: <value1> }}
{
"data": {
"$push": {
"tags": {
"$each": ["tag1", "tag2", "tag3"]
}
}
}
}
$pop
Removes the last element from an array.
Syntax: { $pop: { <field>: <-1 | 1> }}
A value of 1 indicates removing an element from the end of the array, and -1 indicates removing an element from the beginning of the array.
{
"data": {
"$pop": {
"tags": 1
}
}
}
Dot Operator
Cloud Development database supports dot notation for accessing array elements and fields of nested documents.
Array
"<array>.<index>"
In the following array, you can use contribs.2 to get the third element C of the colors array.
{
colors: [ "A", "B", "C" ]
}
Nested Documents
"<embedded document>.<field>"
In the following document, you can use address.city to get the value of city, and use contact.phone.number to get the value of number.
{
address: { city: "Sans" },
contact: { phone: { type: "cell", number: "111-222-3333" } }
}